Solving Cubic Equations (Cambridge (CIE) IGCSE Additional Maths): Revision Note
Exam code: 606
Did this video help you?
Solving cubic equations
What is a cubic equation?
A cubic function is an polynomial of degree 3
i.e. the highest power of
is 3
A cubic equation can be written in the form
Solving a cubic equation involves factorising the cubic function first.
How do I factorise a cubic function?
Factorising a cubic (function) combines the factor theorem with the method of polynomial division
The example below shows the steps for factorising a cubic
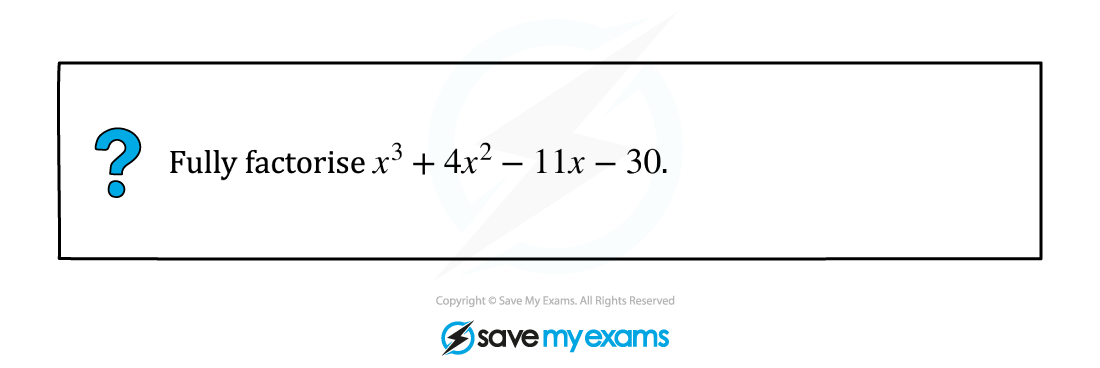
STEP 1
Use factor theorem.
Find a value such that
.
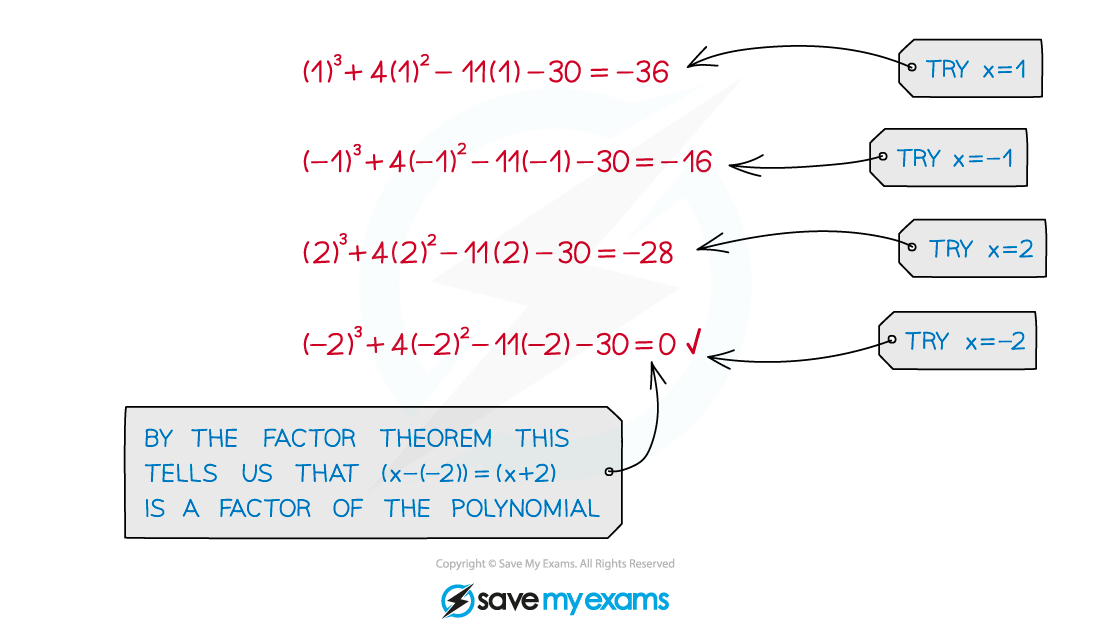
STEP 2
Use polynomial division.
