Glucose Concentration & Insulin (AQA A Level Biology): Revision Note
Exam code: 7402
Factors affecting blood glucose concentration
Blood glucose concentration varies due to factors such as:
consumption of foods containing carbohydrates
exercise
secretion of hormones that affect blood glucose
Hormones that affect blood glucose levels include:
insulin: reduces blood glucose
glucagon: increases blood glucose
adrenaline: increases blood glucose
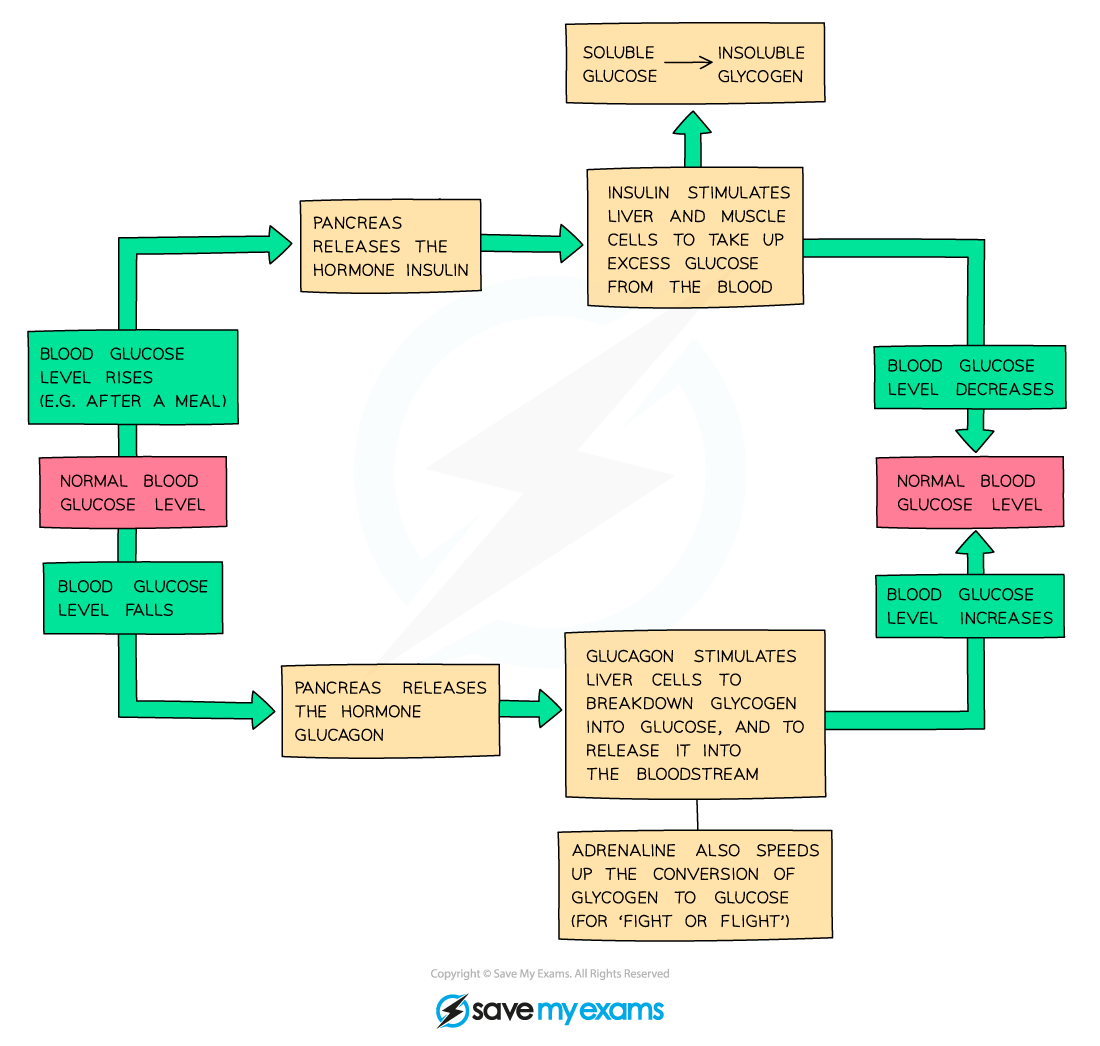
These hormones form part of a negative feedback loop that maintains blood glucose levels within narrow limits
Examiner Tips and Tricks
Be careful not to confuse the effects of insulin and glucagon on blood glucose.
The action of insulin
An increase in blood glucose concentration to a level that is above the normal range is detected by cells in the pancreas
In response to this stimulus, β cells in the pancreas secrete the hormone insulin
Insulin causes a reduction in blood glucose as follows:
Insulin binds to specific receptors on the membranes of target cells, e.g.:
liver cells
muscle cells
More glucose transporter proteins are added to the cell surface membranes of target cells, increasing their permeability to glucose
This is achieved when vesicles containing glucose transporters fuse with the cell surface membrane
Glucose moves into target cells by facilitated diffusion
Enzymes are activated that convert glucose into glycogen
This is glycogenesis

Examiner Tips and Tricks
When describing the action of insulin, you should be sure to include all of the important steps; don't miss out important ideas, such as:
the binding of insulin to receptors
the increase in glucose transporter proteins
the activation of enzymes

Unlock more, it's free!
Did this page help you?