Inverse Functions (Cambridge (CIE) IGCSE Additional Maths): Revision Note
Exam code: 606
Inverse functions
What is an inverse function?
An inverse function does the exact opposite of the function it came from
For example, if the function “doubles the number and adds 1” then its inverse is
“subtract 1 and halve the result”
It is the inverse operations in the reverse order
How do I write inverse functions?
An inverse function f-1 can be written as
or
For example, if
its inverse can be written as
or
How do I find an inverse function?
The easiest way to find an inverse function is to 'cheat' and swap the
and
variables
Note that this is a useful method but you MUST remember not to do this in any other circumstances in maths
STEP 1 Write the function in the form
e.g.
STEP 2 Swap the
's and
's to get
e.g.
STEP 3 Rearrange the expression to make
the subject again
STEP 4 Rewrite using the correct notation for an inverse function
either as f-1(x) = … or f-1 : x ↦ …
should not exist in the final answer
e.g.
How does a function relate to its inverse?
If
then the input of 3 gives an output of 10
The inverse function undoes f(x)
An input of 10 into the inverse function gives an output of 3
If
then
If you apply a function to x, then immediately apply its inverse function, you get x
Whatever happened to x gets undone
f and f-1 cancel each other out when applied together
If
and you want to solve
Finding the inverse function
in this case is tricky (impossible if you haven't studied logarithms)
instead, take f of both sides and use that
cancel each other out:
What condition is needed for an inverse function to exist?
For the inverse function to exist,
, the original function
must be one-to-one
Substituting 1 input into
must give 1 output only
Substituting this 1 output into
must give back the original input only
At no point are more values allowed to be created!
Worked Example
Find the inverse of the function .
Write the function in the form and then swap the
and
Rearrange the expression to make the subject again.
Rewrite using the correct notation for an inverse function.
Domain & range of inverse functions
How do I find the domain and range of inverse functions?
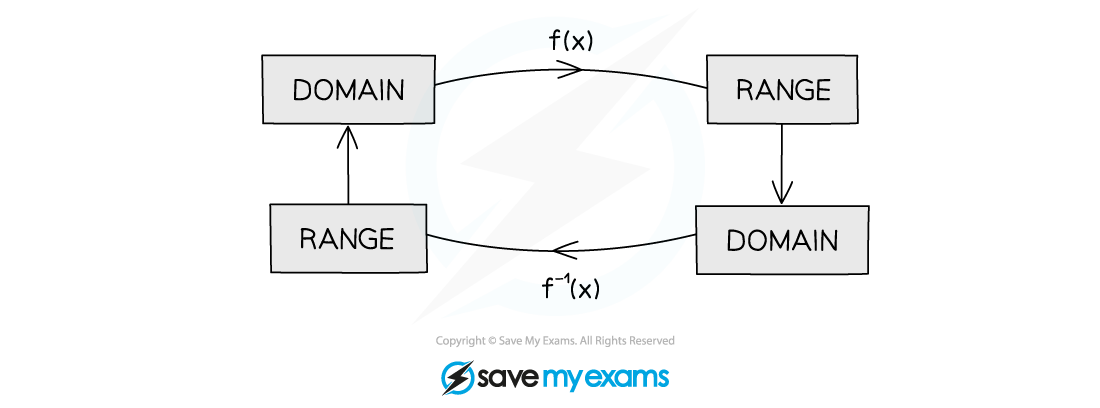
The range of a function will be the domain of its inverse function
The domain of a function will be the range of its inverse function
Worked Example
A function is defined as .
Write down the domain and range of .
The domain of an inverse function is the range of the function.
The range of is
The domain of
is
The range of an inverse function is the domain of the function.
The range of
is
Graphs of inverse functions
How are the graphs of a function and its inverse related?
The graph of an inverse function,
, is a reflection of the graph of the function,
, in the line
Key features of the graph of
will be reflected, such as
and
axes intercepts
turning points
asymptotes
How do I sketch the graph of an inverse function?
STEP 1
Sketch the line
, and if need be, the graph of
STEP 2
Reflect the graph of
in the line
Remember it is a sketch, but the graphs together should look like reflections
Consider points where the reflected graph will intersect the
and
axes
e.g. The point
will be reflected to the point
Consider any asymptotes on the graph of
- these will also be need reflecting
e.g. The asymptote (line)
will be reflected to the line
Consider any restrictions on the domain and range of
e.g. If the domain is
only sketch the graph for positive values of
STEP 3
Label key points on the sketch of
and state the equations of any asymptotes
This process works the other way round - the graph of
can be sketched from the graph of
Examiner Tips and Tricks
If not given, sketch the graphs of
and
to help sketch the graph of the inverse,
If the graph of
is given you do not need to know the expression for
to sketch
Just reflect whatever is given in the line
Worked Example
The diagram below shows the graph of , where
.
