Geopolitics of Energy and Ore Minerals
- Geopolitics refers to how politics, and in particular international relations, is affected by geographical factors
- The increasing demand and finite supply of energy and mineral resources make them vulnerable to political tension between countries
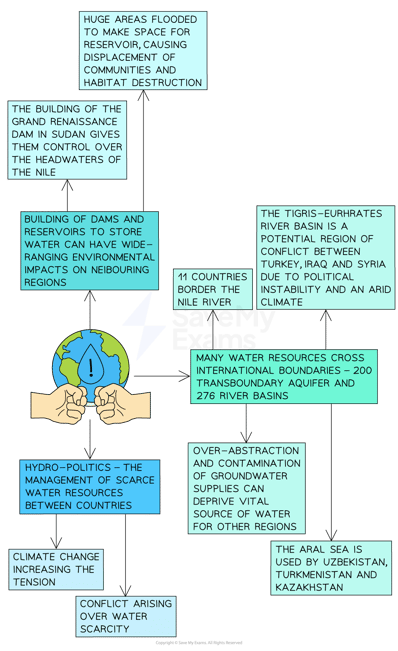
|
|
|
|
Coal |
Difficulty in controlling pollution as it crosses boundaries HICs phasing out coal due to climate concerns but LICs and NICs are reluctant to do so as it is cheap energy and they feel it is inequitable ‘Green’ funds set up to help LICs convert from coal to lower carbon alternatives |
1980s emissions from coal-fired power stations in the UK caused severe acid rain across Scandinavia India refused to agree to phase out coal completely at the COP26 summit |
Oil |
OPEC (Organisation of Petroleum Exporting Countries) manages the supply of oil and sets world prices distorting free market forces in setting oil prices The Middle East is politically unstable impacting global prices and markets TNCs can exploit LICs |
In March 2020, the Saudi Arabia/Russia price war caused a 60% fall in oil prices Shell operates in the Niger Delta and has been criticised for not investing enough in local area |
Natural Gas |
Impacts of pipelines on environment Limited in geographical distribution so a few countries control supply lines |
EU is heavily dependent on Russia for gas supplies (40% before 2021 Russia has ‘weaponised’ gas supply in war with Ukraine Turkey and Greece engaged in conflict over new natural gas reserves found in the eastern Mediterranean near Cyprus |
Nuclear |
Concerns over long-term damage from radiation leakage cause political uncertainty Concerns over the potential misuse of uranium for nuclear weapon development |
Japan shut down most of its nuclear reactors after the Fukushima disaster in 2011 (although it has since committed to re-opening them) |
Renewables |
Global pressure to convert from fossil fuels but high start-up costs are a barrier to conversion for many LICs |
An ‘Adaptation Fund’, set up following the 1997 Kyoto Protocol to help vulnerable countries adapt to climate change, has grown to US$1 billion |
Mineral ores |
LICs over-reliance on overseas expertise and investment from TNCs to mine and process resources, but profits ‘leak’ from the local economy Poor working conditions and profits are often not re-invested REEs widespread but difficult to process and China dominates with 95% of global production |
Inhumane Conditions and child exploitation in Congolese cobalt mines China reduced exports of REEs in 2010 to protect domestic demand leading to a shortage on the world market with the potential to inhibit manufacturing in other countries of the world |
Exam Tip
Geopolitics is an ever-changing picture and so try and use as many contemporary examples as you can in your exam answers. Keep an eye out for news stories about energy, minerals and water issues between countries and make a note of them in your notes.