Syllabus Edition
First teaching 2025
First exams 2027
Competitive Markets (Cambridge (CIE) IGCSE Economics): Revision Note
Exam code: 0455 & 0987
An introduction to competitive and monopoly markets
Each firm operates in a specific market
The conditions in different markets can vary significantly and are determined by the market structure in which the firm operates
Competitive markets are those with an extremely high degree of competition
A monopoly is a market structure in which one firm dominates the market and has significant market power
Characteristics that determine if a firm is in a competitive or monopoly market
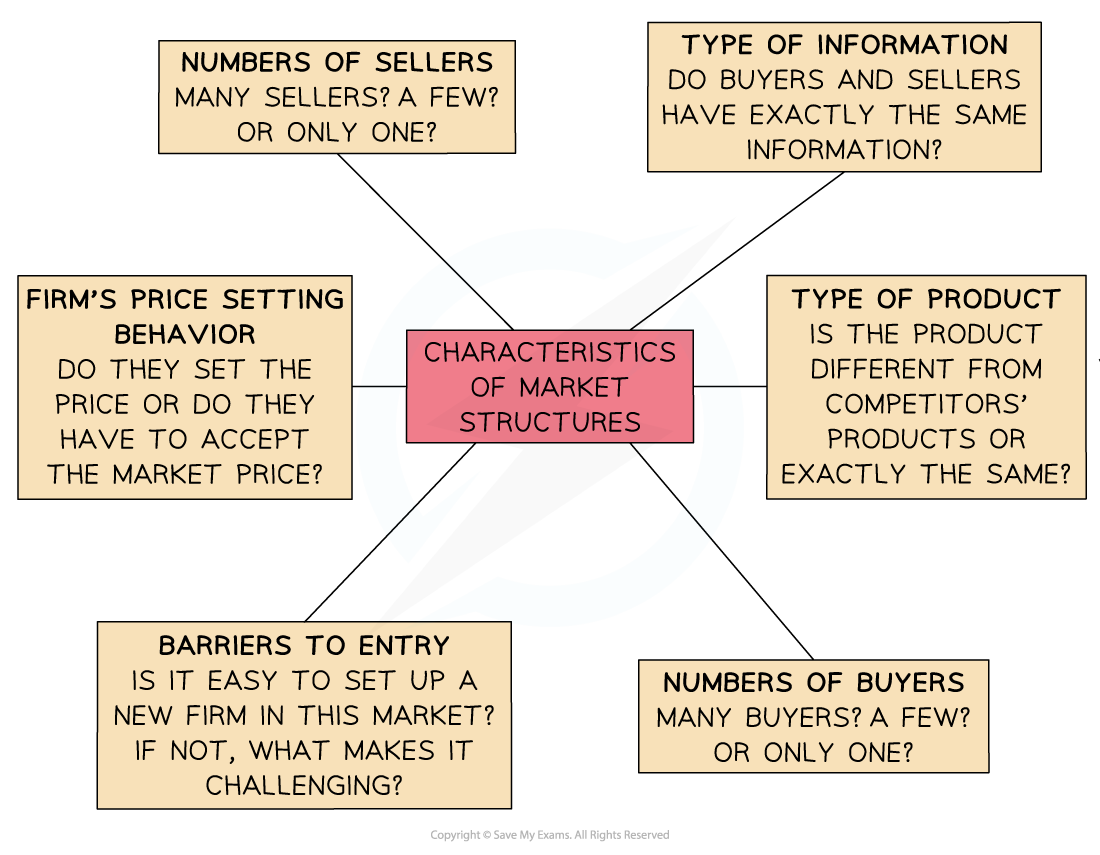
The answers to the questions above determine the type of market structure in which a firm is operating in
If a firm is selling a unique product (e.g. handmade car) it is likely operating in a monopoly market and setting high prices
Examiner Tips and Tricks
There are a range of market structures; however, your syllabus only requires you to know the characteristics of two – competitive markets and monopolies
Characteristics of competitive markets
A competitive market is a market structure where a large number of buyers and sellers trade similar or identical products, and no single buyer or seller can influence the market price
1. Many buyers and sellers
There are many sellers, as it is easy to set up businesses in a competitive market structure
Often, low capital or specialist knowledge is required
There are many buyers; competitive markets often sell mass-produced goods such as t-shirts
2. No barriers to entry and exit from the industry
Barriers to entry are conditions that make it difficult or expensive for a firm to enter a market to compete with the existing suppliers, e.g., high start-up costs
Firms can start-up or leave the industry with relative ease, which increases the level of competition
3. Buyers and sellers possess perfect knowledge of prices
This assumption presupposes perfect information, e.g., if one seller lowers their price then all buyers will know about it
4. The products are homogenous
Homogeneous products mean that products sold by competing firms are identical and indistinguishable from each other
This means firms are unable to build brand loyalty, as perfect substitutes exist and any price changes will result in losing customers
5. Price takers
Individual firms cannot influence market price; they must accept the market price set by demand and supply forces
Advantages and disadvantages of competitive markets
Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
|
|
Effect of a high number of firms
Price: More competition drives prices down towards the cost of production
Quality: Firms must improve quality or service to stand out
Choice: Consumers benefit from a wide range of suppliers and product variations
Profit: Individual firm profits are likely to be lower, especially in the long run, as competition erodes abnormal profits

Unlock more, it's free!
Did this page help you?