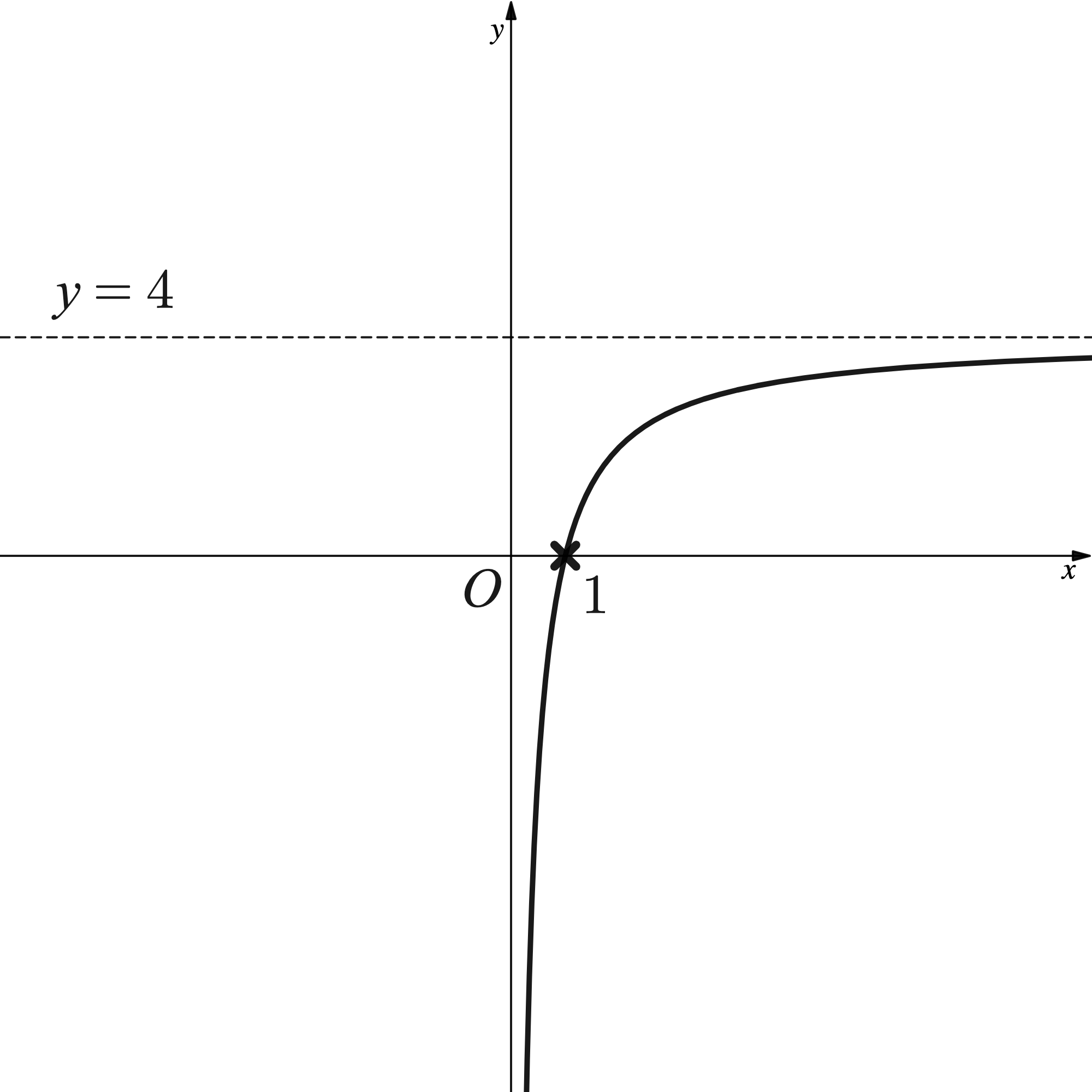
a)On a copy of the diagram, sketch the graph of . Label the point where the graph crosses the
-axis and write down the equation of the asymptote.
