Neurones (AQA A Level Biology): Revision Note
Exam code: 7402
Myelinated motor neurones
Information is transmitted through the nervous system as nerve impulses; electrical signals that pass along neurones
A bundle of neurones is known as a nerve
Different types of neurone carry nerve impulses in different parts of the nervous system:
Sensory neurones carry impulses from receptors to the CNS
Relay neurones connect sensory and motor neurones within the CNS
Motor neurones carry impulses from the CNS to effectors
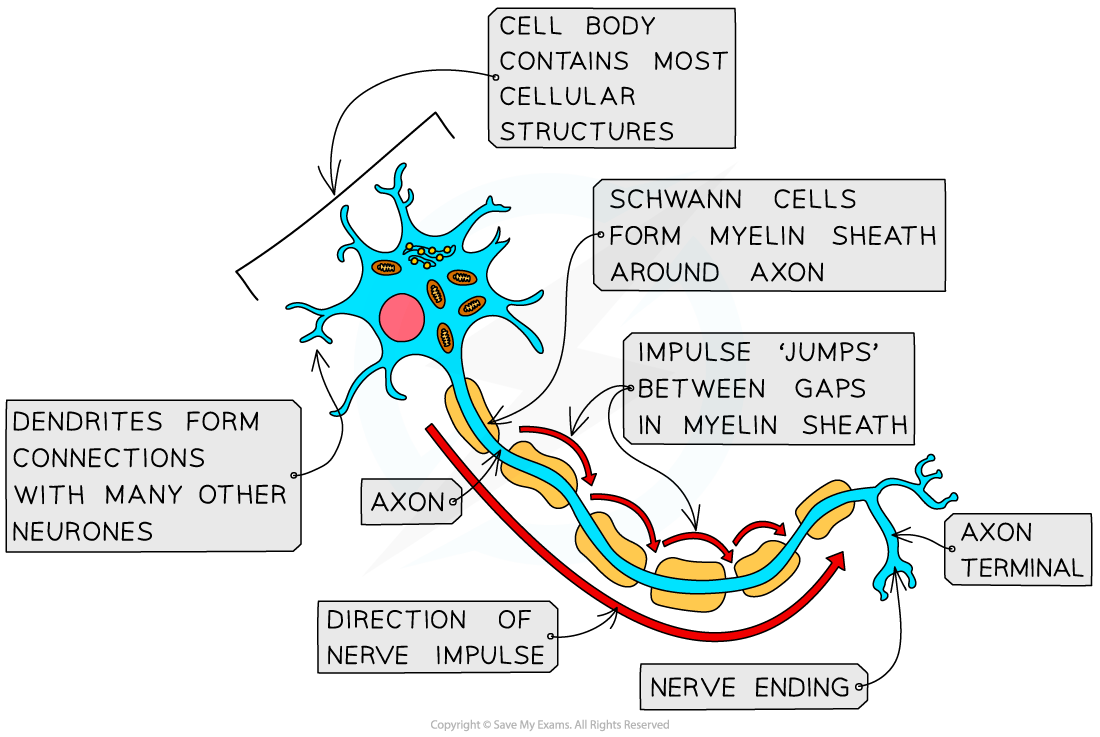
While each type of neurone differs slightly in structure, motor neurones can be identified by the presence of the following features:
a cell body at one end, within the CNS
a long axon
axon terminal endings, located within effectors
Some motor neurones also have a myelin sheath; these cells are said to be myelinated
Myelin is a fatty substance made by Schwann cells which wrap themselves around the axon
The presence of myelin speeds up the conduction of nerve impulses
Examiner Tips and Tricks
It is a good idea to be able to link structure to function when considering any type of specialised cell, e.g. for motor neurones:
the long axon can extend through the body and allow impulses to be transmitted over long distances
dendrites allow motor neurones to form connections with other neurones
The myelin sheath speeds up conduction of nerve impulses

You've read 0 of your 5 free revision notes this week
Unlock more, it's free!
Did this page help you?

