Electrolysis (OCR GCSE Chemistry A (Gateway)): Revision Note
Exam code: J248
The Process of Electrolysis
When an electric current is passed through a molten ionic compound the compound decomposes or breaks down
The process also occurs for aqueous solutions of ionic compounds
Liquids and solutions that are able to conduct electricity are called electrolytes
Covalent compounds cannot conduct electricity hence they do not undergo electrolysis
An electrolytic cell is the name given to the set-up used in electrolysis and which consists of the following:
Electrode: a rod of metal or graphite through which an electric current flows into or out of an electrolyte
Electrolyte: ionic compound in molten or dissolved solution that conducts the electricity
Anode: the positive electrode of an electrolysis cell
Anion: negatively charged ion which is attracted to the anode
Cathode: the negative electrode of an electrolysis cell
Cation: positively charged ion which is attracted to the cathode

The basic set-up of an electrolysis cell
Examiner Tips and Tricks
Use the PANIC mnemonic to remember which electrode is the positive and which is the negative: Positive (is) Anode Negative Is Cathode.
Ionic compounds in the solid state cannot conduct electricity since they have no free ions that can move and carry the charge
The ions must be able to move and can only do so in the molten state or when dissolved in a solution, usually aqueous
When the cell is turned on and an electric current is passed through an electrolyte the ions in the solution start to move towards the electrodes
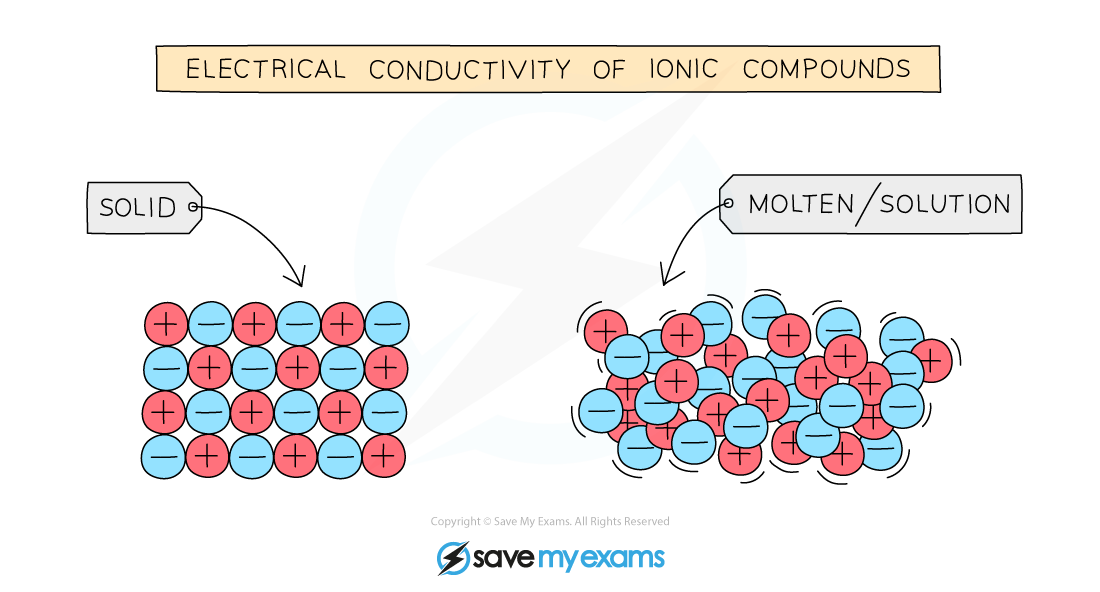
Particles in ionic compounds are in fixed position in the solid state but can move around when molten or in solution
During electrolysis the electrons move from the power supply towards the cathode
Electron flow in electrochemistry thus occurs in alphabetical order as electrons flow from the anode to the cathode
Positive ions within the electrolyte migrate towards the negatively charged electrode which is the cathode
Negative ions within the electrolyte migrate towards the positively charged electrode which is the anode

Diagram showing the direction of movement of electrons and ions in the electrolysis of NaCl
Examiner Tips and Tricks
When a metal conducts it is the electrons that are moving through the metal. When a salt solution conducts it is the ions in the solution that move towards the electrodes while carrying the electrons.
Electrolysis of Ionic Compounds
Lead(II) bromide is a binary ionic compound meaning that it is a compound consisting of just two elements joined together by ionic bonding
When these compounds are heated beyond their melting point, they become molten and can conduct electricity as their ions can move freely and carry the charge
These compounds undergo electrolysis and always produce their corresponding elements
To predict the products of any binary molten compound first identify the ions present
The positive ion will migrate towards the cathode and the negative ion will migrate towards the anode
Therefore the cathode product will always be the metal and the product formed at the anode will always be the non-metal

Diagram showing the electrolysis of lead (II) bromide
Examiner Tips and Tricks
Remember electrodes need to be inert such as graphite or platinum so that they don’t participate in a side reaction with the electrolyte.

Unlock more, it's free!
Did this page help you?