International Trade (Cambridge (CIE) A Level Business): Revision Note
Exam code: 9609
An introduction to international influences
International trade is the exchange of goods and services across national borders
Exporting is the selling of goods or services from the home country to a customer in another country
E.g. A UK chocolate manufacturer ships bars to supermarkets in Germany
Importing is buying goods or services from producers in another country for use or resale at home
E.g. A Mexican furniture shop sells flat-pack desks manufactured by a producer in Poland
Exports generate extra sales revenue for businesses selling their goods abroad
Imports result in money leaving the country, which generates extra revenue for foreign businesses
Trends in international trade
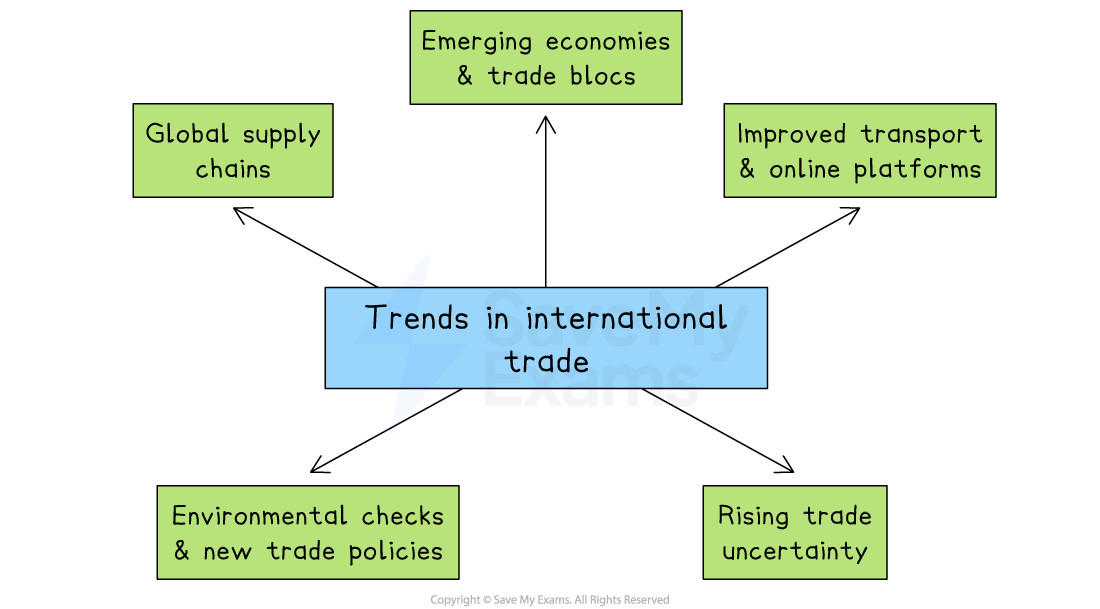
Global supply chains and digital services
Many products are made in several countries before they reach the customer.
E.g. A smartphone can be designed in the United States, use chips from Taiwan, be assembled in Vietnam and sold around the world
Emerging economies and trade blocs
China, India and Mexico now produce much of the world’s manufactured goods
Trade blocs like the EU and USMCA lower tariffs for members, but businesses must follow each bloc’s rules
Improved transport and online platforms
Container ships and air freight make international delivery faster and cheaper
Even small firms can sell online to customers in other countries
Environmental checks and new trade policies
Customers and governments examine carbon footprints, working conditions and data security before buying or approving goods
New trade rules encourage firms to adjust their supply chains to meet these higher standards and reduce risk
Rising trade uncertainty
Exchange rates, tariffs and political tensions change more often, making international trade less predictable
E.g. The USA has recently applied high levels of tariffs to a wide range of consumer goods manufactured in China
This encourages firms to develop more flexible supply chains
Benefits of increased international trade
Benefit | Explanation |
|---|---|
Larger customer base |
|
Economies of scale |
|
Lower input costs |
|
Risk spreading |
|
Access to new ideas and technology |
|
The importance of international trade links
International trade links, such as shared markets, digital agreements and transport routes, lower barriers to trade and reduce risk when trading internationally
They can help managers make decisions, including
Where to source supplies
Where to produce
How to distribute goods or services
International trade links and business decisions
International trade link | How it shapes business decisions |
|---|---|
|
|
|
|
|
|
The impact of trade agreements on business
International trade agreements set the ground rules for buying and selling across borders
By lowering tariffs, standardising product rules or protecting foreign investors, these agreements reduce risk and cost for firms
As a result, managers decide where to locate factories, how to price products and which new markets to enter based on the protection and opportunities each agreement offers
Examples of trade agreements
Trade agreement | Example | How it shapes business decisions |
|---|---|---|
Free Trade Agreements (FTAs) |
|
|
Customs unions and common markets |
|
|
Global trade rules |
|
|
The role of technology in international trade
Technology removes many barriers, such as distance, paperwork and payment difficulties, that once limited international trade
Uses of technology in international trade
Technology | Explanation | How it helps firms trade across borders |
|---|---|---|
Mobile payment systems |
|
|
Digital sales platforms |
|
|
Cloud collaboration & digital freight tools |
|
|
Blockchain for trade finance and traceability |
|
|
Artificial Intelligence (AI) applications |
|
|

Unlock more, it's free!
Was this revision note helpful?