The graph of an inverse function is the reflection of the graph of that function in the line .
Draw the line to help sketch the inverse function.
The -axis intercept
becomes the
-axis intercept,
.
The (horizontal) asymptote will. become the (vertical) asymptote
.
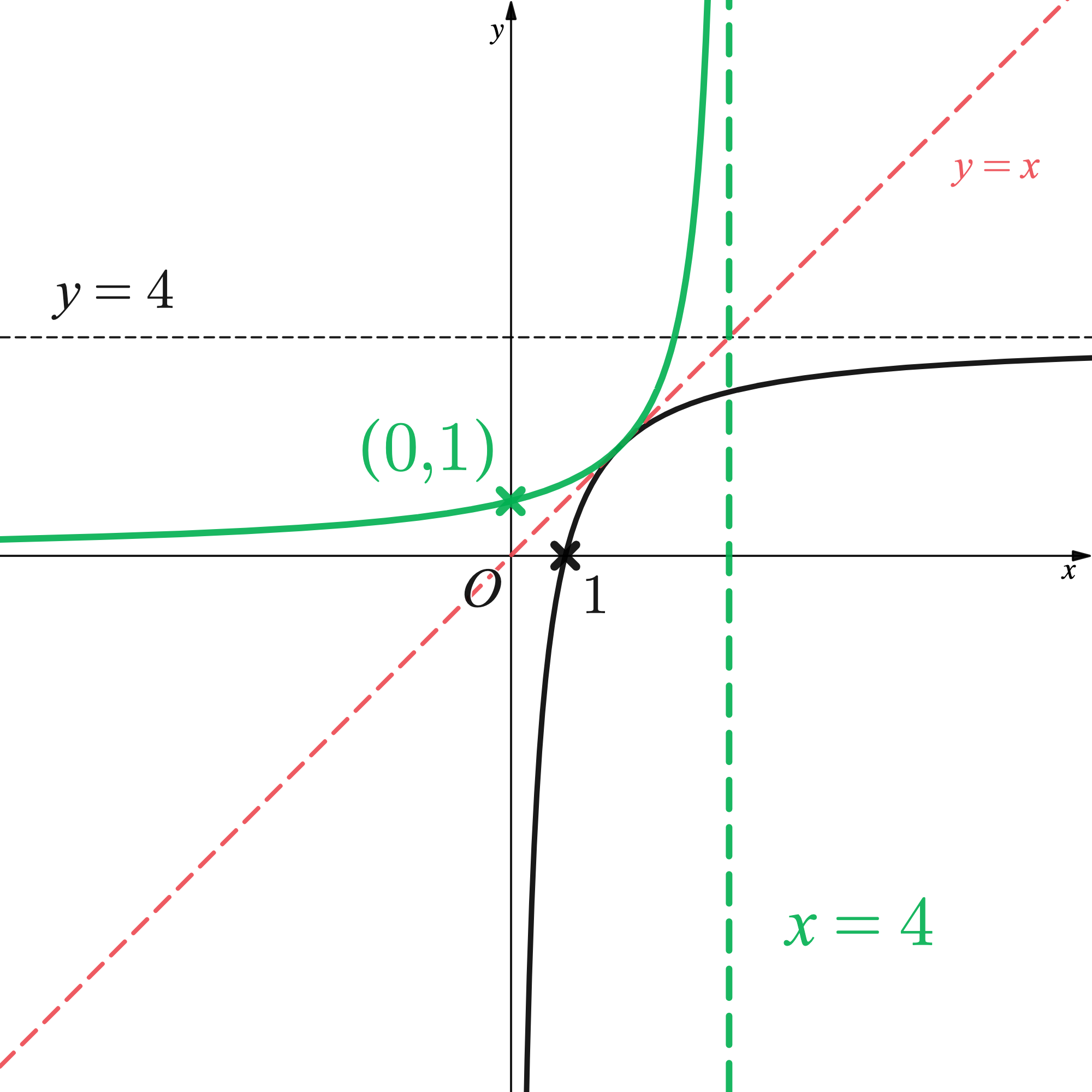
b) Use your sketch, or otherwise, to write down the value of such that
.
This will be the point at which the two graphs meet.
The point will be on the line so there is no need to work out
.
By sketching the graph in part (a) this point (with coordinates ) should have already been considered. Only the
value is required.
The value could also be found by solving
.

Unlock more, it's free!
Was this revision note helpful?
