Sigma & Pi Bonds (HL) (DP IB Chemistry): Revision Note
Sigma & pi bonds
Bond overlap in covalent bonds
A single covalent bond forms when two non-metal atoms each contribute an unpaired electron
These unpaired electrons occupy atomic orbitals that overlap to form a molecular orbital
This molecular orbital contains a shared pair of electrons
The shape of the molecular orbital depends on the types of atomic orbitals involved
The greater the overlap, the stronger the covalent bond
There are two main types of covalent bond formed by orbital overlap:
Sigma (σ) bonds
Pi (π) bonds
What is a sigma bond?
Sigma (σ) bonds are formed by the head-on overlap of atomic orbitals
The electron density is concentrated along the bond axis
The bond axis is an imaginary line between the two nuclei
Sigma bonds:
Are the strongest type of covalent bond
Are always present in single covalent bonds
Are also found in double and triple bonds
In these cases, the sigma bond is accompanied by one or more pi (π) bonds
The sigma bond remains the strongest component of the multiple bond
Sigma bonds can form from:
s–s orbital overlap
s–p orbital overlap
p–p orbital overlap
Sigma bonds from s orbitals - hydrogen
Each hydrogen atom has a 1s orbital with one unpaired electron
The two 1s orbitals overlap directly to form a sigma (σ) bond

Sigma bonds from an s and a p orbital - hydrogen fluoride
The 1s orbital of hydrogen overlaps with 2p orbital of fluorine
This head-on overlap forms a sigma (σ) bond

Sigma bonds from p orbitals - fluorine
Each fluorine atom has an unpaired electron in a p orbital
The p orbitals overlap head-on to form a sigma (σ) bond

What is a pi bond?
Pi (π) bonds form when adjacent p orbitals overlap sideways (laterally)
This creates electron density above and below the plane of the sigma (σ) bond
A single π bond is shown as two electron clouds
Each electron cloud comes from one lobe of the overlapping p orbitals
These clouds together contain two electrons shared between the atoms
The electron density lies on opposite sides of the bond axis
π bonds occur only in double and triple bonds
Pi bonds from p orbitals

Examples of sigma & pi bonding in molecules
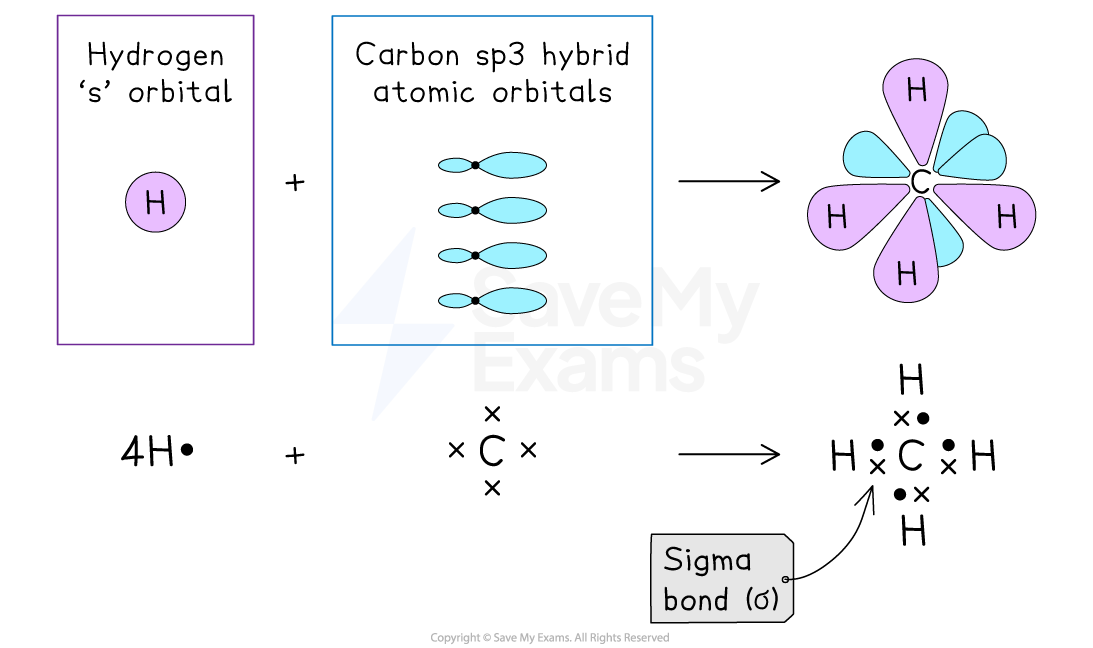
Methane
The carbon atom forms four sigma (σ) bonds with hydrogen atoms
These bonds are formed by the overlap of the hybrid orbitals on carbon with the 1s orbitals of hydrogen
Each bond involves a head-on overlap, creating a sigma bond
Methane contains only sigma bonds
Ethene
Sigma bonds in ethene:
Each carbon atom in ethene is hybridised
It forms three sigma (σ) bonds using three hybrid orbitals:
Two σ bonds are formed with the hydrogen atoms
One σ bond is formed with the other carbon atom

