Managing Employee Performance (Cambridge (CIE) A Level Business): Revision Note
Exam code: 9609
Measurement of employee performance
The effectiveness of a business's workforce can be measured in a number of ways, including
Labour productivity
Absenteeism
Employee costs as a percentage of turnover
These metrics are compared over time, between functional areas, branches or outlets, or against competitors
They can provide the basis for workforce planning and performance management
1. Labour productivity
Labour productivity measures output per worker during a specified period of time
It is expressed as a number of units and calculated using the formula
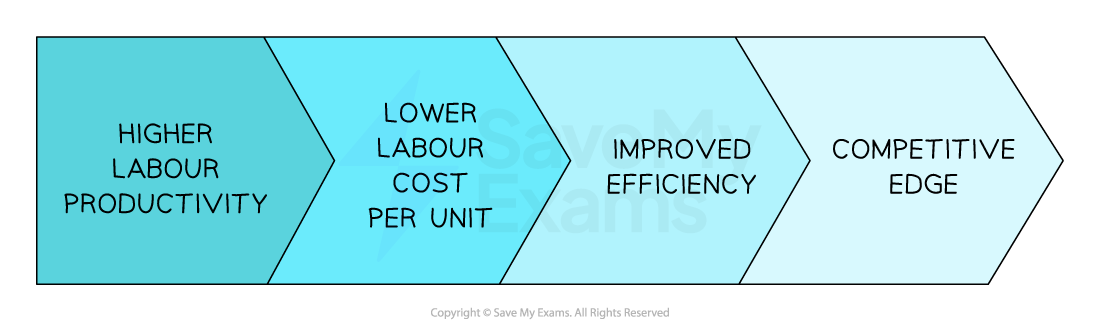
Businesses aim to increase the level of labour productivity to improve competitiveness
The link between high labour productivity and competitive edge
Worked Example
The table shows the number of pairs of luxury wool socks produced by StrumpMani in 2023 and 2024
Year | Units Produced |
|---|---|
2023 | 46,000 |
2024 | 69,000 |
In 2023 StrumpMani employed 50 staff. In 2024 the number of staff employed by the business increased by 20%
Calculate the percentage change in labour productivity between 2021 and 2022.
[4]
Step 1 - Calculate labour productivity for 2023
(1)
Step 2 - Calculate labour productivity for 2024
(1)
Step 3 - Calculate the percentage difference between the two years ((new-old) / old)
(1)
Step 4 - Identify whether the percentage difference is an increase or decrease
Labour productivity has increased by 25% (1 mark)
2. Absenteeism
The absenteeism rate is a measure of the proportion of staff were absent from work during a specific period of time (e.g. a day, week or month)
It is expressed as a percentage and is calculated using the formula
High levels of absenteeism can cause several problems for a business, including
Absence due to illness requires sick pay to be paid
Hiring temporary staff to cover for those absent increases costs
Output is likely to be temporarily reduced if staff are key to production process
Other staff may become demotivated if they have to constantly cover for absent workers
A wider culture of absenteeism may develop
Worked Example
On January 16th twenty-two of Belling Stoneworks Ltd's 189 employees were absent.
Calculate Belling Stoneworks Limited's absenteeism rate on January 16th.
(2)
Step 1: Substitute the values into the formula
(2)
3. Employee costs as a percentage of turnover
This metric shows how much of a business’s revenue is spent on paying employees
It helps assess how efficiently the workforce is being used
It is calculated using the formula:
Worked Example
In the 2022–2023 financial year, Tesla had:
Revenue = £5,297 million
Employee costs = £2,894 million
Calculate the employee costs as a % of turnover between 2022 and 2023.
