Environmental Impacts of Agricultural Practices (College Board AP® Environmental Science): Study Guide
Environmental damage caused by agricultural practices
Agricultural activities provide food and raw materials but often have negative environmental consequences
Key farming techniques such as tilling, slash-and-burn farming, and fertilizer use contribute to soil degradation, pollution, and biodiversity loss
Tilling
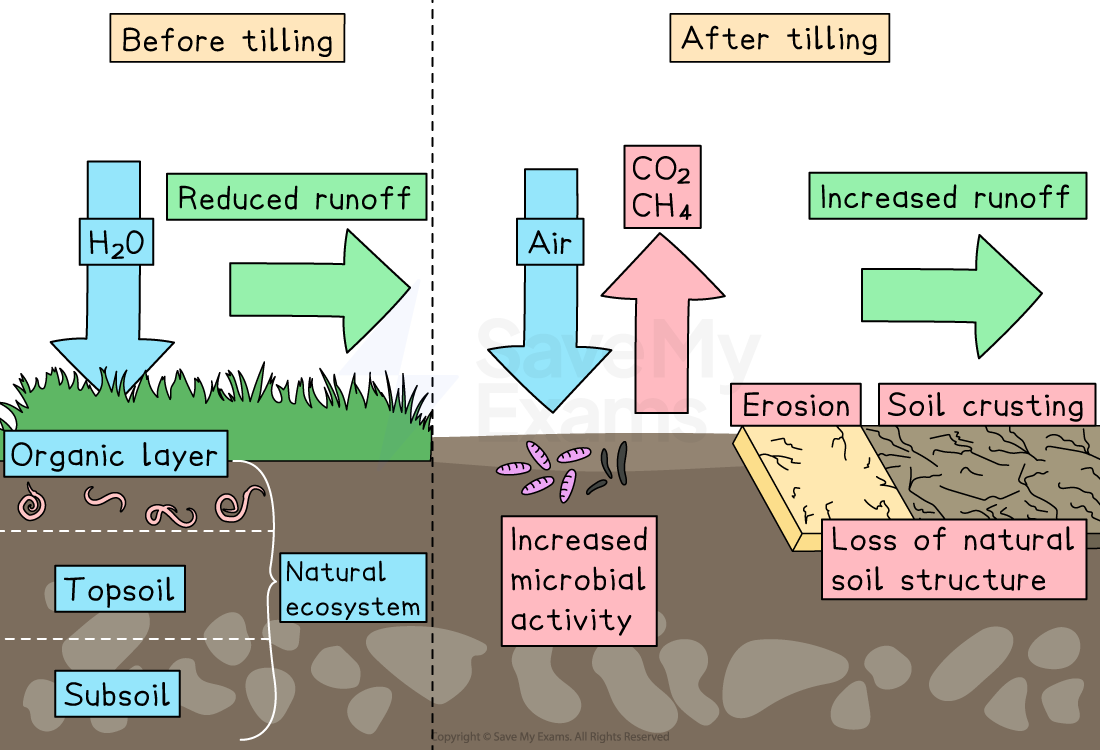
Tilling is the practice of mechanically turning over soil to prepare for planting
Environmental impacts:
Soil erosion: Loosens soil, making it more prone to being washed away by rain or blown away by wind
Loss of soil fertility: Disrupts soil structure and depletes nutrients
Carbon release: Disturbs stored carbon in soil, contributing to greenhouse gas emissions
When soil is tilled, carbon stored in organic matter is exposed to oxygen
This accelerates microbial decomposition and releases carbon dioxide (CO₂) into the atmosphere
Healthy, undisturbed soil acts as a carbon sink, storing carbon for long periods—frequent tilling reduces this capacity, increasing net carbon emissions
In some cases, tilling can disturb anaerobic (oxygen-lacking) environments, leading to the release of methane (CH₄), a potent greenhouse gas
Example: Intensive tilling in the U.S. Midwest has led to widespread topsoil erosion and declining soil fertility
Slash-and-burn farming
Slash-and-burn is a method where forests or grasslands are cleared by cutting and burning the vegetation to prepare land for agriculture
Environmental impacts:
Deforestation: Large areas of forests are lost, reducing carbon storage
Air pollution: Burning releases CO₂ and other pollutants into the atmosphere
Soil degradation: Burning depletes nutrients, making land less productive over time
Example: Slash-and-burn practices in the Amazon Rainforest contribute to deforestation and biodiversity loss
Fertilizer use
Chemical fertilizers provide essential nutrients to crops but can harm the environment when overused
Environmental impacts:
Water pollution: Excess nutrients run off into rivers and lakes, causing eutrophication and harmful algal blooms
Soil acidification: Continuous use of fertilizers can alter soil pH, reducing its productivity
Greenhouse gas emissions: Fertilizers release nitrous oxide (N₂O), a potent greenhouse gas
Example: Excess fertilizer runoff from farms in the Mississippi River Basin contributes to the Gulf of Mexico dead zone, where low oxygen levels kill marine life


Unlock more, it's free!
Was this revision note helpful?
