The Need for Business Finance (Cambridge (CIE) A Level Business): Revision Note
Exam code: 9609
Why do businesses need finance?
Businesses need finance to get started, allow them to grow and fund continuing activity
Finance may be needed for capital expenditure, which is spending on fixed assets such as equipment, buildings, IT equipment and vehicles
Similarly, finance is required for operating expenditure, spending on raw materials or day-to-day expenses, such as wages or utilities

Why business finance is needed
1. Start-up finance
Start-up finance funds fixed assets and current assets such as inventory before a business can begin trading
The amount needed is identified in the business plan
Owners often invest their own capital into a new business
Some small new business owners obtain a start-up loan to cover initial costs
2. Finance for growth
As a business grows, it may need to purchase capital equipment
It may require more machinery, buildings, IT infrastructure or vehicles, which help the business to increase output
If a business wants to grow by developing new products, large amounts may need to be invested in research and development (R&D)
E.g. Apple's annual R&D expenses for 2023 were $29.915bn, a 13.96% increase from 2022, to invest heavily in artificial intelligence (AI) and product innovation
3. Working capital
Finance is required for working capital, day-to-day spending on raw materials, wages or utilities
Having a steady flow of working capital is essential
Without working capital, the business would be unable to cover its regular expenses
It may suffer cash-flow problems, which could lead to business failure
Short-term and long-term finance needs
Short-term finance needs
Short-term sources of finance are needed to meet regular costs such as paying for utilities, suppliers and employee wages
They are likely to be relatively small amounts and are rarely needed beyond a year
Important short-term finance needs include marketing costs and recruitment costs
These are closely linked to short-term business objectives
Where revenue from sales does not cover these expenses, sources such as overdrafts or trade credit may be useful
Long-term finance needs
Longer-term sources of finance are needed to fund the purchase of non-current assets such as buildings and other types of capital resources or to acquire other businesses
These are likely to be large sums that may be required for a significant period of time
Where retained profit is not sufficient to meet these needs, businesses may consider taking out long-term loans, mortgages or raising share capital
Cash versus profit
Profit is the difference between revenue generated and total business costs during a specific period of time
Profit is an important indicator of a company's financial health and long-term sustainability, as it helps to assess the effectiveness of a company's operations
Cash is measured by taking into account the full range of money flowing in and out of a business
This includes revenue from sales, operating expenses, investments, loans, and any other cash-related transactions
It performs a variety of functions in a business
It is used to cover regular operating expenses such as workers' pay, supplier invoices and overheads such as rent and utility bills
It can also be used to meet unexpected expenses, such as the replacement of broken equipment
Profit versus cash flow

While a business may ultimately make a profit, they may lack cash at times
Some customers may not have paid them yet
They may have paid some large bills
Cash-poor businesses will struggle to pay suppliers, employees and operating expenses
This is called insolvency
Lifestyle retailer Joules announced plans to liquidate in December 2022 as a result of cash-flow difficulties, despite making a profit of £2.6 million during the previous year
Business failure and finance
Financial problems are one of the most common causes of business failure, especially for small and new businesses
Without sufficient finance, even a business with effective financial planning, good products and healthy demand may fail due to poor cash flow or unpaid debts
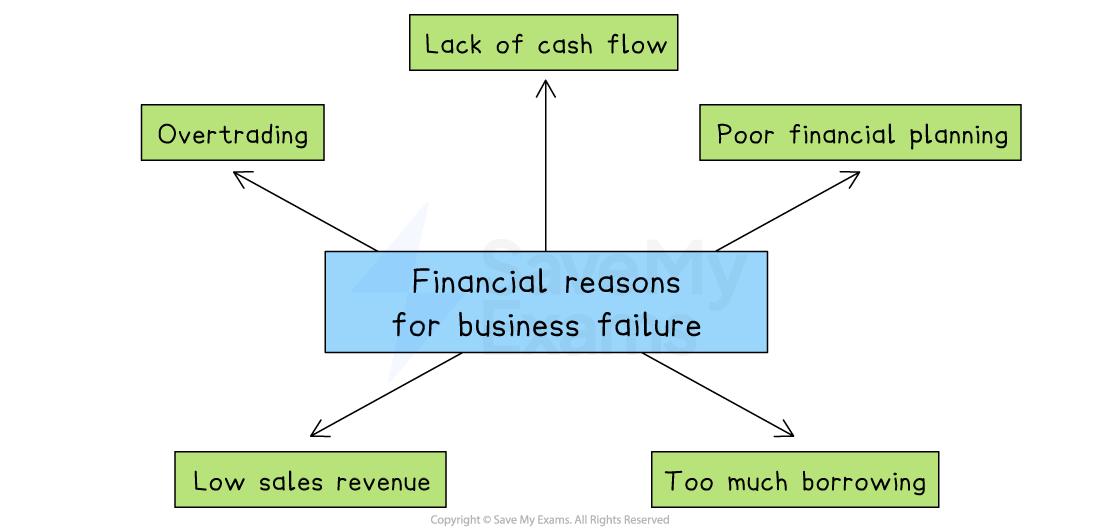
Financial reasons for business failure
Lack of cash flow
A business may be profitable on paper but still run out of cash
If customers delay payments or unexpected bills arise, the business may not have enough money to pay suppliers or wages
Poor financial planning
If a business does not forecast cash flow accurately or budget properly, it may overspend or run out of money
Poor planning can lead to missed loan repayments or unpaid bills
Too much borrowing
Relying heavily on loans or overdrafts increases pressure on the business to make regular repayments
High interest costs can add to financial stress, especially if revenue falls
Low sales revenue
If the business is not generating enough income from sales, it may not cover its costs
This is a particular risk if demand is seasonal, falls unexpectedly or pricing is too low
Overtrading
This happens when a business grows too quickly without enough capital to support its expansion
It may take on large orders or open new branches but run out of cash before it receives payments from customers

Unlock more, it's free!
Was this revision note helpful?
