Arrays (Cambridge (CIE) O Level Computer Science): Revision Note
Exam code: 2210
1-Dimensional Arrays
What is an array?
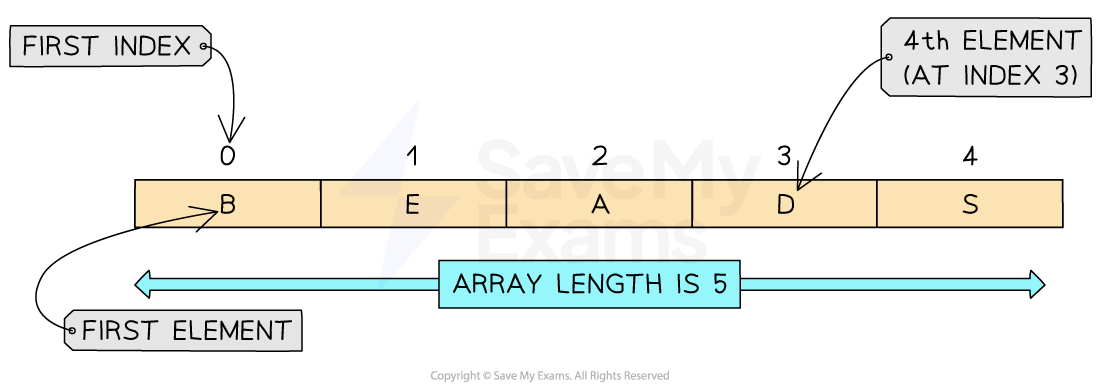
An array is an ordered, static set of elements in a fixed-size memory location
An array can only store 1 data type
A 1D array is a linear array
Indexes start at generally start at 0, known as zero-indexed
Concept | Pseudocode | Python |
|---|---|---|
Create |
|
|
Creates a blank array with 5 elements (0-4) | Creates a blank array | |
|
| |
Creates an array called scores with values assigned | ||
Assignment |
|
|
Assigns the colour "Red" to index 4 (5th element) | ||
Example in Python
Creating a one-dimensional array called ‘array’ which contains 5 integers.
Create the array with the following syntax:
array = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]Access the individual elements of the array by using the following syntax:
array[index]Modify the individual elements by assigning new values to specific indexes using the following syntax:
array[index] = newValueUse the len function to determine the length of the array by using the following syntax:
len(array)In the example the array has been iterated through to output each element within the array. A for loop has been used for this
Python |
|---|
|
2-Dimensional Arrays
What is a 2-dimensional array?
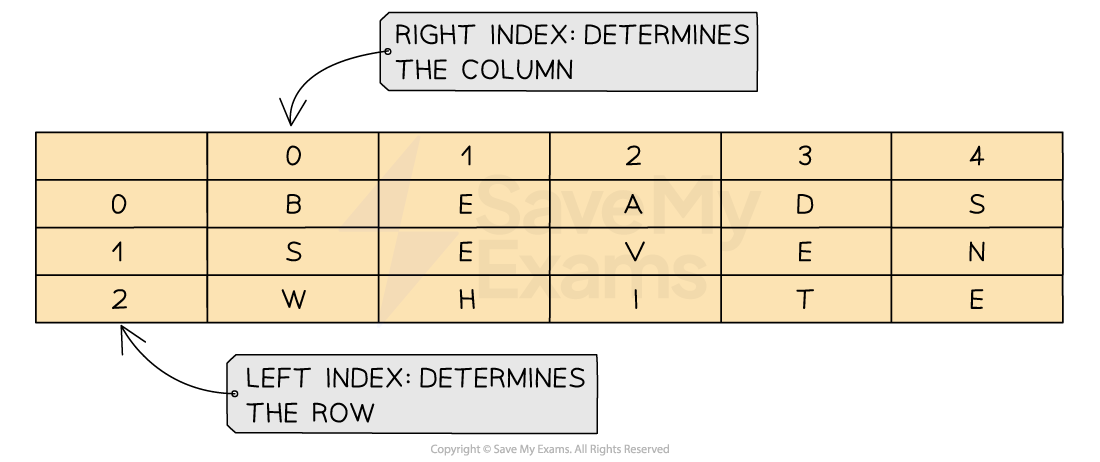
A 2D array extends the concept on a 1D array by adding another dimension
A 2D array can be visualised as a table with rows and columns
When navigating through a 2D array you first have to go down the rows and then across the columns to find a position within the array
Concept | Pseudocode | Python |
|---|---|---|
Create | Declare a 2D array with name and number for 3 people | Creates a 3x2 blank array (3 people, each with name and number) |
|
| |
Declare a 2D array called | ||
|
| |
Assignment | Assigning the name | |
|
| |
Example in Python
Initialising a 2D array with 3 rows and 3 columns, with the specified values |
|---|
|
Iterating through a 2-dimensions array
When iterating through an array, a nested for loop can be used
Nested iteration to access items in the 2D array |
|---|
|
Examiner Tips and Tricks
In the exam, the question will always give an example to demonstrate which order the array is being read from.
Some questions can be X,Y and others can be Y, X. Always refer to the example before giving your answer!
Worked Example
A parent records the length of time being spent watching TV by 4 children
Data for one week (Monday to Friday) is stored in a 2D array with the identifier minsWatched.
The following table shows the array
| Quinn | Lyla | Harry | Elias | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | ||
Monday | 0 | 34 | 67 | 89 | 78 |
Tuesday | 1 | 56 | 43 | 45 | 56 |
Wednesday | 2 | 122 | 23 | 34 | 45 |
Thursday | 3 | 13 | 109 | 23 | 90 |
Friday | 4 | 47 | 100 | 167 | 23 |
Elias watched 78 minutes of TV on Monday:
Identify the row for Monday: Row
0.Identify the column for Elias: Column
3.Find the value at
minsWatched[0][3]: The value is78
Write a line of code to output the number of minutes that Lyla watched TV on Tuesday [1]
Write a line of code to output the number of minutes that Harry watched TV on Friday [1]
Write a line of code to output the number of minutes that Quinn watched TV on Wednesday [1]
Answers
print(minsWatched[1][1]ORprint(minsWatched[1,1]print(minsWatched[4][2]ORprint(minsWatched[4,2]print(minsWatched[2][0]ORprint(minsWatched[2,0]

Unlock more, it's free!
Did this page help you?