Natural Logarithmic Models (DP IB Applications & Interpretation (AI)): Revision Note
Did this video help you?
Logarithmic functions & graphs
What are the key features of logarithmic graphs?
A logarithmic function is of the form
Examiner Tips and Tricks
Remember the natural logarithmic function .
The graphs always pass through the point
The graphs do not have a y-intercept
The graphs have a vertical asymptote at the y-axis
The graphs have one root at
This can also be found using your GDC
The graphs do not have any minimum or maximum points
The graphs are monotonic
The value of
determines whether the graph is increasing or decreasing
If
is positive then the graph is increasing
If
is negative then the graph is decreasing
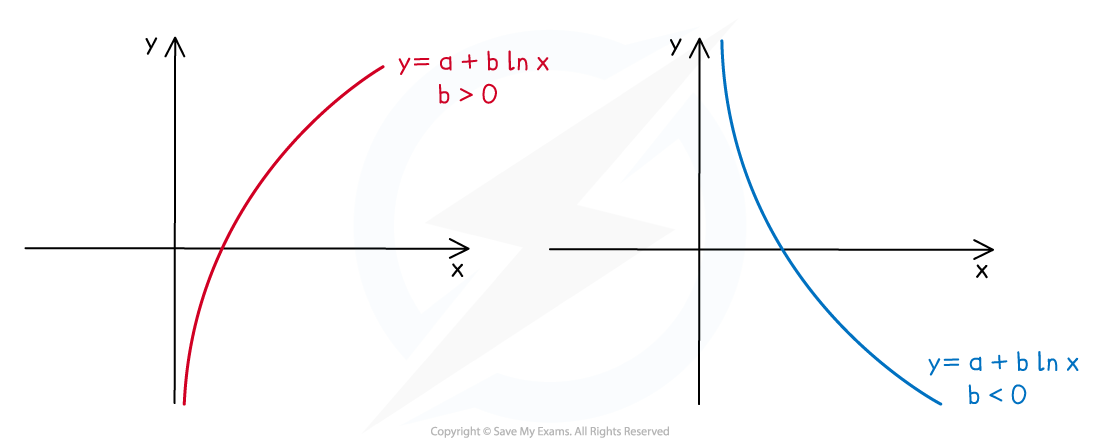
Natural logarithmic models
What are the parameters of natural logarithmic models?
A natural logarithmic model is of the form
The value of
represents the value of the function when
The value of
determines the rate of change of the function
A bigger absolute value of b leads to a faster rate of change
What can be modelled as a natural logarithmic model?
A natural logarithmic model can be used when the variable increases rapidly for a period followed by a much slower rate of increase with no limiting value
M(I) is the magnitude of an earthquake with an intensity of I
d(I) is the decibels measured of a noise with an intensity of I
What are possible limitations a natural logarithmic model?
A natural logarithmic graph is unbounded
In real-life this might not be the case
The variable might have a limit
The rate of change varies rapidly initially
In real-life it might change slowly and then speed up
Worked Example
The sound intensity level, , in decibels (dB) can be modelled by the function
,
where is the sound intensity, in watts per square metre (Wm-2).
