Capacity Utilisation & Outsourcing (Cambridge (CIE) A Level Business): Revision Note
Exam code: 9609
Measuring capacity utilisation
Capacity utilisation measures how effectively a business uses its assets to produce output
It compares current output to the maximum possible output a business can produce using all of its assets
Capacity utilisation is calculated using the following formula and expressed as a percentage
Worked Example
Bäkkerei Lola produces specialist Indian and Bangladeshi breads, which are sold to restaurants in the Munich area
Batch production is used in the factory to manufacture the range of breads and the factory can produce a maximum of 68,400 units per month
In May factory output was 51,420 units
Calculate Bäkkerei Lola's capacity utilisation in May.
(2)
Step 1: Divide the current output by the maximum output
(1 mark)
Step 2: Multiple the outcome by 100 to obtain the percentage capacity utilisation
(1 mark)
Examiner Tips and Tricks
In your exam, you may need to rearrange the capacity utilisation formula. You may be given the percentage of capacity utilisation and have to calculate the volume of output.
The impact of under-capacity utilisation
Low capacity utilisation means resources are being underused
This may lead to inefficiencies and lost potential output
Positive and negative impacts of undercapacity utilisation
Positive impacts | Negative impacts |
|---|---|
|
|
Improving capacity utilisation
High capacity utilisation means a business is making the most of its resources, such as staff, machines, and buildings
This helps to lower unit costs, improve efficiency, and increase profits
Ways to increase capacity utilisation
Increase customer demand
Boost sales through marketing, special offers, or new products so more output is needed
Make better use of staff and equipment
Improve planning and scheduling to ensure that workers and machines are kept busy and productive
Accept more orders, even at lower profit margins
Taking on additional work, like bulk or discounted orders, can help fill unused capacity and reduce unit costs
Use spare capacity to produce for other businesses
If a business has too much capacity, a business could offer manufacturing services to other companies
Launch products or services at different times of year
Spreading demand across the year avoids quiet periods and helps keep production steady
Close under-used parts of the business
If some facilities are regularly unused, shutting them down can cut costs and improve overall efficiency
The impact of operating over maximum capacity
High capacity utilisation may mean flexibility to respond to new orders is lost
Staff are under pressure to increase output
Overworked staff may leave, increasing staff turnover
Machinery operates at its limit and is more prone to breakdowns, which disrupts production
High capacity utilisation minimises unit costs and increases competitiveness
Busy workers feel secure in their employment
A busy business is likely to be well thought-of and attract customers who are willing to wait for products to be delivered
Outsourcing
Outsourcing is the process where a business delegates specific business activities (IT, customer support, HR etc) to external service providers
Businesses choose to outsource these functions to reduce costs, access specialised expertise, or focus on core competencies
Advantages of outsourcing
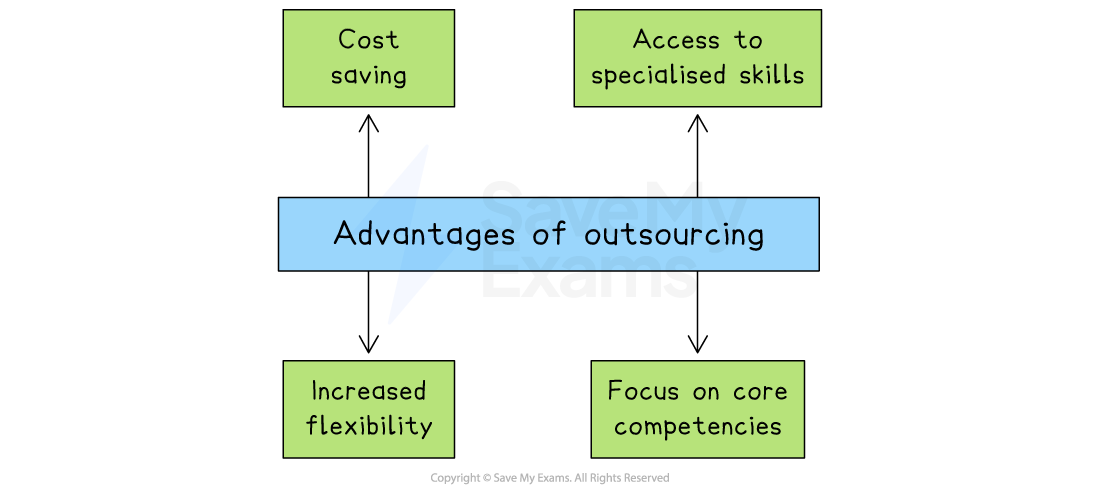
Cost savings
Businesses can often reduce expenses associated with operations such as hiring and training employees, maintaining infrastructure and managing IT systems
Access to specialised skills
External specialists have resources that the business lacks internally, which allows it to benefit from the knowledge and experience of industry specialists when required
Increased flexibility
Outsourcing provides greater flexibility to scale operations up or down based on demand fluctuations, which is particularly valuable in industries with seasonal or unpredictable demand
Focus on core competencies
Businesses can concentrate their resources and efforts on their core competencies, where they can add value
Disadvantages of outsourcing
Quality control
Outsourcing makes it harder to ensure consistent quality and adherence to company standards
Loss of control
Handing direct control over those activities to others outside of the business may be risky
Companies must carefully select reliable partners and establish clear contractual terms to protect their interests
Data security and confidentiality
Sharing sensitive information outside of the business introduces risks to data security and confidentiality

Unlock more, it's free!
Was this revision note helpful?
