Location (Cambridge (CIE) A Level Business): Revision Note
Exam code: 9609
Factors determining location and relocation
Choosing a good production location can have significant impacts on a business.
A range of factors influence the location a business chooses for production or where it chooses to relocate
Factors affecting business location

Proximity to the market
This refers to how close the business is to its target customers
Being near the market can reduce transport costs and make it easier for customers to access the business
Proximity to labour
This means being located near areas where skilled and qualified workers are available
Businesses often choose locations with a strong local workforce to make it easier to recruit the right people and run operations efficiently
Proximity to materials
This refers to how close a business is to the raw materials or supplies it needs
Being near materials helps reduce transportation costs and ensures a steady supply
Proximity to competitors
Some businesses choose to locate near competitors to attract the same customer base or to offer something different
Others may avoid locating near competitors to reduce direct competition
The nature of the business activity
Different types of businesses have different location needs based on what they do
For example, a manufacturing plant may need large space and delivery access, while a law firm may need a smaller, more central office
E.g. A factory needs room for machinery and deliveries, while a law office needs a professional, easy-to-access location
Infrastructure
This includes transport links and electronic networks like internet connections
Good transport is essential for businesses that deliver physical goods
Fast and reliable internet access is key for online businesses
E.g. An online fashion retailer needs a location close to the motorway for quick delivery and fast service, helping it compete in the market
Local, national and international location decisions
When a business chooses where to locate, the scale of that decision can be local, national or international
1. Local location decisions
Local location decisions involve choosing where in a particular town or city to place the business, such as in the city centre, on an industrial estate or near transport links
E.g. A hair salon might choose a busy high street over a quiet side road to attract walk-in customers
Key factors affecting local location decisions
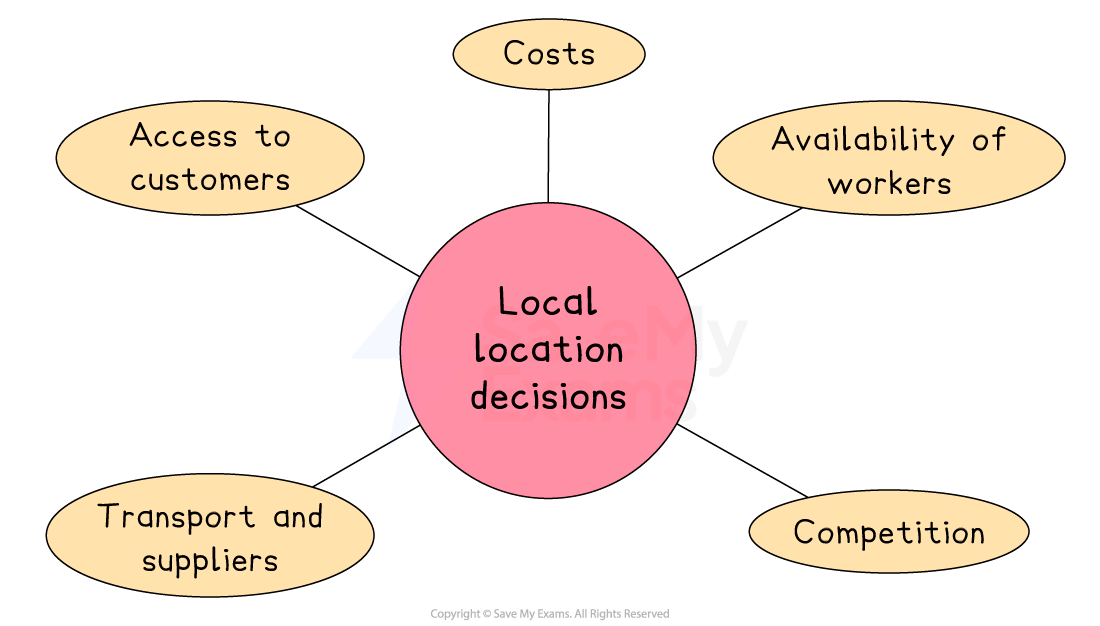
Access to customers
Retail shops often choose high footfall areas like shopping centres to attract more sales
Major Turkish retail brands, for example, locate their flagship stores on İstiklal Caddesi, a busy shopping street in Istanbul.
Availability of workers
Businesses benefit from locating near skilled or affordable labour
Hi-tech firms choose business parks around MIT in the USA to access a strong pool of computing graduates
Costs
Rent and business rates can vary widely even within one town or city
Retail space on Berlin’s Kurfürstendamm is expensive, but nearby Prenzlauer Berg offers more affordable options
Competition
Locating near rivals can create a customer hub but may also reduce market share
Hatton Garden in London is home to many high-end jewellery and gold businesses, attracting specialist customers.
