Marketing Mix: Promotion (Cambridge (CIE) A Level Business): Revision Note
Exam code: 9609
The objectives of promotion
Promotion plays a crucial role in generating customer awareness, interest and desire for a product
It communicates a business's value proposition to potential customers and helps to differentiate the product or business from competitors
The main aims of promotion
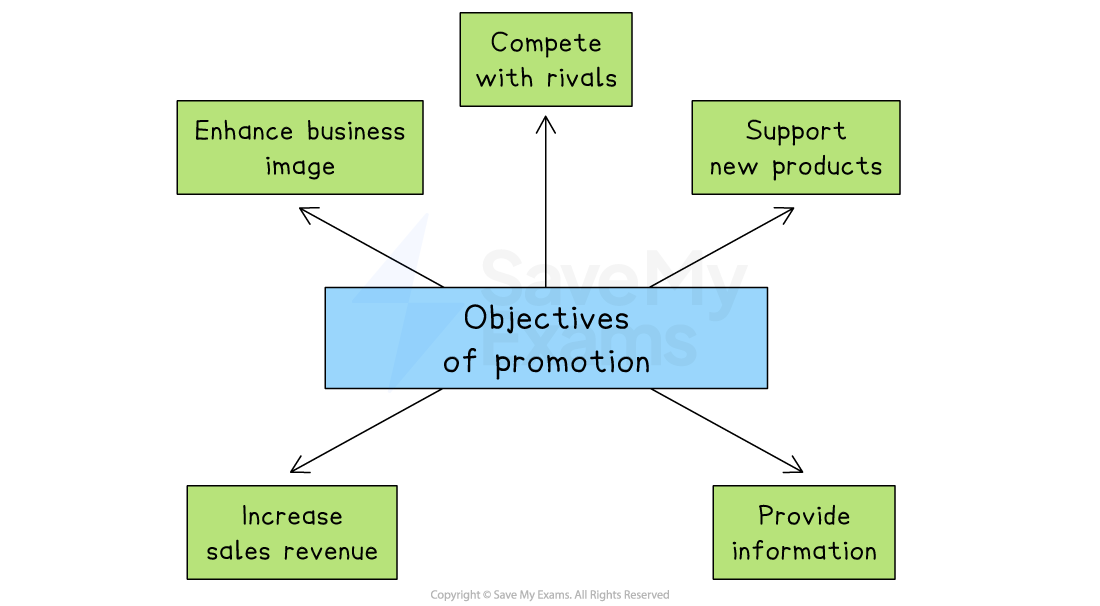
Enhance business image
Promotion helps build a strong, positive reputation that encourages trust and customer loyalty
Compete with rivals
It allows a business to stand out in a crowded market and attract customers away from competitors
Support new products
Promotion creates awareness and interest when launching a new product, helping it gain early sales
Increase sales revenue
By encouraging more people to buy, promotion helps boost the volume of sales and overall income
Provide information
Promotion informs customers about product features, prices, availability or special offers
Advertising
Advertising makes use of the media, such as television, newspapers and radio, to promote products or brands
It can reach large audiences and increase brand awareness
Advertising can also be used to create a specific brand image or message
E.g. The advertising campaign run by Compare the Market (Meerkat) uses humour to make shopping for financial products more attractive
Specialist media can target specific market segments
E.g. Upmarket furniture brands place advertisements in magazines such as Homes & Antiques and Country Life
Advertising is an expensive promotional strategy
E.g. In the US high viewership for the Super Bowl means that 30-second tv advertisements have been sold for as much as $6.5 million
In most cases, external specialists or media agencies create attractive and creative advertisements
Sales promotion
Sales promotion involves the use of incentives or discounts to encourage customers to buy products
They are often temporary and are designed to attract new customers to try a product for the first time and become loyal to the brand
Examples of sales promotions include free samples, buy one get one free (bogof), discount coupons, loyalty cards, and competitions
Examples of sales promotions

Sales promotions can quickly boost sales though impulse purchases or customer engagement
They are also an effective tool to clear out excess stock, promote a new product or raise cash quickly
However, for a limited period, revenue per item is reduced
This is likely to increase the break-even point
Customers may be unwilling to pay a higher price once the sales promotion has come to an end
Direct promotion
Direct promotion involves communicating directly with customers through email, text message, social media or post
E.g. Takeaway restaurants distribute menus to households in the local community
Businesses can target specific audiences and personalise the message to individual customers
Its impact is measurable, which enables businesses to track their results and adjust strategy accordingly
However, direct promotion can be intrusive, as customers may perceive it as spam
It can also be costly, especially if businesses do not have an established customer database or need to purchase leads
Digital promotion
Digital promotion refers to the use of online and electronic technologies to promote a business’s products or services to consumers
Examples of digital promotional activity
Social media marketing
Promoting products through platforms like Instagram, Facebook, TikTok or X
Email marketing
Sending promotional emails to target customers
Search engine marketing (SEM)
Paid adverts that appear in search engine results (e.g. Google Ads)
Influencer marketing
Paying social media personalities to promote a brand
Website banners and pop-ups
Digital adverts placed on websites
Video marketing
Promotional content shared on platforms like YouTube or embedded in websites
Content marketing
Creating blogs, articles or videos to provide value and attract customers
Evaluating digital promotion
Benefits | Drawbacks |
|---|---|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
The role of packaging in promotion
Packaging is the physical container or wrapping for a product. It is also used for promotion and selling appeal
Packaging is normally designed to
Present products in the most practical yet attractive way
Communicate the quality of the product
Catch the customer's eye when they shop
Provide key information to customers
Establish the business brand image
Protect a product from damage
To stand out from the competition and establish a long-lasting relationship with consumers, brands are investing more money than ever before in creative and environmentally friendly packaging designs
This is becoming increasingly important for businesses as they place a greater emphasis on sustainability and their CSR policies
Examples of memorable packaging
Apple iPhone | Ferrero Rocher |
|---|---|
 |  |
|
|
Tiffany | Pringles |
 |  |
|
|
The role of branding in promotion
A brand is the set of names, symbols, design elements and associations that customers link to a product, service or business
It can be considered as the promise of a consistent experience every time a customer buys a branded product
The UK's favourite brands

Why strong brands matter
Clear differentiation
A strong brand makes a product instantly recognisable among near‑identical alternatives
This simplifies choices for time‑pressed shoppers
For example, Innocent’s playful tone and halo logo help its smoothies stand out in crowded supermarket chiller cabinets
Customer loyalty and repeat sales
Familiar, trusted brands reduce perceived risk, so buyers return without comparing prices each time
This loyalty lowers the firm’s long‑run promotion costs
For example, Colgate maintains the market‑leading toothpaste share despite many cheaper own‑label options
Ability to charge premium prices
A well‑regarded brand lets the firm add value beyond improvements to the physical product, increasing profit margins
For example, Apple sells iPhones at higher prices than comparable rivals because the customers associate the brand with design and quality
Easier new‑product launches
Positive associations of a strong brand rub off on new items, cutting the need for heavy introductory advertising
For example, Cadbury's reputation for quality chocolate ensured success for its launches of hot chocolate powder and ice cream bars
Stronger bargaining power with retailers
Stockists such as supermarkets want well-known names that pull in customers, so big brands gain better shelf space and promotional support
For example, supermarkets run prominent displays on end aisles for Coca‑Cola, knowing it attracts shoppers
Intangible asset value
A respected brand appears on balance sheets under goodwill and can be sold or licensed, generating extra income
For example, Manchester United licenses its crest for global merchandise, creating revenue far beyond match tickets

Unlock more, it's free!
Was this revision note helpful?
