Generalist & Specialist Species (College Board AP® Environmental Science): Study Guide
Differences between generalist & specialist species
Organisms can be broadly categorized as generalists or specialists based on their adaptability and ecological requirements
Generalist and specialist species differ in their ability to survive and thrive in various environments
These differences influence their roles in ecosystems and their responses to environmental changes
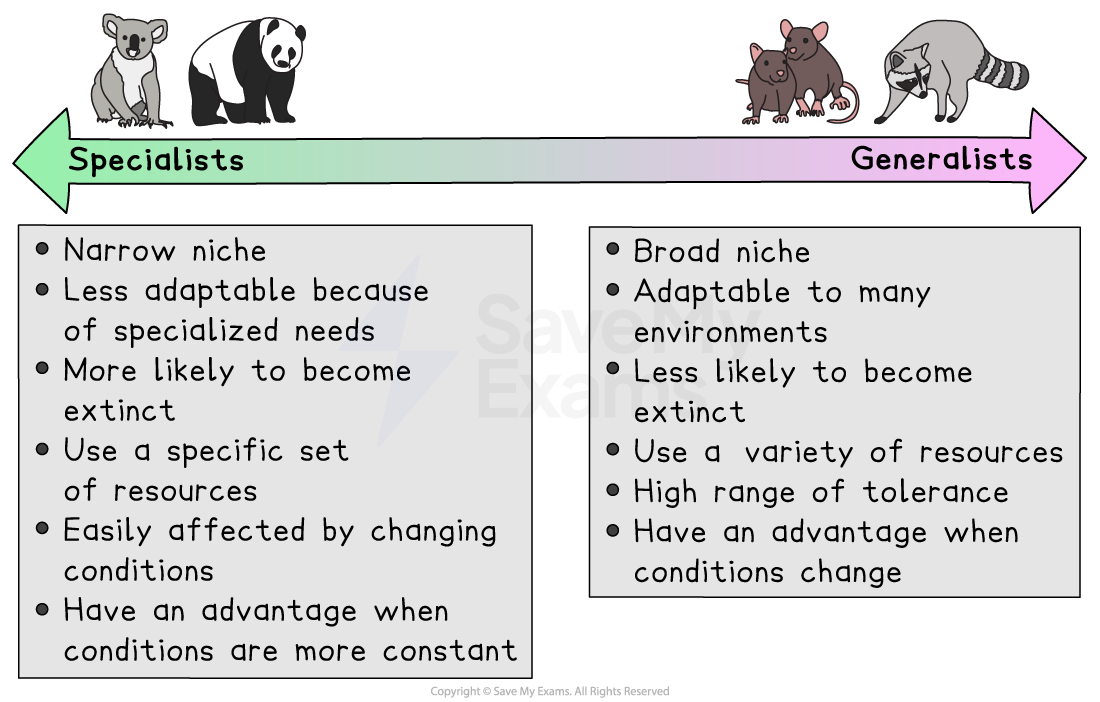
Key differences between generalist and specialist species
Definition:
Generalist species:
Can thrive in a wide range of environmental conditions
Have a varied diet and flexible behaviors
Example: Cockroaches can survive in a variety of environments ranging from urban areas to forests and have a diverse diet, including decaying organic matter, food scraps, and even paper products
Specialist species:
Thrive in specific environmental conditions
Depend on a narrow range of resources or habitats
Example: Koalas primarily eat eucalyptus leaves
Habitat preference:
Generalists:
Are adapted to changing or variable habitats
Their adaptability allows them to survive in diverse ecosystems
Example: Rats can inhabit urban, agricultural, and forested areas
Specialists:
Are suited to stable, unchanging habitats
Depend on specific conditions for survival
Example: Coral species require precise water temperature, clarity and pH
Diet:
Generalists:
Have diverse diets and can consume a variety of foods
Example: Bears eat plants, fish, and small mammals
Specialists:
Have highly specific diets, often relying on one or a few food sources
Example: Pandas eat primarily bamboo
Adaptability:
Generalists:
Are more adaptable to environmental disturbances
Can shift behaviors or resources in response to new challenges
Specialists:
Are less adaptable and more vulnerable to disturbances
May struggle to survive if their specific resource or habitat is lost
Advantages and disadvantages:
Generalists:
Advantage: Can outcompete specialists in changing environments
Disadvantage: May face more competition in stable environments
Specialists:
Advantage: Can outcompete generalists in stable, unchanging habitats
Disadvantage: High vulnerability to habitat loss or environmental changes
Examiner Tips and Tricks
Make sure you understand how habitat stability or change influences which species are advantaged. It is not always advantageous to be a generalist species, as they may face greater competition for food or habitat, e.g. from other generalists.

Unlock more, it's free!
Did this page help you?