Geostationary Orbits (Cambridge (CIE) A Level Physics): Revision Note
Exam code: 9702
Geostationary orbits
Many communication satellites around Earth follow a geostationary orbit
This is a specific type of orbit in which the satellite:
Remains directly above the equator, therefore, it always orbits at the same point above the Earth’s surface
Moves from west to east (same direction as the Earth spins)
Has an orbital time period equal to Earth’s rotational period of 24 hours
Geostationary satellites are used for telecommunication transmissions (e.g. radio) and television broadcast
A base station on Earth sends the TV signal up to the satellite where it is amplified and broadcast back to the ground to the desired locations
The satellite receiver dishes on the Earth's surface must point towards the same point in the sky
Since the geostationary orbits of the satellites are fixed, the receiver dishes can be fixed too
Geostationary satellite in orbit
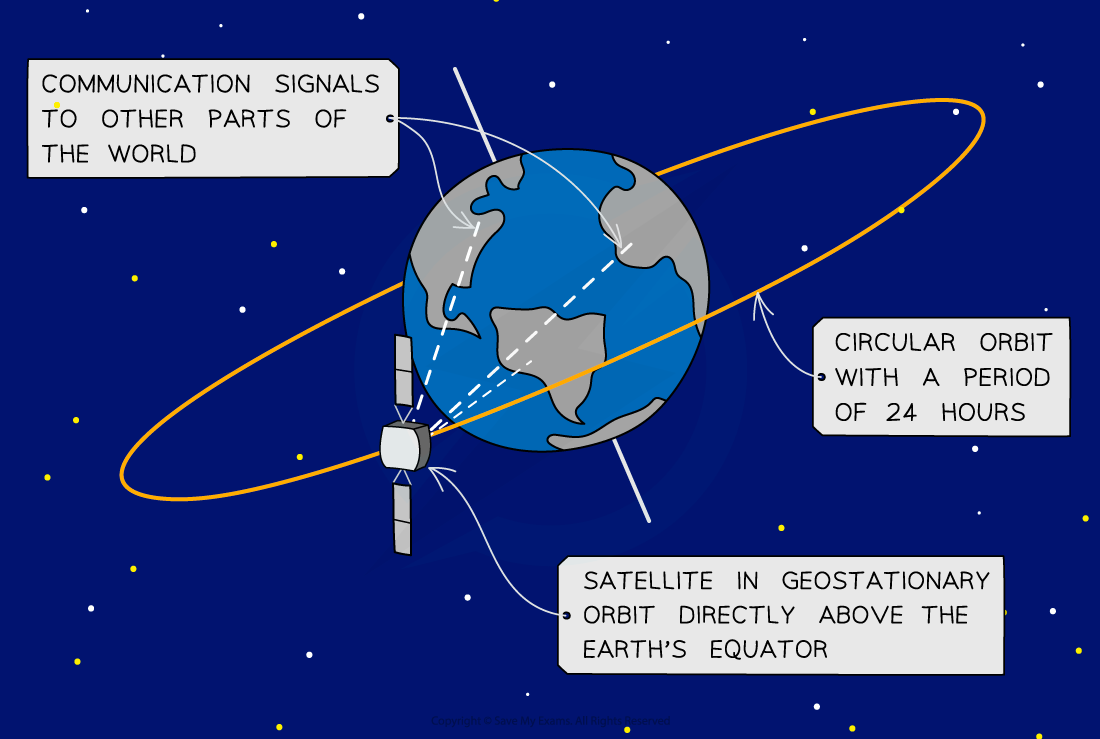
Satellite in geostationary orbit remain directly above the equator, and a circular orbit equal to that of the Earth
Ready to test your students on this topic?
- Create exam-aligned tests in minutes
- Differentiate easily with tiered difficulty
- Trusted for all assessment types

Did this page help you?