Rates - Activation Energy (OCR A Level Chemistry A): Revision Note
Exam code: H432
PAG 10.3: Rates – Activation energy
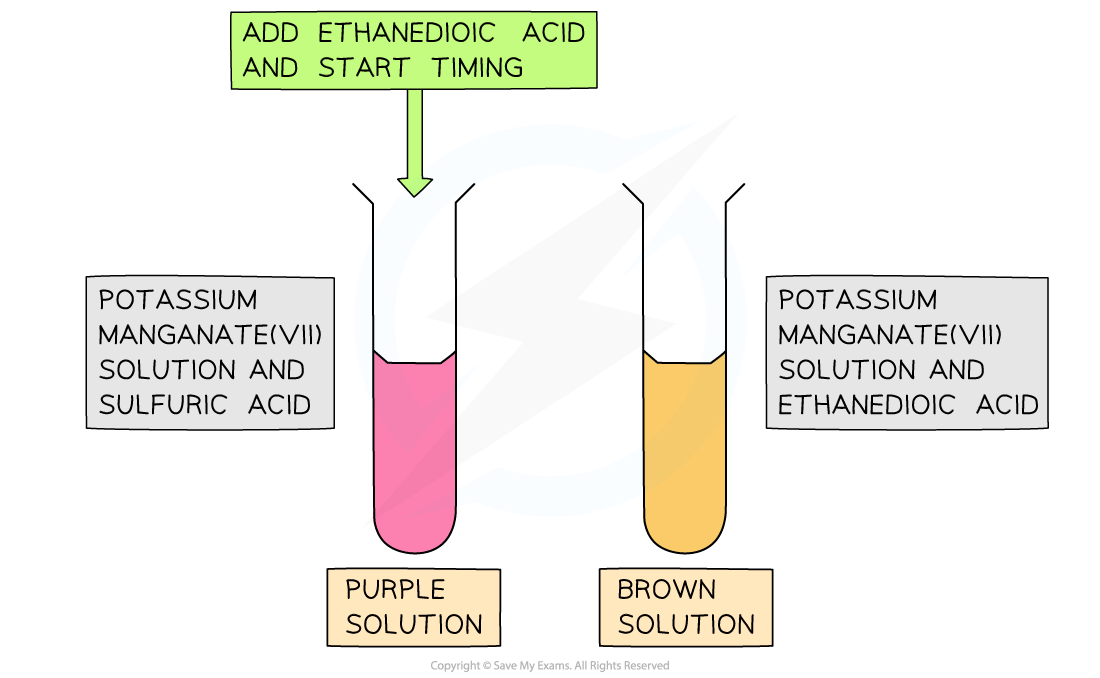
Ethanedioic acid and potassium manganate(VII)
This experiment investigates the effect of temperature on rate using potassium manganate(VII) and ethanedioic acid in acidic solution:
2MnO4– (aq) + 5H2C2O4 (aq) + 6H+ (aq) → 2Mn2+ (aq) + 8H2O (l) + 10CO2 (g)
The key observable change is a colour change from purple to pale brown as Mn7+ is reduced to Mn2+
Method
Using a different / clean measuring cylinder for each chemical, transfer 10.0 cm3 of each of the following into a separate boiling tube
0.1 mol dm-3 potassium manganate(VII) solution, KMnO4 (aq)
2.0 mol dm-3 sulfuric acid, H2SO4 (aq)
0.25 mol dm-3 ethanedioic acid, H2C2O4 (aq)
Warm all three boiling tubes in a water bath to the same temperature
Record the temperature of each solution
Into a clean test tube, add in order:
0.5 cm3 potassium manganate(VII) solution
0.5 cm3sulfuric acid
1.0 cm3 ethanedioic acid
Immediately start the stopwatch and swirl the mixture
Stop the stopwatch when the purple colour changes to pale brown
Record the time
Repeat the experiment at least four more times at different temperatures
Specimen results
Temperature, T (K) | 1 / T | Time, t (s) | 1 / t | ln (1 / t) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
297.0 | 0.003367 | 63 | 0.015873 | -4.1431 |
