Environmental Influences (Cambridge (CIE) A Level Business): Revision Note
Exam code: 9609
Environmental issues and business decisions
Businesses can have a range of negative impacts on the environment
Business impacts on the environment

Pollution is caused by industrial processes that release harmful gases into the air or harmful substances into the ground
Land and buildings may become unusable when businesses process dirty or toxic materials, leading to dereliction
Traffic congestion is caused by vehicles delivering materials to and from businesses, as well as by commuting employees
Visual pollution is caused by unattractive buildings or business works that worsen inhabitants' views of their surroundings
Ways businesses reduce their environmental impact
Method | Example |
|---|---|
Increasing the amount of waste they recycle or reuse |
|
Encouraging employees to use public transport or walk/cycle to work, |
|
Switching to electric vehicles for staff |
|
Becoming carbon-neutral |
|
Improving the appearance of their surroundings |
|
Responding to climate change |
|
Responding to water scarcity |
|
Governments encourage businesses to reduce their environmental impact
Strict regulations dictate the way businesses dispose of waste to avoid pollution
Higher charges for disposal, as well as limits on the volume of permitted waste, increase business costs
Fines for businesses that break environmental regulations and order them to clean up environmental damage
Banning of hazardous materials in manufacturing processes means alternatives must be sourced or developed
Some governments are focused on the switch from fossil fuels to green energy production, such as solar and wind power
In the long term, this should mean that businesses are likely to enjoy lower and more consistent energy costs
Many governments have introduced curbs on business activities that cause environmental damage
E.g. Pollution permits allow businesses to pollute up to a certain limit
Examiner Tips and Tricks
Chains of analysis should link an issue to a business decision, leading to an outcome
For example, 'As water is scarce (issue), the brewery invests in water recycling equipment (decision), cutting both costs and environmental risk (outcome)'
Environmental audits
An environmental audit is a systematic check of how a business affects the environment
Independent reviewers compare what the firm actually does with laws, company policies, and best-practice standards, then report the findings
What an environmental audit includes
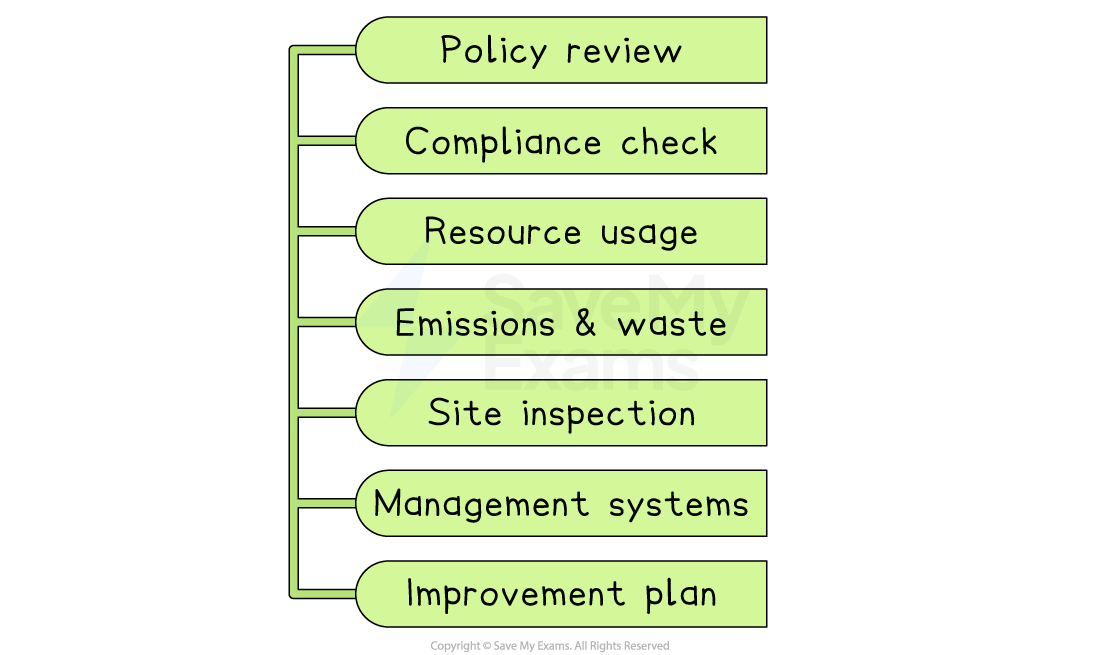
Policy review
Does the firm have clear environmental goals and responsibilities?
Legal compliance check
Is it meeting all relevant regulations on air, water, waste and chemicals?
Resource use assessment
Measurement of energy, water, and raw-material consumption
Emissions and waste analysis
Quantities of greenhouse gases, effluent, waste, and recycling rates
Site inspection
Examination of equipment, storage areas and emergency procedures
Management-system evaluation
How well staff training, record-keeping, and monitoring systems work
Improvement plan
Recommendations, targets, and deadlines for reducing the business’s environmental impact
How businesses and stakeholders use environmental audits
Business use | Stakeholder use |
|---|---|
|
|
|
|
|
|
The importance of sustainability
Sustainability means meeting our current needs without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their own needs
Businesses can contribute to sustainability by changing their operations in a variety of ways
Improving sustainability

Using renewables in production
More than 99% of the wood used in IKEA's furniture products is either sourced from sustainable sources or recycled
Reducing water use in industrial processes
Introduced in 2011, Levi's Water<Less programme reduces the use of water in the manufacture of the company's denim products, so far saving over 4.2 billion litres of water in shortage areas
Using green transportation, such as electric vans
Almost 40% of delivery company Evri’s London vehicles are zero-emission and the company operates e-cargo bikes across four UK cities
Avoiding the use of toxic substances
Home accessories brand Parachute uses organically-grown textiles, with no harmful chemicals used at any stage of production
Using renewable energy, such as solar
Unilever uses 100% renewable electricity across all its factories, offices, R&D facilities, data centres, warehouses and distribution centres. They also generate their own solar power at production facilities in 23 countries.
Implementing recycling
Revive Innovations Ltd recycles compact discs, turning them into beautiful items of furniture and home accessories
Trade-offs between sustainability and profits
Adopting sustainable practices can involve significant upfront costs and operational expenses
Sustainable raw materials and components may be more expensive
Adapting production processes and machinery may require significant capital investment
These additional costs can potentially reduce profitability, at least in the short term
On the other hand, prioritising short-term profits over sustainability can lead to long-term consequences, such as resource depletion and environmental damage
This can create legal issues or cause damage to a business's reputation
These factors undermine a company's long-term viability and profitability

Unlock more, it's free!
Was this revision note helpful?
