Management Functions (Cambridge (CIE) A Level Business): Revision Note
Exam code: 9609
Traditional management functions
A manager is an individual within an organisation who is responsible for overseeing a team or a specific function
Large businesses usually have several layers of management with distinct responsibilities
Directors or owners establish the business’s overall goals and set long-term targets for the business
They are ultimately responsible for business performance
Senior managers work to achieve the targets set by the owners or directors
They are often responsible for a function within the business, e.g. marketing or finance
Supervisors and team leaders support senior managers to achieve their targets
They report problems and pass on instructions
They may make simple decisions, such as allocating jobs among different employees
Managerial functions
Planning | Organising |
|---|---|
|
|
Directing | Controlling |
|
|
The role of managers: Fayol
Fayol identified five functions of management that provide a framework to help managers determine how to best allocate their time
Fayol's five functions of management
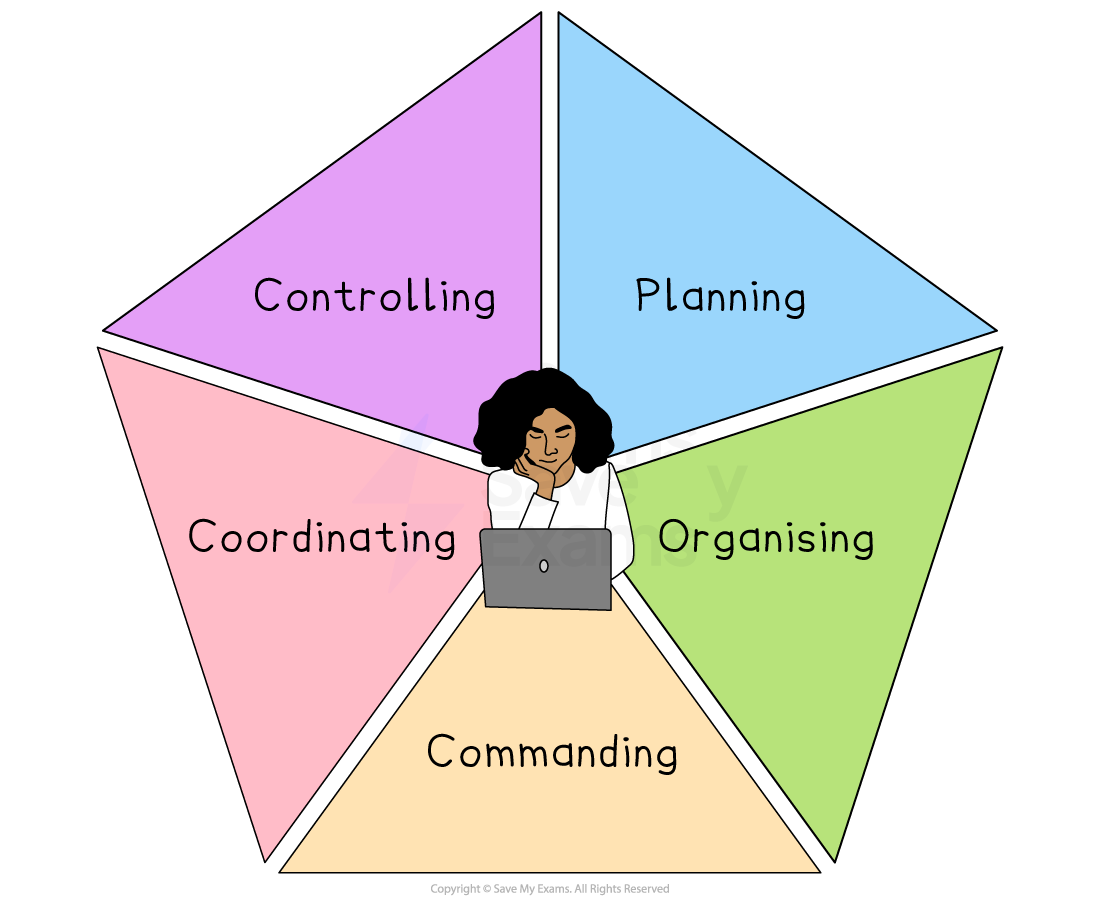
Planning
Managers assess the future and make sure the organisation is prepared for it
They should develop flexible business plans that consider available resources and future market trends
Organising
Managers define team members' roles and responsibilities and make sure that everyone understands what is expected of them
They should hire, train and allocate staff so that every role is covered
Commanding
Managers get the most from their staff
They should be familiar with team members' strengths and delegate tasks that match them
They should also set a good example by "walking the talk" to build a strong and dependable team
Coordinating
Managers ensure that every department understands its responsibilities and knows what other teams need from them
They should aim to create a smooth workflow, prevent disruptions and solve problems
Controlling
Managers regularly check that everything is running as it should be
They should be prepared to amend rules, plans and processes if necessary
They should always be alert for areas for growth and improvement
Evaluation of Fayol's five functions
Fayol's ideas promote skills such as teamwork and agility, which are important in modern workplaces
However, some have criticised his ideas for being too inhuman for modern management
One man's observations cannot possibly apply to all organisations
The role of managers: Mintzberg
Henry Mintzberg argued that Fayol's five functions do not fully describe the activities that managers undertake in their roles
He identified ten roles that are common to all managers, categorised into three groups
Interpersonal roles
Informational roles
Decisional roles
Mintzberg's ten managerial roles
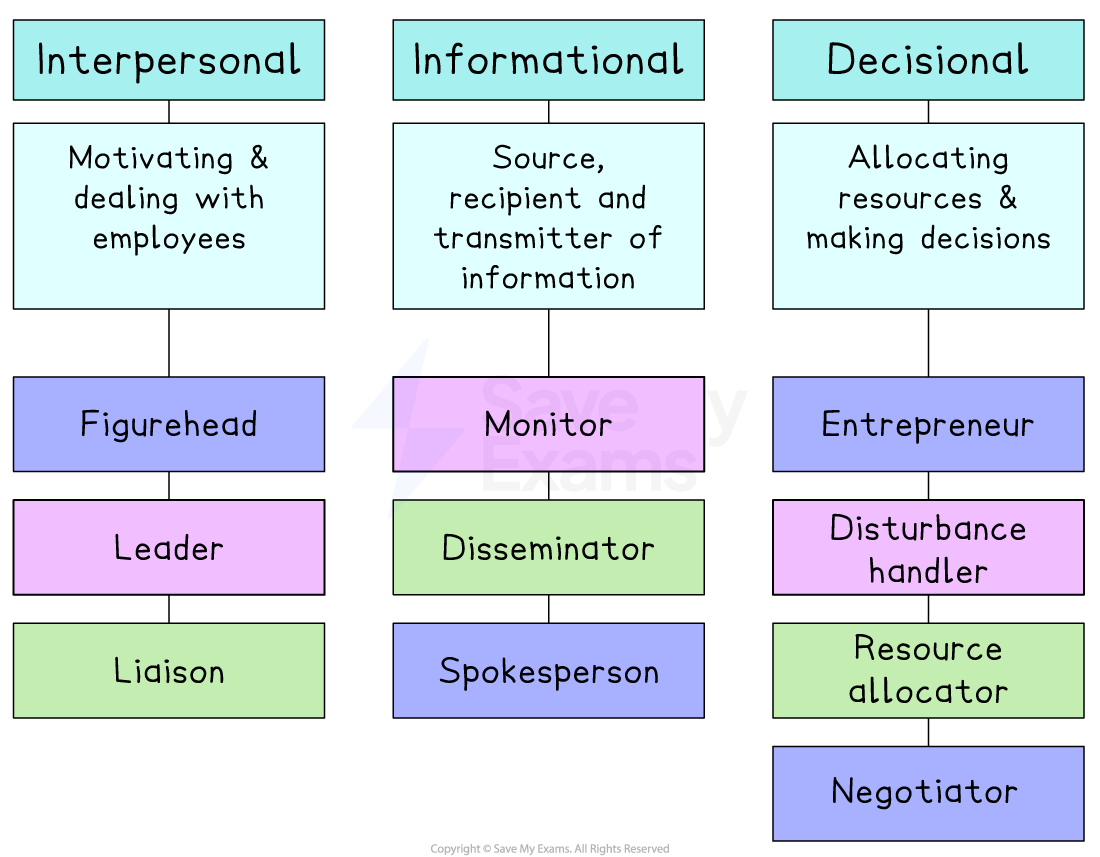
Interpersonal roles
A manager's interpersonal roles are those which focus on motivation and dealing with employees and, sometimes, other external stakeholder groups
The three roles are
Acting as a figurehead
E.g. Appearing in press conferences, hosting product launches and being the 'face' of the business