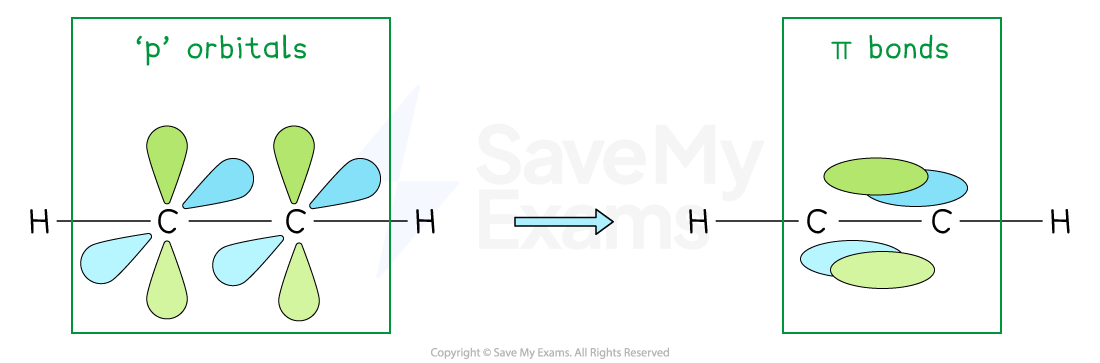
Pi bonds in ethene:
The fourth electron from each carbon atom occupies a p orbital
This overlaps sideways with another p orbital on the other carbon atom to form a π bond

This creates a carbon-carbon double bond consisting of:
One σ bond
One π bond
Ethyne
Sigma bonds in ethyne:
Each carbon atom in ethyne is hybridised
It forms two sigma (σ) bonds using its two hybrid orbitals:
One σ bond is formed with a hydrogen atom
One σ bond is formed with the other carbon atom

Pi bonds in ethyne:
Each carbon atom has two unhybridised p orbitals
These overlap sideways with p orbitals on the other carbon atom
This forms two perpendicular π bonds
This creates a carbon-carbon triple bond consisting of:
One σ bond
Two π bonds
Predicting the type of bonds
The number and type of sigma (σ) and pi (π) bonds can be deduced by analysing the bonding in a molecule
Worked Example
What types of covalent bonds are found in the following molecules?
Nitrogen, N2
Hydrogen cyanide, HCN
Answer 1:
Nitrogen, N2, contains a triple bond between the nitrogen atoms.
The triple bond consists of:
One σ bond formed by the head-on overlap of two hybrid orbitals
Two perpendicular π bonds formed by sideways overlap of two pairs of unhybridised p orbitals

Nitrogen, N2, has one sigma bond and two pi bonds
Answer 2:
Hydrogen cyanide, HCN, contains:
A single covalent bond between carbon and hydrogen
A triple covalent bond between carbon and nitrogen
The single C-H bond is a σ bond
The triple C
N bond consists of:
One σ bond between carbon and nitrogen formed by the head-on overlap of two hybrid orbitals
Two perpendicular π bonds between carbon and nitrogen formed by sideways overlap of two sets of unhybridised p orbitals

Hydrogen cyanide, HCN, has two sigma bonds and two pi bonds

Unlock more, it's free!
Was this revision note helpful?
