Speed of Impulse Conduction (AQA A Level Biology): Revision Note
Exam code: 7402
Factors that affect speed of impulse conduction
The speed at which nerve impulses are conducted along an axon is determined by multiple factors, including:
the presence or absence of myelin
axon diameter
temperature
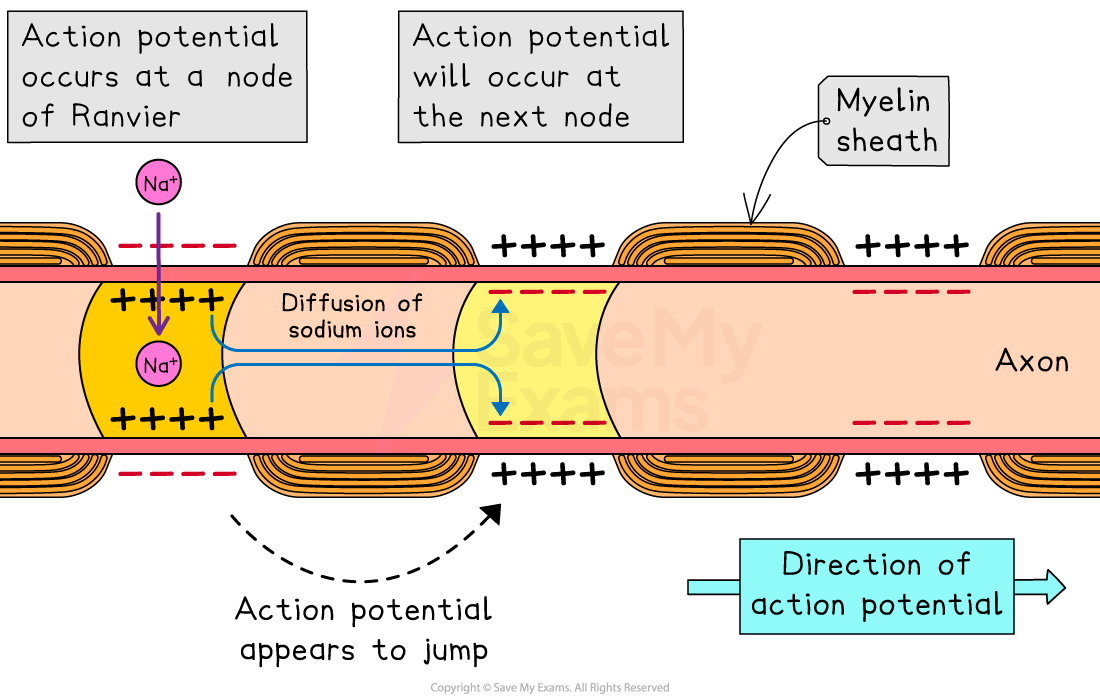
Myelination
Nerve impulses are conducted more quickly in myelinated neurones than in unmyelinated neurones
In unmyelinated neurones:
depolarisation must occur along the whole membrane of the axon; this is relatively slow
In myelinated neurones:
depolarisation only occurs at the nodes of Ranvier, and transmission relies on the diffusion of sodium ions within the axon; this is very fast
action potentials appear to jump from one node to the next; this is saltatory conduction
Axon diameter
Nerve impulses are conducted more quickly in axons with a wider diameter; this is because:
axons with a larger diameter have a higher volume of cytoplasm; this reduces the resistance to the flow of ions
larger axons lose fewer ions at the membrane due to leakage, meaning that membrane potential is maintained more easily

Temperature
Nerve impulses are conducted more quickly at higher temperatures because molecules have more kinetic energy; this means that:
diffusion of ions across membranes and along axons is faster
respiration happens faster, providing more ATP for active transport of ions
At a whole organism level the impact of temperature will depend on whether the organism regulates their body temperature, e.g.:
mammals maintain stable body temperatures, so environmental temperatures have a limited effect on the speed of nerve impulse transmission
the body temperature of reptiles fluctuates with their environment, so nerve impulse transmission will be affected by external temperatures
Examiner Tips and Tricks
You should be prepared to apply your understanding of impulse conduction speed to unfamiliar contexts, e.g. impulse conduction data from different species.

Unlock more, it's free!
Was this revision note helpful?
