File Management (Edexcel IGCSE ICT): Revision Note
Exam code: 4IT1
File formats
What is a file format?
A file format is a way of saving data created in an application so that it can be opened again later in the same application
Different applications use different file formats, so it is good practice to save work using a compatible file format
There are occasions when you may wish to change to a different file format, for example you may have to save work in an older format for older software versions to be able to open it
Software is often backward compatible, which means newer versions will open older file formats
Older software cannot open newer file formats
After editing your work in one application you may want to export in to a different format, for example:
Creating a poster in a desktop publishing application and then once complete, exporting as a generic file format such as PDF
PDFs can be opened on most devices, even without the application it was created in
Example application file formats
Application type | Application | File format |
|---|---|---|
Word processor | Microsoft Word | .docx |
Spreadsheet | Microsoft Excel | .xlsx |
Database | Microsoft Access | .accdb |
Presentation | Microsoft PowerPoint | .pptx |
Image editing | GIMP | .xcf |
Web authoring | Serif WebPlus | .wpp |
File & folder structures
What is a file & folder structure?
A file & folder structure is a way of organising digital information on a computer
Files are individual documents, images, video, or other data that is stored on a computer
Folders are digital containers for files
Folders can be nested inside other folders to create a hierarchical structure
The purpose of a file & folder structure is find information quickly
Saving work
It is important to save work regularly, in case of a loss of power or the application crashes
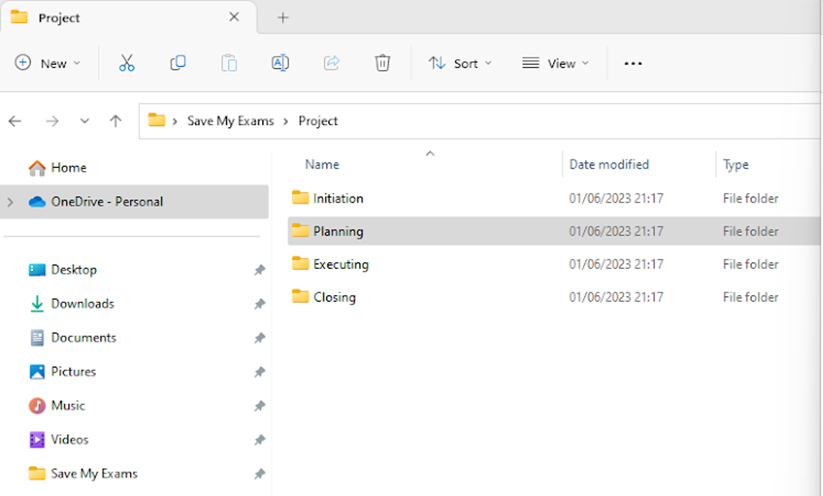
The below screenshot shows a project structure broken into 4 different sections, Initiation, Planning, Executing and Closing
Within each folder, files are saved according to the which part of the project they are relevant to
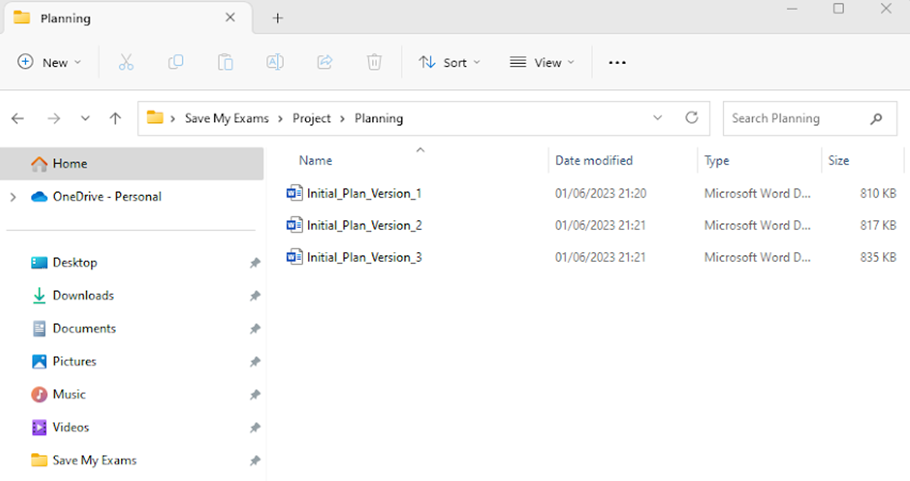
Files are saved inside folders with version numbers allowing the user to go back and review previous versions
This is known as version control
Naming files
Meaningful file names should give a clue as to what the document contains

'Doc1’ does not give any idea about the contents of the file and is not a meaningful file name
‘Plan’ is a partially meaningful name but could be any plan or any version of the plan
‘Initial_Plan_Version_1' is a meaningful name as it determines that it is an initial plan and is the first version
Locating stored files
Secondary storage contains files and folders
Within a folder, there may be files or other folders which are known as subfolders
There are multiple ways to locate files
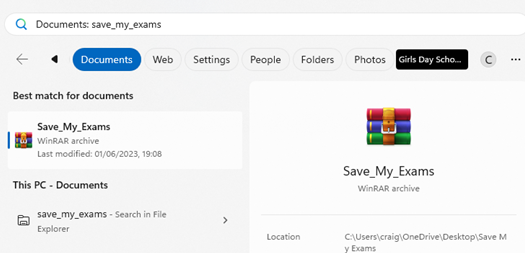
Using Windows search
Click on the Windows Icon at the bottom of the screen and type the file that is required and click on the ‘documents’ button

You've read 0 of your 5 free revision notes this week
Unlock more, it's free!
Did this page help you?