Bearings (Cambridge (CIE) IGCSE Maths): Revision Note
Exam code: 0580 & 0980
Did this video help you?
Bearings
What are bearings?
Bearings are a way of describing an angle
They are commonly used in navigation
There are three rules which must be followed when using a bearing:
They are measured from North
North is usually straight up on a scale drawing or map, and should be labelled on the diagram
They are measured clockwise
The angle should always be written with 3 digits
059° instead of just 59°
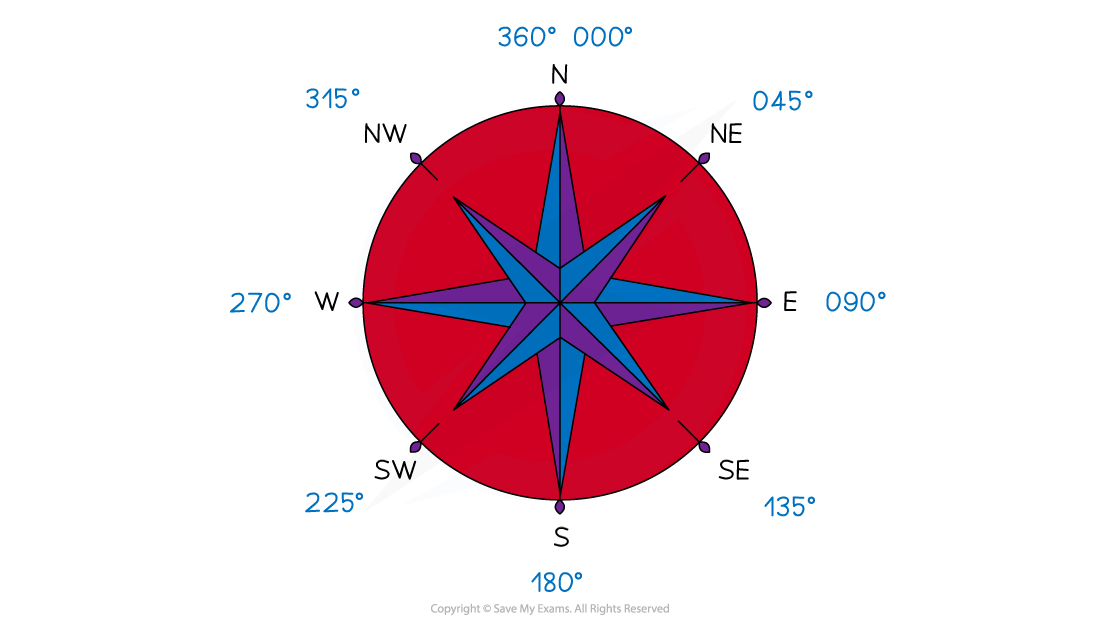
Knowing the compass directions and their respective bearings can be helpful
How do I find a bearing between two points?
Identify where you need to start
"The bearing of A from B" means start at B and find the bearing to A
"The bearing of B from A" means start at A and find the bearing to B
Draw a North line at the starting point
Draw a line between the two points
Measure the angle between the North line and the line joining the points
Measure clockwise from North
Write the angle using 3 figures
How do I draw a point on a bearing?
You might be asked to plot a point that is a given distance from another point and on a given bearing
STEP 1
Draw a North line at the point you wish to measure the bearing fromIf you are given the bearing from A to B draw the North line at A
STEP 2
Measure the angle of the bearing given from the North line in the clockwise directionSTEP 3
Draw a line and add the point B at the given distance
How do I find the bearing of B from A if I know the bearing of A from B?
If the bearing of A from B is less than 180°
Add 180° to it to find the bearing of B from A
If the bearing of A from B is more than 180°
Subtract 180° from it to find the bearing of B from A
How do I answer trickier questions involving bearings?
Bearings questions may involve the use of Pythagoras or trigonometry to find missing distances (lengths) and directions (angles)
You should always draw a diagram if there isn't one given
Examiner Tips and Tricks
Make sure you have all the equipment you need for your maths exams
A rubber and pencil sharpener can be essential as these questions are all about accuracy
Make sure you can see and read the markings on your ruler and protractor
Always draw a big, clear diagram and annotate it, be especially careful to label the angles in the correct places!