Being a leader and enthusing others
E.g. Be available to meet staff, encourage and praise employees
Liaison with others inside and outside of the business
E.g. Communicate with stakeholders, participate in events, respond to complaints
Informational roles
These roles involve the collection, communication and presentation of information within and outside of the business
The three roles are
Being a monitor and collector of information relevant to business circumstances
E.g. Attend conferences, keep up-to-date with industry research
Acting as a disseminator of information to both subordinates and other key stakeholder groups
E.g. Share key developments with staff, calm fears and communicate positively
Being the business spokesperson
E.g. Lead seminars, communicate with the media and government
Decisional roles
These roles are focused on making decisions and organising resources so that business objectives can be met
The four roles are
Being an entrepreneur on behalf of the business
E.g. Bring new ideas and empower others to become intrapreneurs
Acting as a disturbance handler during periods of upheaval or change
E.g. Determine rapid responses in crisis situations, act as a key point of contact
Being a resource allocator to ensure adequate financial and physical resources are available
E.g. Determine budgets and source finance, staff and equipment
Representing the business as a negotiator with external stakeholders
E.g. make deals with significant suppliers and customers, network with key business allies
Evaluation of Mintzberg's ten managerial roles
Mintzberg emphasises the importance of interpersonal roles in effective management, which Fayol's five functions overlook
However, his informational and decisional roles are largely the same as those identified by Fayol, albeit more defined and of more practical use to managers
The contribution of managers to business performance
Managers contribute to business performance by planning, leading, organising, and making appropriate decisions
Good managers help businesses run smoothly, adapt to change and meet objectives effectively
Poor management can lead to confusion, low morale and missed opportunities
Case Study
Better management at Café Verde
Café Verde is a small chain of eco-friendly coffee shops in South Africa.

When the business began struggling with high staff turnover and inconsistent customer service, the owner promoted Lindiwe, an experienced team leader, to the role of operations manager.
Lindiwe introduced several key changes:
She reorganised staff rotas to ensure each shift had a good mix of experienced and new employees
She arranged training sessions to improve customer service skills and product knowledge
Lindiwe held weekly team meetings to gather feedback and set targets for quality and service
She also introduced a bonus scheme linked to customer satisfaction scores
Outcomes
Within three months, customer complaints fell by 40%, staff morale improved and staff turnover reduced significantly
Sales increased as more customers returned and left positive reviews online

Unlock more, it's free!
Was this revision note helpful?
