Choosing the Right Business Ownership (Cambridge (CIE) A Level Business): Revision Note
Exam code: 9609
The appropriateness of different types of business ownership
When starting or growing a business, it is important to choose the right type of ownership
Businesses consider several factors when deciding which ownership structure is best suited to their needs and goals
Factors affecting the choice of ownership type
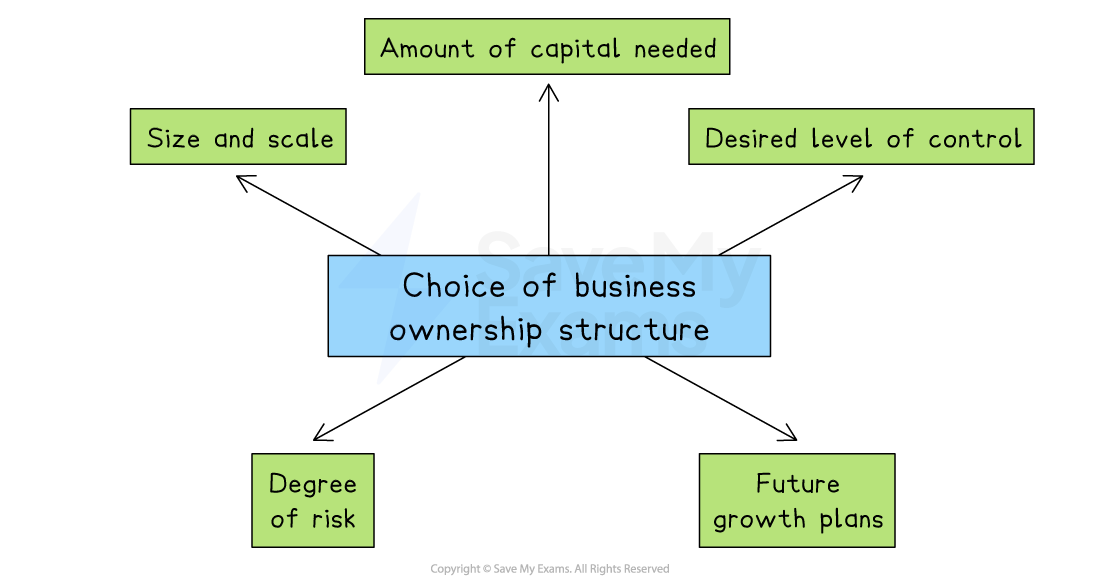
1. Size and scale of business
The size of the business (small, medium, or large) helps determine the most suitable ownership type
Smaller businesses often choose simpler structures, while larger firms may require more complex forms like public limited companies
E.g., A small local café would likely operate as a sole trader, whereas a multinational company like Samsung operates as a public limited company (Plc)
2. Amount of capital needed
Different ownership types allow businesses to raise different amounts of money
Businesses needing large amounts of capital typically choose structures that allow share sales
E.g., Public limited companies raise large amounts of capital by selling shares publicly, whereas a local hair salon (sole trader) usually needs only a small initial investment
3. Desired level of control
Business owners must consider how much control they wish to maintain
Some structures offer complete control, while others involve sharing decision-making responsibilities
E.g., A sole trader has full control over all business decisions, while a franchise owner must follow strict rules set by the franchisor
4. Degree of risk (liability)
The choice of ownership determines the level of personal financial risk
Limited liability protects owners’ personal assets, whereas unlimited liability could mean personal assets are at risk
E.g., Owners of private limited companies (Ltd) have limited liability, protecting personal possessions. In contrast, sole traders face unlimited liability, risking personal property if the business fails
5. Future growth plans
Businesses planning rapid growth or international expansion must choose a structure that supports raising funds and managing growth effectively
E.g., A fast-growing technology startup might choose a private limited company to attract investors easily, while businesses intending to stay small, like family-run restaurants, might remain as partnerships or sole traders
The appropriateness of different ownership types
Type | Appropriate for |
|---|---|
Sole Trader |
|
Partnership |
|
Private Limited Company (Ltd) |
|
Public Limited Company (Plc) |
|
Franchise |
|
Joint Venture |
|
Cooperative |
|
Social Enterprise |
|
The concepts of unlimited liability and limited liability
When an entrepreneur starts a business, they need to consider what kind of legal structure they want for their business
Sole traders and partnerships offer no legal protection to the owners in that the business assets and the owner's personal assets are viewed as being the same (unlimited liability)
The other forms of business ownership offer limited liability in which the assets of the owners are considered to be separate from those of the business
Comparing unlimited and limited liability
Liability | Description | Implications |
|---|---|---|
Unlimited liability |
|
|
Limited liability |
|
|
The advantages and disadvantages of changing the type of business ownership
Businesses sometimes change their type of ownership as they grow or when they seek new opportunities
Changing from sole trader or partnership to private limited company
As a business grows, the owner may need more capital to expand or want to reduce their personal financial risk
Switching to a private limited company offers limited liability and allows the business to raise money through selling shares privately
E.g. A local bakery that started as a sole trader may become a private limited company to open more branches and attract investors to help fund expansion
Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Buying a franchise
Entrepreneurs who want to expand a business with less risk may choose to buy a franchise
It allows them to run a business with an existing brand, support and customer base rather than growing a less well-known brand
E.g., A fast food entrepreneur may choose to buy a Subway franchise because the brand is well known and the franchisor provides training and equipment
Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Changing from private limited company to public limited company
A successful private limited company may want to raise large amounts of money quickly for major expansion
Becoming a public limited company allows it to sell shares to the public on the stock exchange
E.g. Facebook began as a private limited company and later became Meta Plc to raise billions of dollars for global growth and development
Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Forming a joint venture
Sometimes two or more businesses want to work together on a project, especially if it involves entering a new market or sharing expertise
A joint venture lets them share the risks, costs, and skills
E.g. Sony and Ericsson formed a joint venture to combine their strengths in electronics and mobile phone technology and create competitive mobile phones for the global market
Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
|
|
|
|
|
|

Unlock more, it's free!
Was this revision note helpful?