Divide by
.
(It is possible to do this step 'by inspection', see the worked example below)
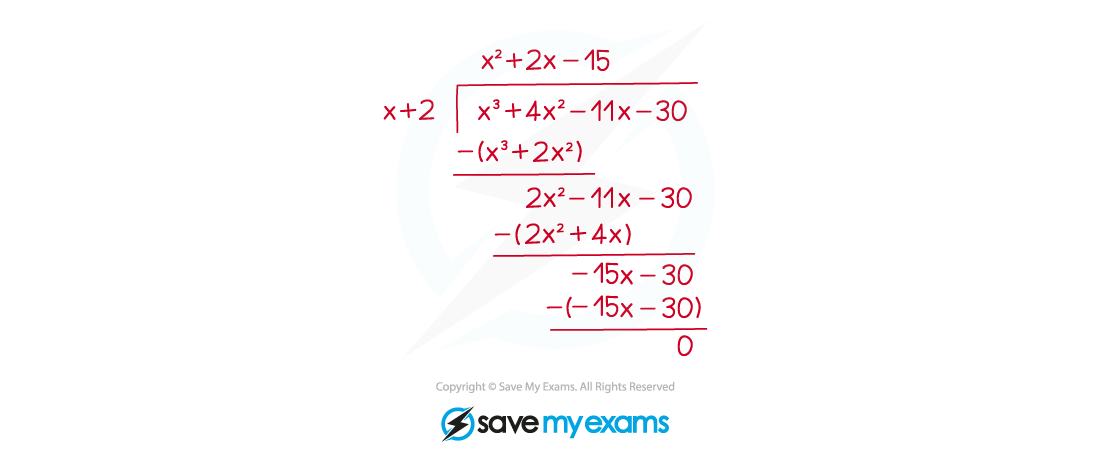
STEP 3
Use the result of your division to write .
STEP 4
If the quadratic can be factorised, do so.
can then be written as the product of three linear factors.
If the quadratic cannot be factorised, then the result from STEP 3 is the final factorisation.

How do I solve a cubic equation?
A cubic equation will have either 1, 2 or 3 (real) solutions
(The cubic function will have either 1, 2 or 3 (real) roots)
Once the cubic function is factorised using the four steps above, there is one more step to carry out
STEP 5 Find the solutions to the cubic equation by making each factor equal to zero
For each linear factor,
so
is a solution
This is the factor theorem!
For a quadratic factor,
use either the quadratic formula or completing the square (as it won't factorise)
this will give two of the solutions to the cubic equation
if there are no solutions to the quadratic equation there are no solutions other than that from the linear factor
From the example above,
so the solutions to the cubic equation
are
and
Cubic equations can have equal (repeated) solutions
e.g.
has two (equal and real) roots,
(repeated) and
e.g.
has three (equal and real) roots,
Examiner Tips and Tricks
When
(i.e. there is no constant term) then
is a factor of the cubic function, and so
is a solution
This is a special case of factor theorem, where
spotting the factor of
means there is no need to test values
Take out a factor of
and a quadratic function will remain
Deal with the quadratic in any of the usual ways
Worked Example
a) Solve the cubic equation .
STEP 1 - use factor theorem with
is a factor of
STEP 2 - polynomial division () or 'by inspection' By inspection ...
('cubic' ÷ 'linear' = 'quadratic')
(because the is generated only from
)
(because the constant term is generated only from )
Equate coefficients of (or
) terms to find
,
STEP 3
STEP 4 - the quadratic does not factorise
STEP 5 - Use the factors to find the solutions
(using the quadratic formula)
The solutions to are
and
.

Unlock more, it's free!
Was this revision note helpful?