Transport and suppliers
Good transport links are essential for service and delivery-based businesses
Logistics firms favour northern Calais due to its excellent road, rail and ferry connections.
2. National location decisions
National location decisions involve choosing which part of a country to set up or expand a business
E.g. A call centre might choose a city in the north of the UK to benefit from lower wages and government support.
Key factors affecting national location decisions
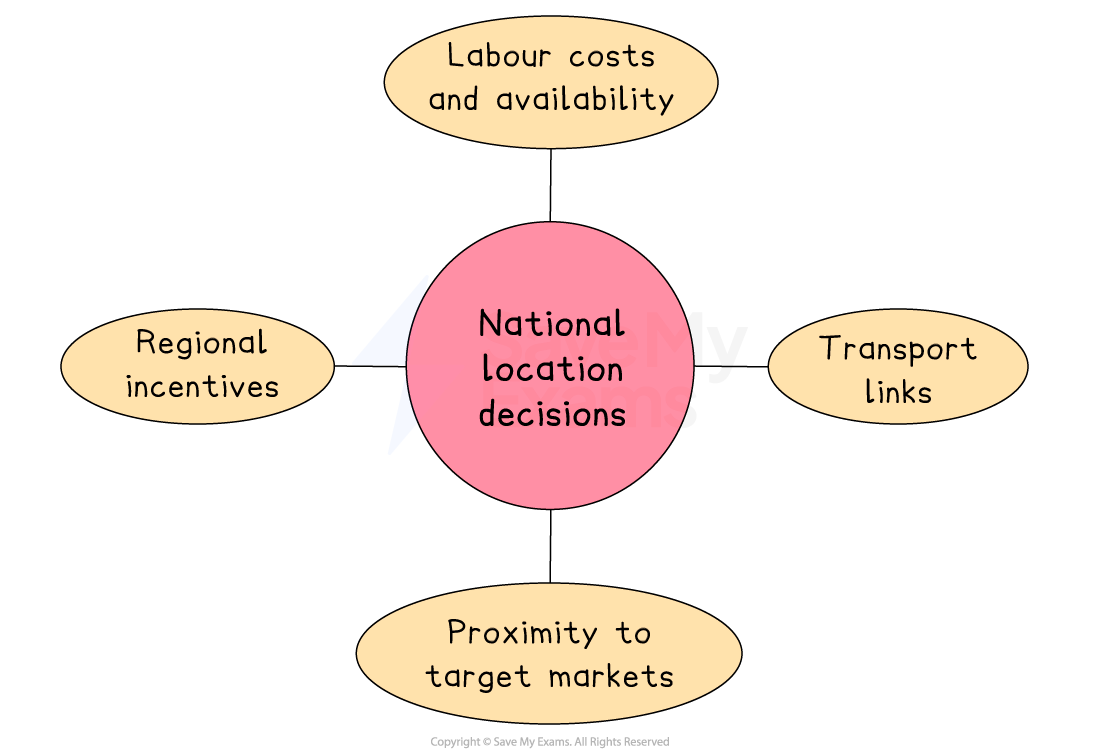
Regional incentives
Governments may offer grants or tax breaks to attract businesses to poorer areas, aiming to reduce unemployment and support local economies
E.g. The Welsh Government has funded companies locating in places like Cardiff and Swansea
Labour costs and availability
Wages and skills vary by region
Cities may offer highly skilled workers at higher wages, while rural areas may be cheaper but with fewer qualified employees
E.g. In India, major cities like Bangalore and Delhi have more skilled workers than rural regions
Proximity to target markets
Locating near areas with high demand helps reduce delivery costs and respond better to local preferences
E.g. Mexican food firms often base themselves near large cities like Mexico City or Guadalajara to reach more consumers
Transport links
Good access to roads, ports, railways or airports helps cut delivery times and transport costs, especially for goods-based businesses
E.g. The Netherlands attracts many distribution centres due to Rotterdam port and a strong road and rail network
3. International location decisions
International location decisions relate to a business considering moving or expanding to another country
E.g. A European clothing brand might open a factory in Vietnam to reduce production costs and sell to Asian markets
Key factors affecting international location decisions
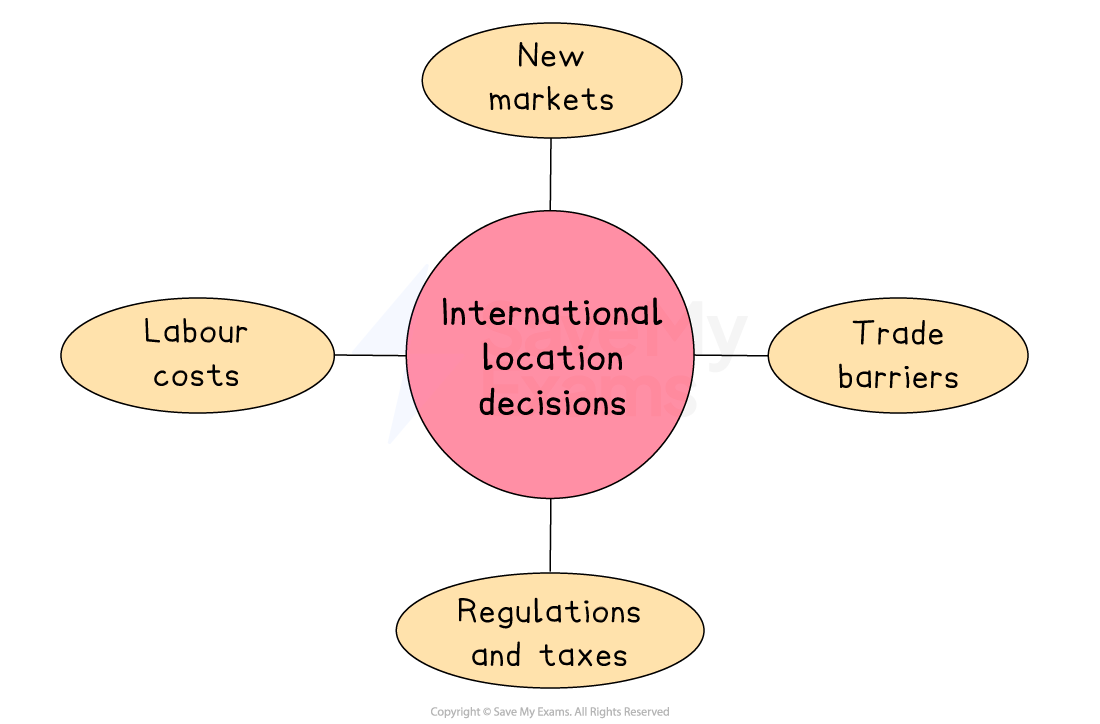
Labour costs
Businesses may locate in countries where wages are lower to reduce production costs, especially in labour-intensive sectors like textiles or electronics
However, they must weigh up lower wages against possible lower skill levels, productivity and working conditions
E.g. Zara and H&M outsource production to countries like Bangladesh and Vietnam, where labour is much cheaper than in Europe or North America
New markets
Expanding abroad helps businesses access new customers, particularly in growing economies
This boosts sales and market share, especially if the home market is saturated
Being based locally also helps firms better understand customer behaviour and respond quickly to demand
E.g. McDonald’s has entered Asian and African markets to tap into rising incomes and growing demand for Western food
Regulations and taxes
Some countries offer lower tax rates and simpler business laws, making them attractive for international firms