310.3 | 0.003223 | 34 | 0.029412 | -3.5264 |
316.9 | 0.003156 | 26 | 0.038462 | -3.2581 |
323.6 | 0.003090 | 22 | 0.045455 | -3.0910 |
335.3 | 0.002982 | 16 | 0.062500 | -2.7726 |
The temperature of the reaction is converted to 1 / T by calculating the reciprocal value
The rate is found by calculating the reciprocal of time, t
This is then converted into the natural logarithm function to give ln(1 / t) or ln(rate)
A graph of ln(rate) versus 1 / T is then plotted:
Analysis
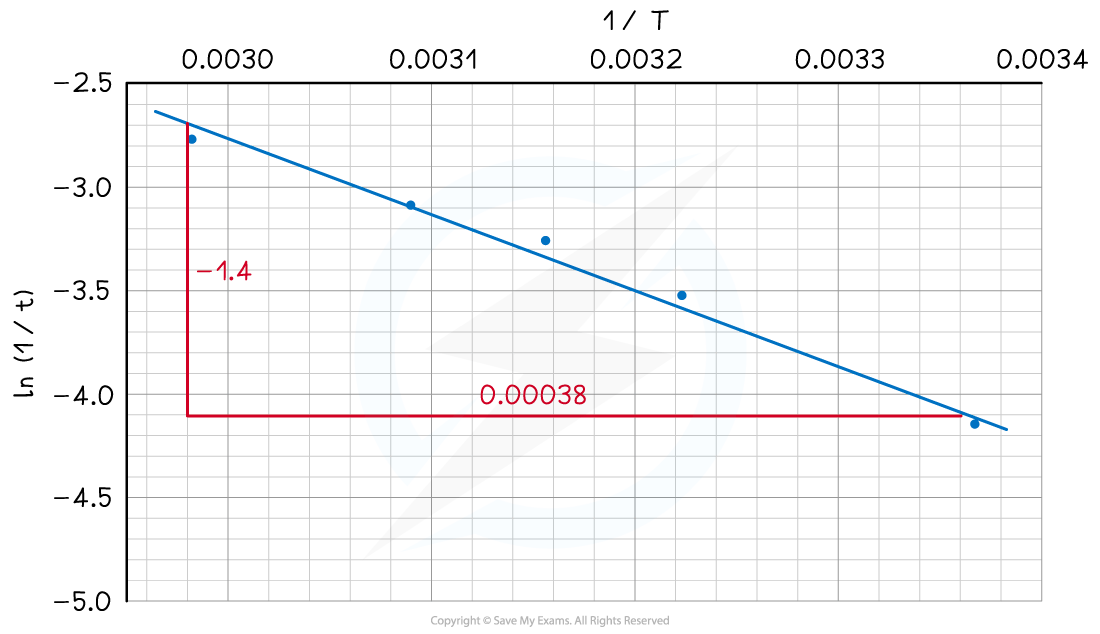
From this graph, we can see that the line of best fit is a straight line
The equation for a straight line is y = mx + c
The Arrhenius equation can be rearranged to ln k = ln A - Ea/RT
Therefore, the gradient of the line is -Ea / R
This means that we can use the gradient from the graph to calculate the activation energy for this reaction:
Gradient = can be rearranged to Ea = –gradient x R
Ea = –x 8.31 = 30616 J mol-1
Ea = = 30.616 kJ mol-1
Practical skills reminder
This practical develops key skills in monitoring reaction rate through visible colour change and temperature control.
It also supports:
Accurately measuring volumes and timing using simple lab apparatus
Controlling temperature using a water bath
Plotting ln(rate) against 1/T to determine activation energy from the gradient of a straight line

You've read 0 of your 5 free revision notes this week
Unlock more, it's free!
Did this page help you?