Transcription (AQA A Level Biology): Revision Note
Exam code: 7402
Did this video help you?
Transcription
The process of protein synthesis occurs in two stages:
Transcription – DNA is transcribed, and an mRNA molecule (messenger RNA) is produced
Translation – mRNA is translated, and an amino acid sequence is produced
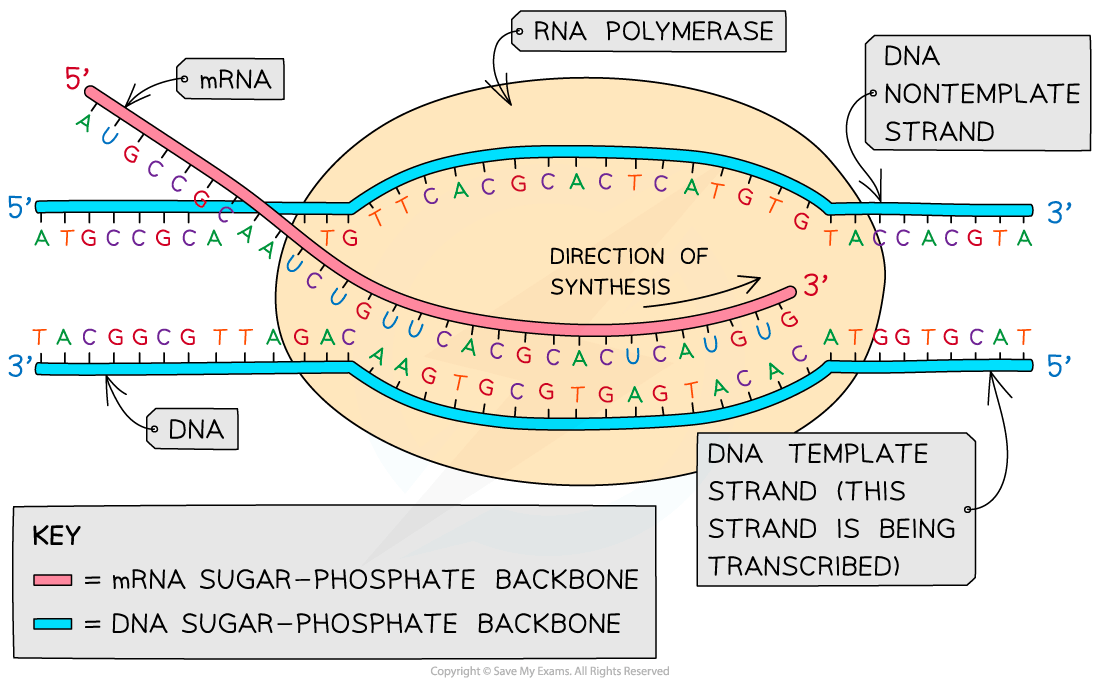
The process of transcription
Transcription occurs in the nucleus of the cell
A section of the DNA molecule unwinds; this section contains the gene from which a particular polypeptide (protein) will be produced
Unwinding occurs due to the breaking of hydrogen bonds between the complementary base pairs; the DNA is said to be 'unzipped'
This reaction is catalysed by the enzyme helicase, as in DNA replication
The gene to be transcribed is now exposed
A complementary copy of the code from the gene is made by creating a molecule of mRNA
Free activated RNA nucleotides pair up (via hydrogen bonds) with their complementary DNA bases on the ‘unzipped’ DNA molecule; this DNA strand is called the template strand
The strand of the DNA molecule that is not transcribed is called the non-template strand or the non-transcribed strand
The base sequence of the non-transcribed strand will be the same as the base sequence of the mRNA transcript, but with uracil replacing thymine
The sugar-phosphate groups of these RNA nucleotides are then bonded together by the enzyme RNA polymerase to form the sugar-phosphate backbone of the mRNA molecule
When the gene has been transcribed, the mRNA molecule is complete, the hydrogen bonds between the mRNA and DNA strands break, and the DNA molecule re-forms into its double helix strcuture
The mRNA molecule then leaves the nucleus via a pore in the nuclear envelope

The role of RNA polymerase
RNA polymerase moves along the template strand in the 3' to 5' direction
This means that the mRNA molecule grows in the 5' to 3' direction
Because the mRNA is formed by complementary pairing with the DNA template strand, the mRNA molecule contains the same sequence of nucleotides as the DNA coding strand (although the mRNA will contain uracil instead of thymine)
Examiner Tips and Tricks
Be careful – DNA polymerase is the enzyme involved in DNA replication; RNA polymerase is the enzyme involved in transcription – don’t get these confused. The mRNA codons have the same base sequence as the non-transcribed strand, and the tRNA anticodons have the same base sequence as the transcribed strand, except RNA, which has the base Uracil, replacing Thymine.
You do not need to know specifically about the directions that the DNA strands are read (e.g. 5' to 3'), but understanding these helps explain how DNA and RNA strands grow and are built.

Unlock more, it's free!
Was this revision note helpful?
