Product Development (Cambridge (CIE) A Level Business): Revision Note
Exam code: 9609
The process of product development
One way to stay ahead of the competition is by developing new products and innovating existing ones
New product development can be valuable for a number of reasons
A successful launch opens up a new income stream
Nintendo's launch of its Switch console in 2017 turned falling sales into record profits
Tastes change, so fresh products keep a business in fashion
Skechers Slip Ins are easy to put on, making them a comfortable alternative to lace-up shoes that align well with less formal working lives
Novel features create a competitive advantage over rivals
The Samsung Galaxy Z Fold offers a folding screen that mainstream phones lack
Extra product lines spread risk across different segments
The LEGO Botanical Collection targets adult hobbyists, not just children, diversifying sales
Regular innovation can improve brand image
Unilever’s Dove refillable deodorant pods underline its sustainability credentials
Key factors that influence new product development
Factor | Why it shapes the new product plan | Example |
|---|---|---|
Market demand and insight |
|
|
Technology advances |
|
|
Competitor activity |
|
|
Resources and R&D budget |
|
|
The product development process
There are several steps in the product development process

Generate ideas
Product concepts are discussed and brainstormed using customer suggestions, ideas from competitors’ products, employees’ ideas and information collected through market and technical research
Select the best idea
Ideas are compared, with some being dropped and others chosen for further research
This decision relates closely to costs and likely demand
Research includes looking into forecast sales, size of market share and cost-benefit analysis for each product idea
Develop a prototype
This allows the operations department to see how the product can be manufactured, any problems or difficulties arising from its production and how to fix them
Computer simulations are often used to produce 3D prototypes on screen
Test launch
The developed product is sold on a small scale to a limited market to see how well it sells before its full launch
Changes may be needed prior to an expensive, large-scale launch
Digital products such as apps and software run beta versions, which is a method of test-launching
Full launch of the product
The finalised version of the product is launched to the entire target market
Sources of ideas for product development
Product development is important for helping a business stay competitive, grow and meet changing customer needs
Before creating a new product, a business will explore different sources to get ideas and understand what customers might want
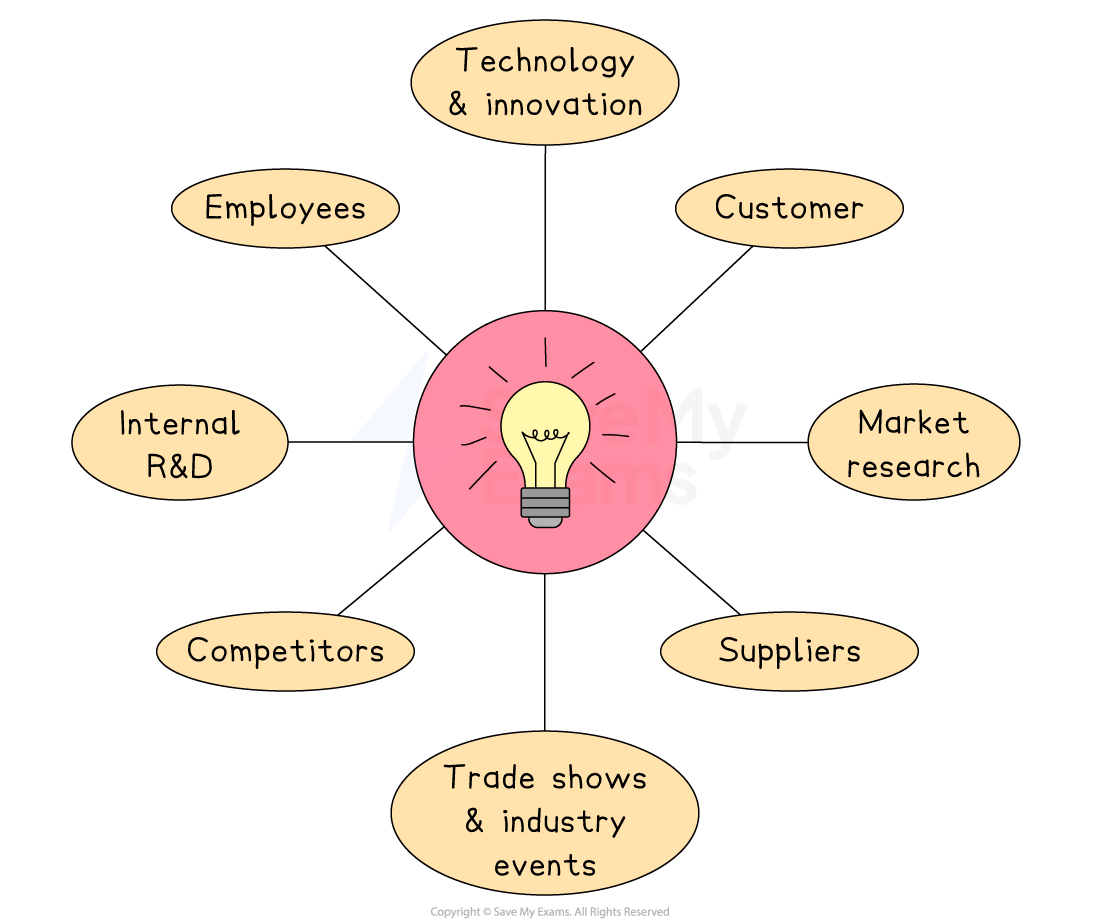
Customers
Feedback, complaints, reviews or suggestions can highlight what people want or need
Employees
Staff working in sales, customer service or production often notice problems or spot opportunities for new ideas
Competitors
Looking at what rivals are offering can inspire new ideas or show gaps in the market
Market research
Surveys, focus groups and trends analysis help businesses understand customer needs and spot new opportunities
Technology and innovation
New inventions or improvements in technology can lead to better or completely new products
Suppliers
A supplier might offer new materials or production methods that help create a new product
Trade shows and industry events
These can show off the latest trends and generate ideas for new products
Internal research and development (R&D)
Some businesses invest in their own R&D teams to create new products or improve existing ones
The importance of research and development
Product development is a key part of business success, as it supports growth and helps a business compete and meet customer needs
Key benefits of product development
It helps a business stay competitive
Developing new products allows a business to keep up with changes in customer preferences and technology
E.g. Apple regularly updates its iPhone models to stay ahead of rival smartphone brands
It supports business growth
New products can open up new markets or increase sales, helping the business grow in size and profits
E.g. Greggs launched vegan options to attract new customers and grow its market share
It builds customer loyalty and strengthens the brand
Offering fresh and useful products shows customers that the business listens and adapts to their needs
E.g. Coca-Cola released zero-sugar versions of its drinks to meet health concerns and keep loyal customers

Unlock more, it's free!
Was this revision note helpful?
