Protons, Neutrons & Electrons (Edexcel GCSE Combined Science): Revision Note
Exam code: 1SC0
Did this video help you?
Relative Mass & Charge
Properties of Sub-atomic particles
The different particles that make up atoms have different properties
Relative mass is a way of comparing particles. It is measured in atomic mass units (amu)
A relative mass of 1 is equal to mass of 1.67 × 10-27 kg
Charge can be positive or negative
Relative charge is, again, used to compare particles
The fundamental charge is equal to the size of the charge on a proton and an electron, however the electron's charge is negative
The properties of each of the particles are shown in the table below:

Positrons
A positron is the antiparticle of an electron
It has the same mass as an electron, and the same size of charge, however it has a positive charge
Positrons can be produced during nuclear beta-plus decay
a proton spontaneously changes into a neutron and a positron
They only exist in normal conditions for a fraction of a second before they react with electrons and are destroyed
Electrons & Protons
Although atoms contain particles of different charge, the total charge within an atom is zero
This is because the number of electrons is equal to the number of protons
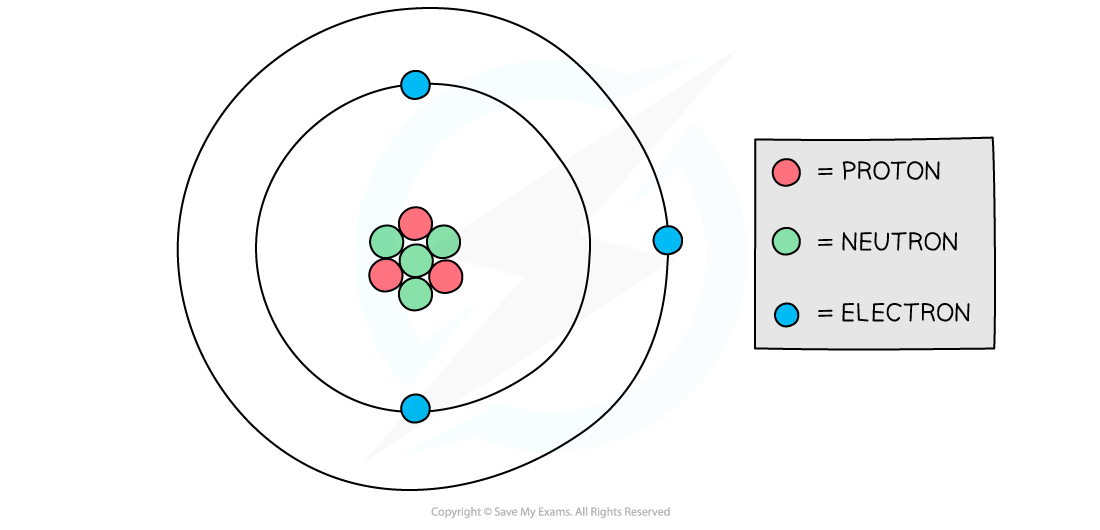
A Lithium atom has three protons, four neutrons and three electrons
The following table sets out the calculation of the total charge in the Lithium atom:
Total Charge Calculation Table

If an atom loses electrons, then it is said to be ionised
Worked Example
A nucleus of carbon-12 is shown below.

How many electrons are there in an atom of carbon-12?
Answer:
Step 1: Count the number of protons in the carbon nucleus
There are 6 protons in the carbon atom
Step 2: Determine the number of electrons
Remember, the number of electrons in an atom is equal to the number of protons
Therefore there must be 6 electrons in the carbon atom

You've read 0 of your 5 free revision notes this week
Unlock more, it's free!
Did this page help you?