Customer Relationship Marketing (Cambridge (CIE) A Level Business): Revision Note
Exam code: 9609
The aims of CRM
Customer relationship marketing (CRM) involves a business focusing their marketing efforts around building a deep understanding of customers, consistently meeting customer needs and developing long-term customer loyalty
Marketing strategies and tactics are focused on four key areas
CRM strategies and tactics
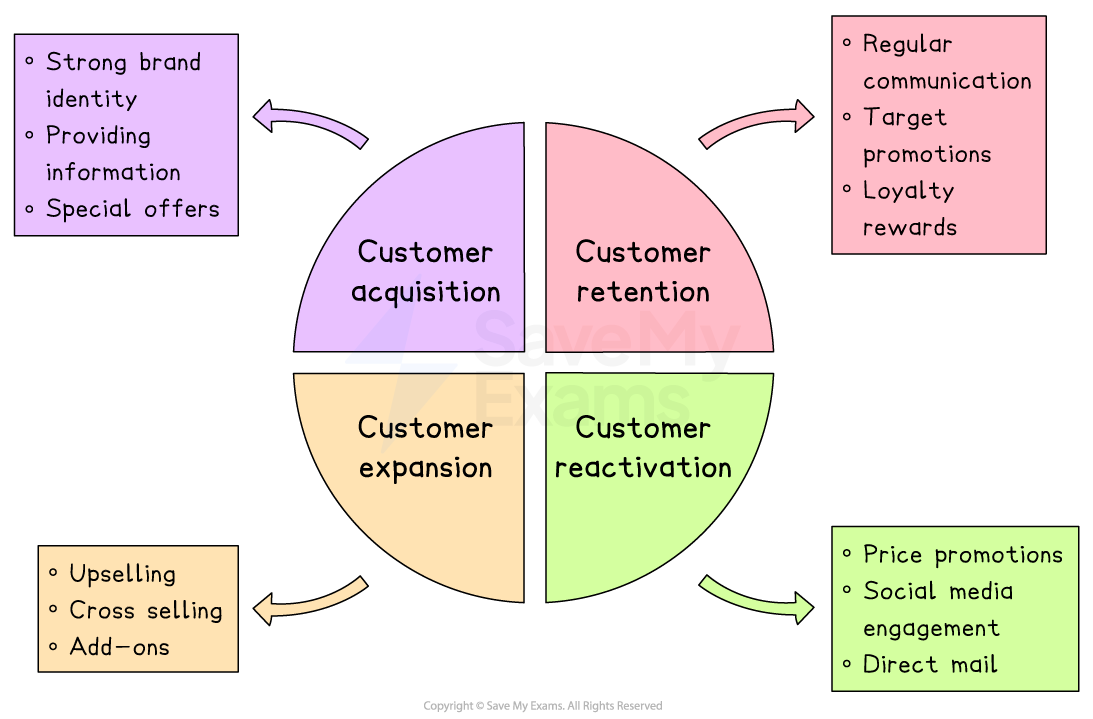
Customer acquisition
Attracting interested consumers and converting them into customers to achieve growth, make money and improve chances of business survival
Businesses can acquire customers in many different ways, including
Building a strong brand identity
Delivering excellent customer experiences
Providing clear information
Offering special rewards, such as price promotions
Customer retention
Customer retention involves encouraging customers to remain loyal to a business and its brands over time
Encouraging loyalty is important for several reasons
Attracting new customers often costs more than retaining current customers
Loyal customers tend to be valuable repeat customers
Retained customers can refer new customers to a business
Word-of-mouth marketing is a form of free marketing for a brand
Happy customers talking about a business or brand in positive ways can help persuade people they know to become loyal customers as well
Businesses can retain customers in many different ways, including
Customer loyalty schemes
Regular communication about new products or promotional offers
Targeted price promotions or other perks for existing customers
Customer expansion
Customer expansion is the process of encouraging existing customers to increase the value and frequency of their spending on products and services over time
Businesses can achieve customer expansion in several different ways, including
Upselling by encouraging customers to upgrade to premium products
Cross-selling by offering customers a related product or service
Providing add-ons such as insurance policies, extra features or extended warranties
Customer reactivation
Customer reactivation involves reaching out to customers who have previously expressed interest in or purchased a product but have since become disengaged
Businesses can adopt a range of techniques to reactivate customers, including
Social media engagement
Targeted price promotions for returning customers
Direct mailings via post or email
Costs and benefits of CRM
Benefits of CRM
CRM allows a business to build a detailed understanding of its customers’ needs and preferences
This helps the business to tailor its products, services and promotional activity more precisely, increasing the chances of customer satisfaction and repeat sales
E.g. A clothing retailer might use CRM data to send personalised offers based on a customer’s past purchases
Retaining loyal customers is usually more cost-effective than attracting new ones
CRM focuses on building long-term relationships with existing customers, which reduces marketing costs
E.g. A mobile phone company offering exclusive upgrades to loyal users instead of spending heavily on advertising to new customers
Costs of CRM
CRM requires significant investment in staff training and development
To deliver consistently good customer service, employees need to understand the CRM system and be committed to meeting customer expectations at every stage of the buying process
E.g. Hotel staff may need to learn how to use CRM software to remember guest preferences and deliver a personalised experience.
CRM is unlikely to succeed without ongoing, expensive customer research
For CRM to be effective, the business must constantly collect, update and analyse customer data, which can be time-consuming and costly
E.g. An airline may need to invest heavily in customer surveys, feedback tools, and data analytics to truly understand traveller needs.

Unlock more, it's free!
Was this revision note helpful?