These benefits can raise profits but must be balanced with maintaining ethical standards
E.g. Ireland’s low corporate tax and EU access have attracted major tech firms like Google and Facebook
Trade barriers
Locating within a country can help businesses avoid tariffs, quotas or other trade restrictions
This is vital for exporters and also improves delivery times and local relationships
E.g. Toyota has built factories in the US and UK to avoid import tariffs and better serve local markets
The impact of offshoring and reshoring
Offshoring
Offshoring occurs when a business sets up operations in another country to carry out certain business processes so as to:
Take advantage of lower labour costs
Gain access to specialised skills
Expand into new markets
Common examples of offshoring practices include call centres in foreign countries, software development teams or manufacturing plants established in countries with cheaper labour
Evaluating offshoring
Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
|
|
Reshoring
Reshoring occurs when a business brings back its production activities to its home country from abroad
It involves reversing the previous decision to offshore or outsource those activities to another country
There are several reasons why a company may choose to reshore its operations
Reasons to reshore

Cost considerations
The initial cost advantages of offshoring may reduce due to rising labour or transportation costs in the foreign country
Quality control
By reshoring, companies can have better control over the manufacturing processes and ensure higher quality standards, which may lead to improved customer satisfaction
Intellectual property protection
By bringing manufacturing back to their home country, they can reduce the risk of intellectual property theft
Supply chain resilience
The COVID-19 pandemic highlighted the vulnerabilities of global supply chains
Disruptions to transportation, logistics and international trade led to delays and shortages of critical goods
Reshoring reduces dependence on foreign suppliers
Market proximity
Can allow companies to be closer to their target markets, which can lead to faster delivery times, reduced transportation costs and improved responsiveness to customer demands
Globalisation and location
Globalisation is the growing integration of economies, markets, and people across the world
It allows businesses to operate more freely across borders and has a strong influence on where they choose to locate
How globalisation impacts business location
Factor | Explanation |
|---|---|
Access to international markets |
|
Cheaper labour and materials |
|
Improved transport and technology |
|
Avoiding trade barriers |
|
Government incentives |
|
Cultural and language factors |
|

Unlock more, it's free!
Was this revision note helpful?
