Reflection (Oxford AQA IGCSE Combined Science Double Award): Revision Note
Exam code: 9204
Law of Reflection
All waves, whether transverse or longitudinal, can be reflected
Reflection occurs when:
A wave hits a boundary between two media and does not pass through, but instead stays in the original medium
Angles are measured between the wave direction (ray) and the normal
The normal is a construction line perpendicular to the surface of the boundaries and is usually represented by a straight dotted line
The angle of the wave approaching the boundary is called the angle of incidence (i)
The angle of the wave leaving the boundary is called the angle of reflection (r)
The angles are the same, so the law of reflection can be written:
Angle of incidence (i) = Angle of reflection (r)
Light reflects from a surface

Examiner Tips and Tricks
When drawing ray diagrams for reflection take care to draw the angle correctly. If it is slightly out it won’t be a problem, but if there is an obvious difference between the angle of incidence and the angle of reflection you will probably lose a mark.
Reflection in a Plane Mirror
When an object is placed in front of a plane mirror, an image of that object can be seen in the mirror
The image will be:
the same size as the object
the same distance behind the mirror as the object is in front of it
virtual
upright
laterally inverted
The formation of this image can be understood by drawing a ray diagram
Ray diagram of an object reflected in a plane mirror
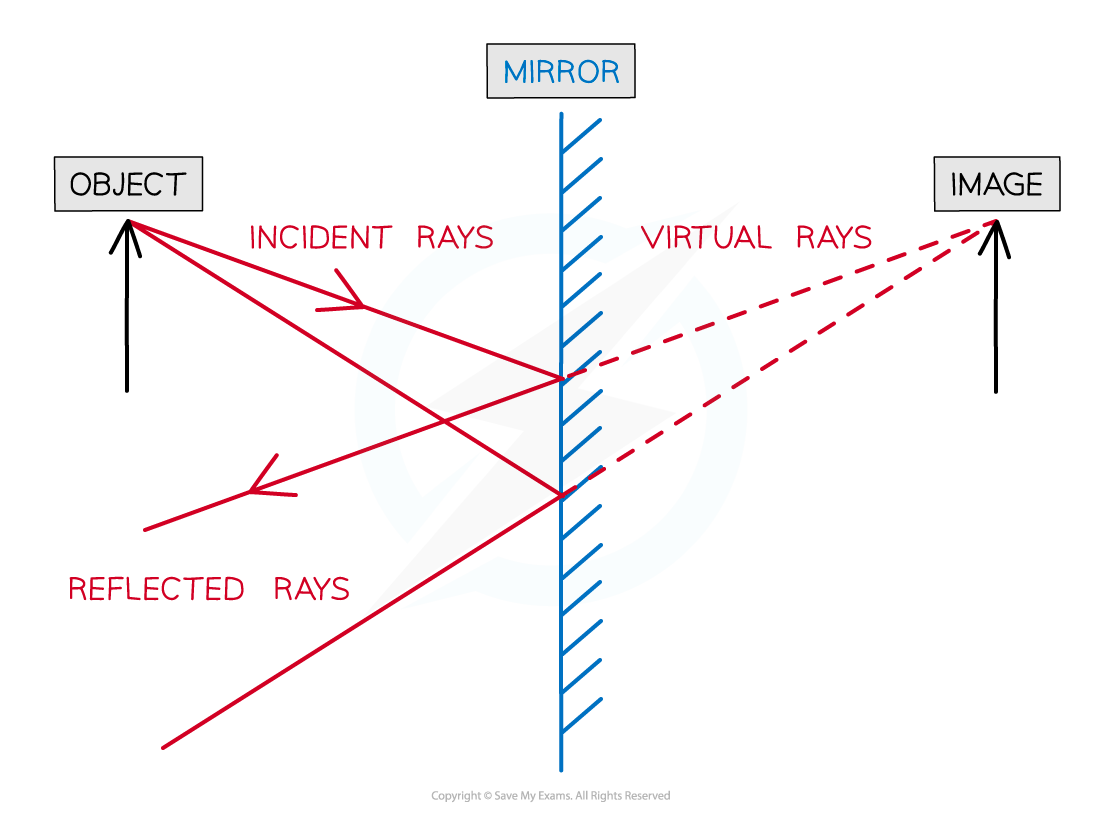
Light from the object hits the mirror and is reflected according to the law of reflection
angle of incidence = angle of reflection
The reflected ray can be traced back forming a virtual ray
This can be repeated for another ray travelling in a slightly different direction
An image of the object will appear where these two virtual rays cross
The type of image formed in the mirror is called a virtual image
Examiner Tips and Tricks
You will be expected to be able to construct ray diagrams to represent reflected rays and the virtual image produced in the mirror.

You've read 0 of your 5 free revision notes this week
Unlock more, it's free!
Did this page help you?