Binary Trees (Cambridge (CIE) A Level Computer Science): Revision Note
Exam code: 9618
Binary trees
What is a binary tree?
A binary tree is a rooted tree where every node has a maximum of 2 nodes
A binary tree is essentially a graph and therefore can be implemented in the same way
You must understand:
Tree traversal of a tree data structure
Add new data to a tree
Remove data from a tree
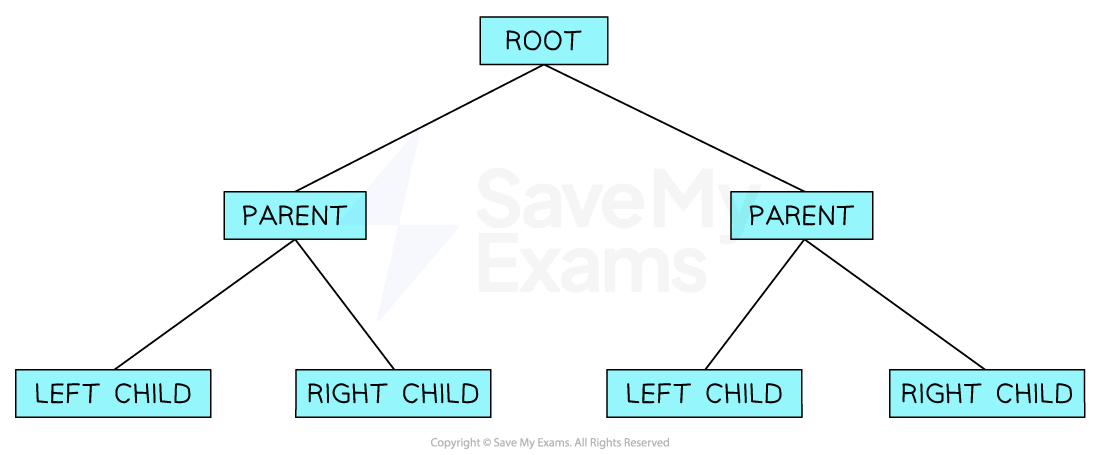
The most common way to represent a binary tree is by storing each node with a left and right pointer
This information is usually implemented using 2D arrays

Tree terminology
Keyword | Definition |
|---|---|
Node | An item in a tree |
Edge | Connects two nodes together and is also known as a branch or pointer |
Root | A single node which does not have any incoming nodes |
Child | A node with incoming edges |
Parent | A node with outgoing edges |
Subtree | A subsection of a tree consisting of a parent and all the children of a parent |
Leaf | A node with no children |
Traversing | The process of visiting each node in a tree data structure, exactly once |
How do you program a tree?
In the following example:
A tree is represented using a
TreeNodestructure, which includes:A
valuefield to store the data held in the nodeA
childrenfield to store a collection (e.g. list or array) of child nodes
The
createTreeNodefunction is used to initialise a new tree node, setting its value and creating an empty collection for its childrenThe
addChildfunction allows a new child node to be added to a parent nodeIt creates a new
TreeNodewith the given value and appends it to the parent'schildrencollection
Finally, the
createTreeNodefunction is used to create the root nodeAdditional child nodes are added using the
addChildfunction, allowing a multi-level tree structure to be built with branches and sub-branches
Pseudocode |
|---|
|
Python |
|---|
|
Java |
|---|
|
Algorithm to traverse a tree structure
Pseudocode - pre-order tree traversal |
|---|
|
Python - pre-order tree traversal |
|---|
|
Java - pre-order tree traversal |
|---|
|
For a tree like:
Root├── Child 1│ └── Grandchild 1.1└── Child 2The output will be:
RootChild 1Grandchild 1.1Child 2
Algorithm to add data to a tree structure
Pseudocode |
|---|
|
Python |
|---|
|
Java |
|---|
|
These examples all create a new node with the provided value and attach it to the given parent node
This approach allows dynamic construction of trees with multiple levels
Algorithm to remove data to a tree structure
Pseudocode |
|---|
|
Python |
|---|
|
Java |
|---|
|
This only removes the first matching child from the direct children of a node
If you want to remove nodes anywhere in the tree, you’d need a recursive version
REMOVEanddeland.remove()work because thechildrencollection is a list/array

Unlock more, it's free!
Was this revision note helpful?