[2]
Step 1 - Substitute the values into the formula
(1)
Step 2 - Present the final answer
54.6% of turnover was spent paying staff (1)
Causes and consequences of poor employee performance
Causes of poor employee performance
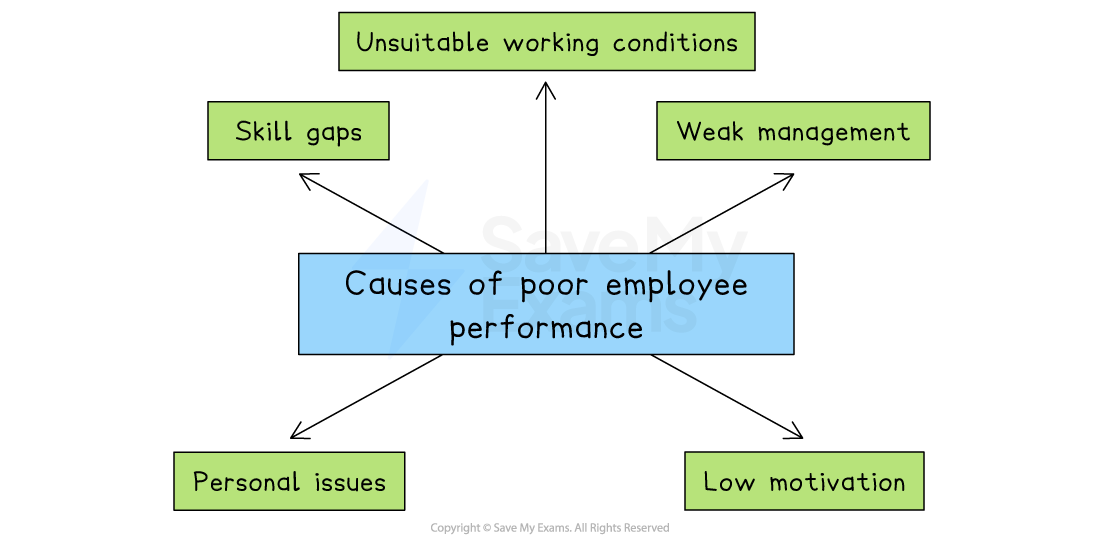
Skills gaps
Weak recruitment or training means staff lack the skills or knowledge to do a job properly
Low motivation
Poor pay, little recognition or limited career prospects may cause employees to make less effort with their work
Weak management
Unclear goals, poor communication or inconsistent feedback can confuse staff, reducing their productivity
Unsuitable working conditions
Unsafe, uncomfortable or poorly equipped workplaces can reduce output
Personal issues
Health, stress or family problems can distract employees from work
Consequences of poor employee performance
Consequence | Impact | Example |
|---|---|---|
Falling productivity |
|
|
Quality errors |
|
|
Missed deadlines and lost sales |
|
|
Higher absenteeism and turnover |
|
|
Low team morale |
|
|
Strategies for improving employee performance
Key HR objectives include
Raising labour productivity, as this lowers labour cost per unit, improving business competitiveness
Reducing absenteeism, as this can reduce training costs and overtime payments, and can build a positive team spirit
Reducing labour costs as a proportion of revenue, as this increases efficiency and lowers unit costs
Ways to improve employee performance
Financial rewards
Paying workers more or sharing profits may increase commitment and effort, leading to higher output and productivity
Bonuses and commissions are only paid when they have been earned or if targets have been met
Attendance and loyalty rewards may improve the intrinsic motivation of workers as they feel valued
Employee share ownership
Rewarding senior executives and managers with shares may increase their commitment to achieving objectives
Employees who own shares in the business may work harder and take less time off as they have a financial stake in the success of the business
Consultation
Consultation involves managers obtaining the views of employees when making decisions
Workers are likely to feel more involved within the business and work hard, and may be less likely to take days off work
Empowerment
Providing employees with autonomy and responsibility to make their own decisions and work on their own behalf encourages them to use knowledge and experience and develop their own solutions
Workers must be properly trained and equipped with the necessary resources to be properly empowered
Leaders need to be prepared to hand over authority and focus on providing encouragement, praise and feedback

Unlock more, it's free!
Was this revision note helpful?
