Correlation (AQA Level 3 Mathematical Studies (Core Maths))
Revision Note

Author
Naomi CExpertise
Maths
Types of Correlation & Conclusions
What is a scatter diagram?
A scatter diagram is a way of graphing bivariate data
You may be asked to plot, or add to, a scatter diagram
One variable will be on the
– axis and the other will be on the
– axis
The variable that can be controlled in the data collection is known as the independent or explanatory variable and is plotted on the
– axis
The variable that is measured or discovered in the data collection is known as the dependent or response variable and is plotted on the
– axis
Scatter diagrams allow statisticians to look for relationships between the two variables
Some scatter diagrams will show a clear relationship known as correlation
Others will not display an obvious relationship
If a scatter diagram shows a relationship you may be asked to identify outliers
Exam Tip
Make sure you check the scales on the axes carefully when plotting any points on a scatter graph.
What is correlation?
Correlation is how the relationship between the two variables is described
Perfect linear correlation means that the bivariate data will all lie on a straight line on a scatter diagram
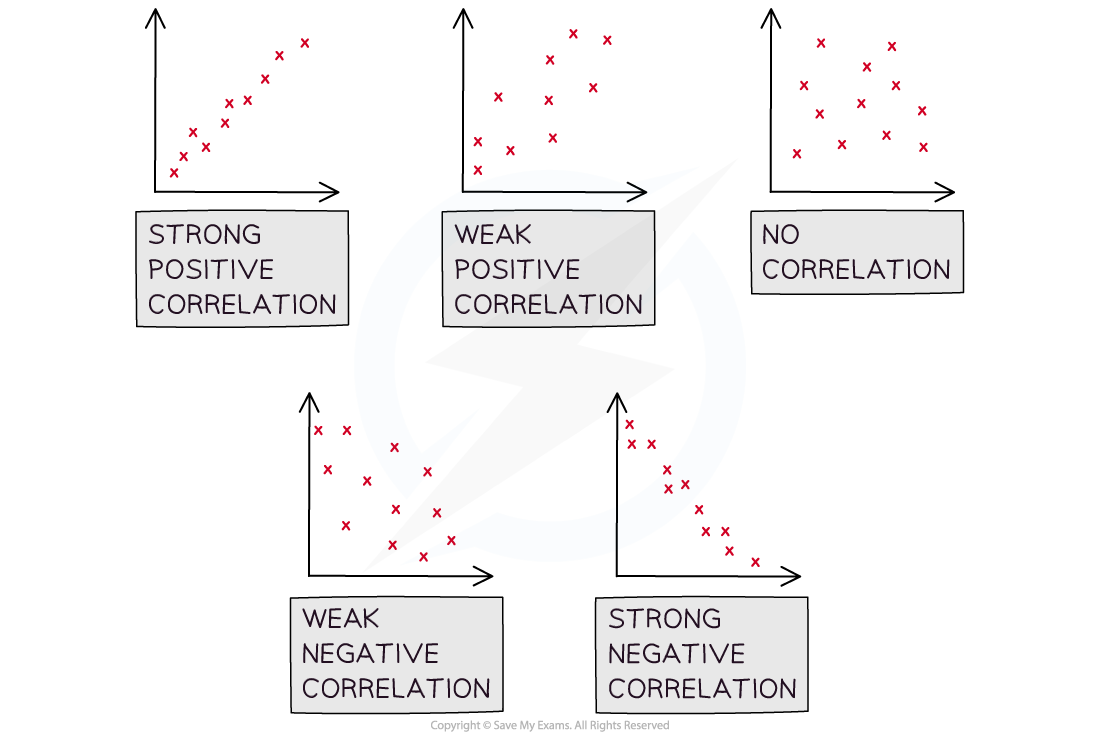
Linear correlation can be positive or negative and it can be strong or weak
Positive correlation describes a data set where both variables are increasing
Negative correlation describes a data set where one variable is increasing and the other is decreasing
When describing correlation you should say whether it is positive or negative and also say whether it is strong or weak
If correlation exists then there could be outliers, these will be data points that do not fit the pattern seen on the graph
There will likely be a maximum of one or two outliers on any scatter diagram
You may be asked to identify the outliers
What is the difference between correlation and causation?
It is important to be aware that just because correlation exists, it does not mean that the change in one of the variables is causing the change in the other variable
Correlation does not imply causation!
If a change in one variable causes a change in the other then the two variables are said to have a causal relationship
Observing correlation between two variables does not always mean that there is a causal relationship
Look at the two variables in question and consider the context of the question to decide if there could be a causal relationship
Observing a relationship between two variables can allow you to create a hypothesis about those two variables
For two variables that are correlated but do not have a causal relationship, there may be a third variable (confounder) that forms a link between them
If the two variables are temperature and number of ice creams sold at a park then it is likely to be a causal relationship
An increase in temperature is likely to make people want to buy an ice cream to cool down
Correlation may exist between rates of skin cancer and exercise but they are unlikely to have a causal relationship
It may be that in locations where there there are more hours of daylight, people spend more time exercising, people in these locations may also have greater exposure to the sun and therefore have greater incidences of skin cancer
Worked Example
The scatter diagram below shows the number of Save My Exams question packs completed by a group of students and the percentage score they received in their Statistics exam.

(i) State which of the variables is the independent variable and which is the dependent variable.
The independent variable can be controlled
The number of question packs completed is the independent variable
The dependent variable is measured
The percentage scored on the statistics exam is the dependent variable
(ii) Another student completed 50 question packs and scored 80% on their Statistics exam, add this data to the scatter diagram.

(iii) Describe the correlation shown in the scatter diagram.
The diagram shows a fairly strong, positive correlation
(iv) Decide if you think there could be a causal relationship between the two variables and explain your reasoning.
It is likely that there is a causal relationship between the number of Save My Exams question packs completed and the result in the student's A Level Statistics exam
Outliers of Scatter Graphs
What is an outlier?
An outlier is a data value that is extreme or does not fit the pattern
These are often easy to spot by sight if there is an obvious relationship between two variables on a scatter graph
Typically an outlier is considered to be
greater than 1.5 times the interquartile range above the upper quartile
or less than 1.5 times the interquartile range below the lower quartile
Exam Tip
In an exam there is no standard measure for the definition of an outlier for a Normal Distribution but a definition may be given to you in a particular question, e.g. more than 2 standard deviations away from the mean.
Should I exclude outliers from my data?
The decision to exclude an outlier from a data set should be given careful consideration
It is reasonable to exclude an outlier from your data set if:
it is a result of human error during measurement or faulty equipment,
the data value is so extreme that it will significantly affect the results
If an outlier is excluded then you must state that it has been excluded and the reason why
Worked Example
Two liquids are mixed and heated to a particular temperature. The time, in seconds, it takes the two liquids to react is recorded.
The scatter diagram below shows the results.

(i) Identify the two outliers shown on the scatter diagram.
Circle the two outliers

(ii) State whether these outliers should be removed. Give a reason for your answer.
The majority of the data points have a strong negative correlation
The outliers should be removed from the data because they are extreme and will significantly affect the results
It is likely that they occurred from errors in the data collection process

You've read 0 of your 0 free revision notes
Get unlimited access
to absolutely everything:
- Downloadable PDFs
- Unlimited Revision Notes
- Topic Questions
- Past Papers
- Model Answers
- Videos (Maths and Science)
Did this page help you?