Composite Functions (Cambridge (CIE) O Level Additional Maths): Revision Note
Exam code: 4037
Did this video help you?
Composite functions
What is a composite function?
A composite function is where one function is applied after another function

The ‘output’ of one function will be the ‘input’ of the next one
Sometimes called function-of-a-function
A composite function can be denoted
All of these mean “
of
”

How do I work with composite functions?

Recognise the notation
means “f of g of x”
The order matters
First apply
to
to get
Then apply
to
to get
Always start with the function closest to the variable
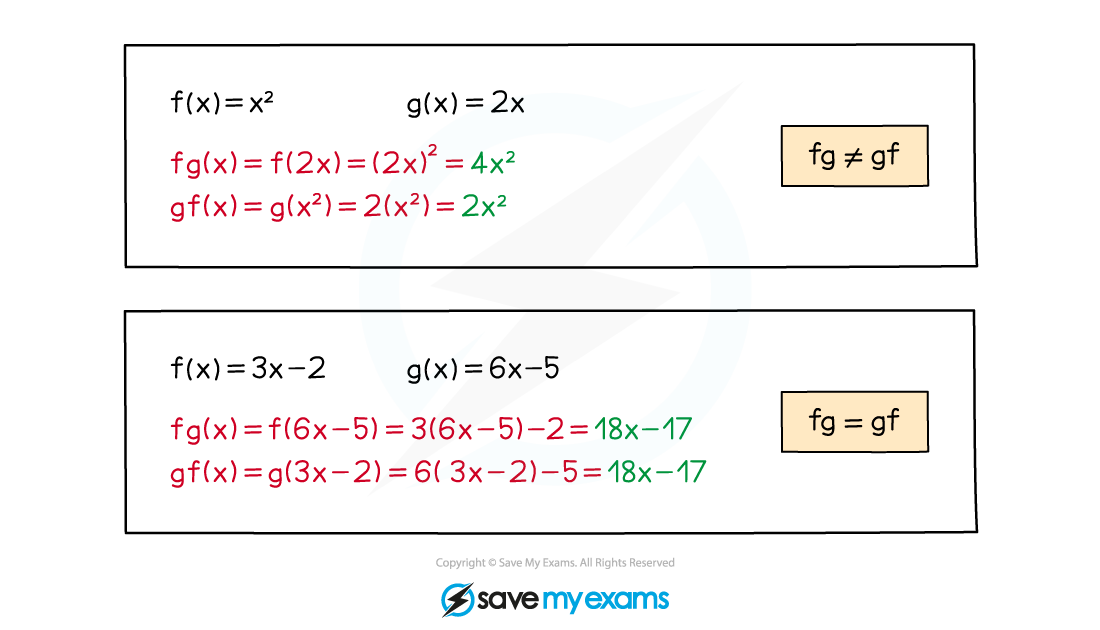
is not usually equal to
Special cases
and
are generally different but can sometimes be the same
is written as
Note that trig functions are exceptions to this rule
e.g.
means
not
For inverse functions,
Worked Example
Two functions, and
are
a) Find and
.
b) Find, in terms of ,
.
is the first function to be applied ...
Domain & range of composite functions
How do I find the domain and range of composite functions?
Use logic to determine the domain and range of a composite function
For
the first function to be applied will be
So, at best, the domain of
will be the same as the domain of
However, for this to be the case, the range of
must be contained within the domain of
If this is not the case, then restrictions on the domain of
will be required
Similarly, at best, the range of
will be the same as the range of
But if the domain of
has been affected, the range of
will also be affected
Examiner Tips and Tricks
Domain and range are important in composite funcitons like
the ‘output’ (range) of g must be in the domain of f(x), so
could exist, but
may not (or not for some values of
)
Worked Example
Two functions, and
are defined as follows
a) Write down the range of and the range of
.
As the domain of is
,
will always be greater than 1,
The range of is
The square of any value will be positive or zero, but here, is not included in the domain for
.
The range of is
b) Use your answers to (a) to help explain why does not exist.
is the first function to be applied The range of
would need to be contained within the domain of
But the range of
is
which is outside the domain of
which is
does not exist
c) Find the range of ,
is the first function. The range of
is
. This is the same as the domain of
.
The range of is

Unlock more, it's free!
Was this revision note helpful?