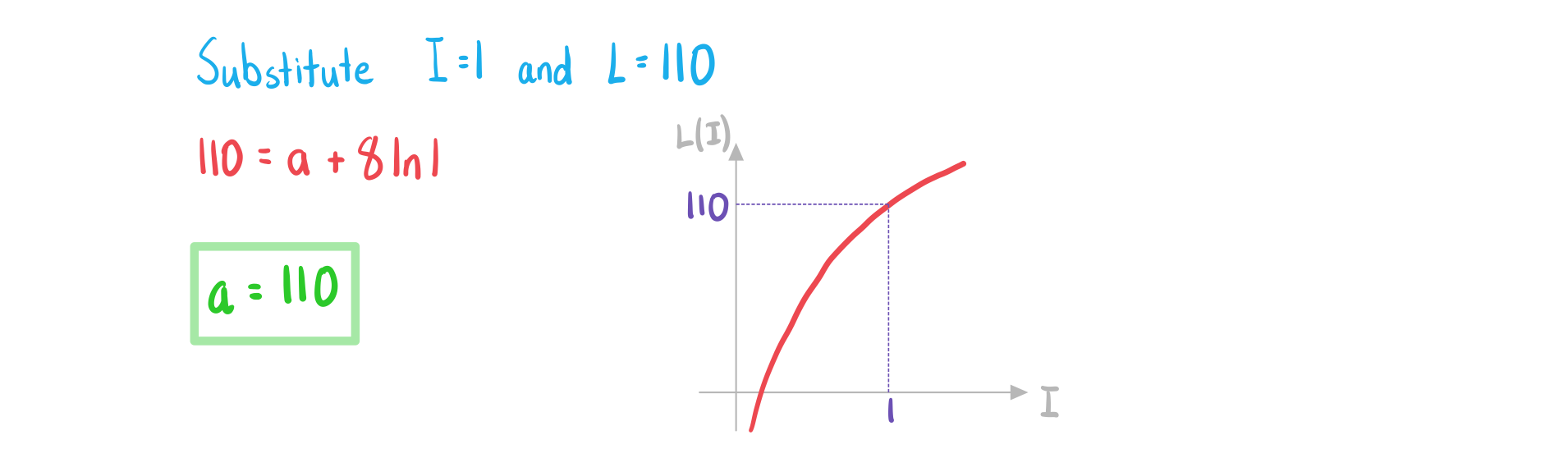
a) Given that a sound intensity of 1 Wm-2 produces a sound intensity level of 110 dB, write down the value of .
Answer:
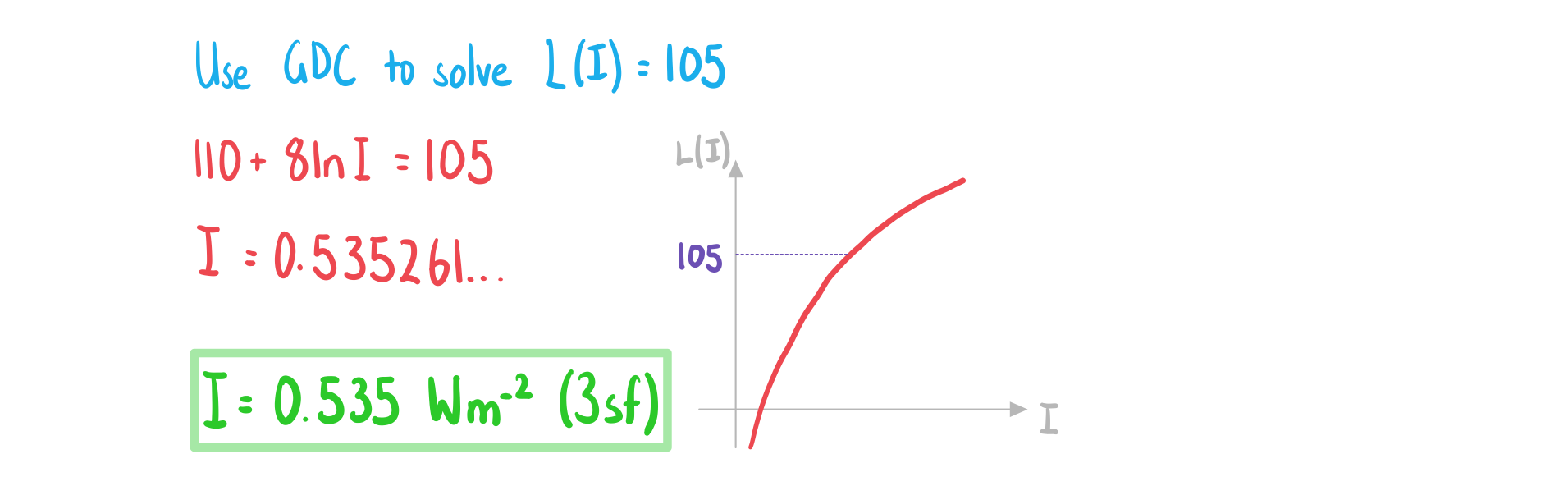
b) Find the sound intensity, in Wm-2, of a car alarm that has a sound intensity level of 105 dB.
Answer:

Unlock more, it's free!
Was this revision note helpful?