Worked Example
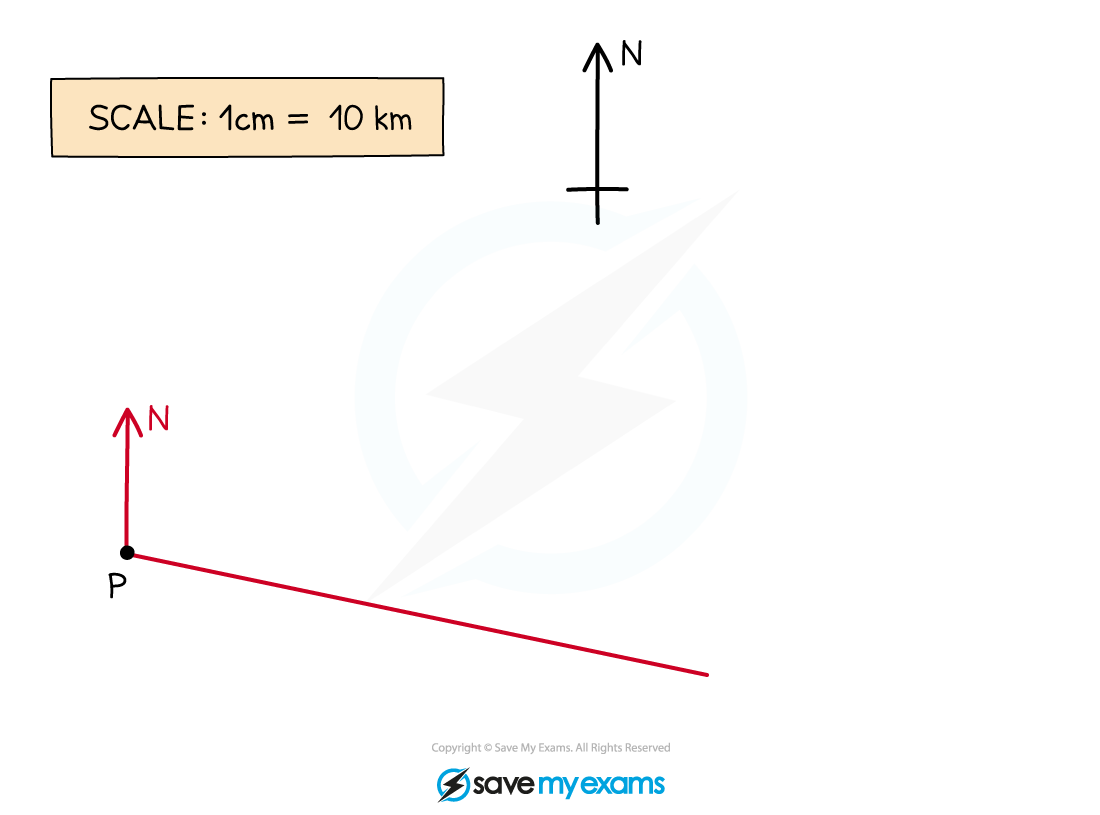
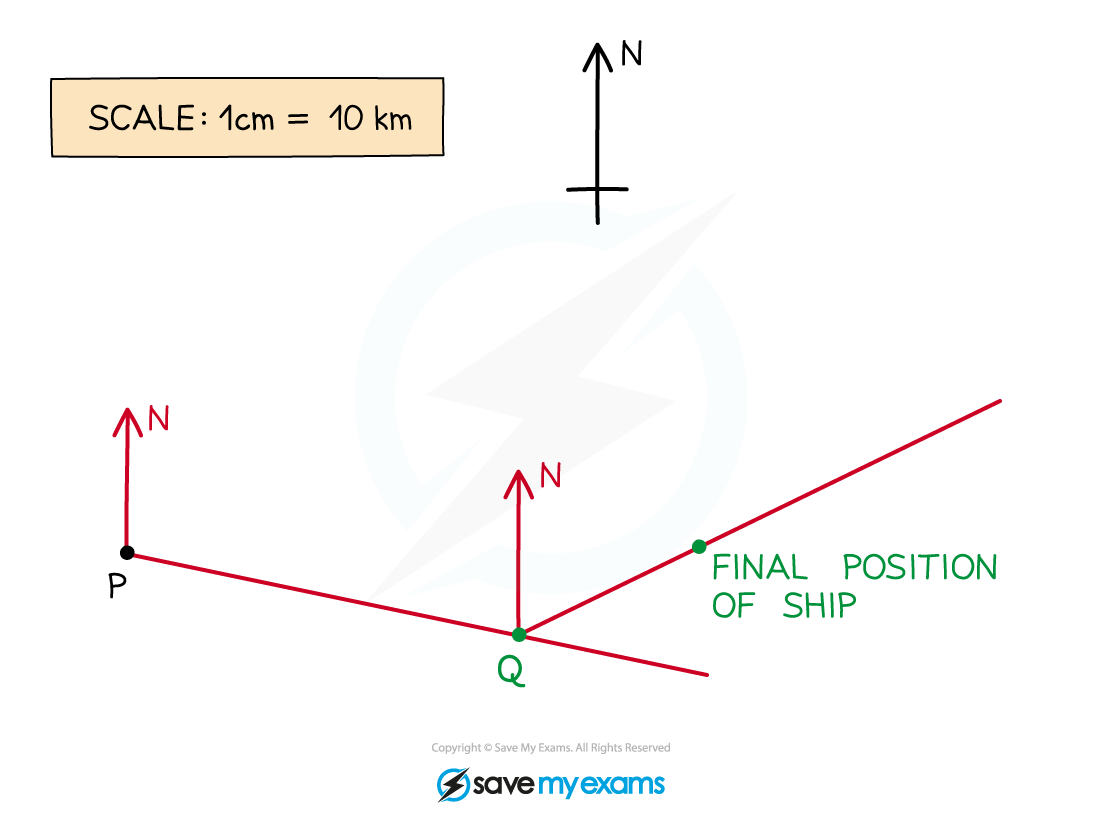
A ship sets sail from the point P, as shown on the map below.
It sails on a bearing of 105° until it reaches the point Q, 70 km away. The ship then changes path and sails on a bearing of 065° for a further 35 km, where its journey finishes.
Show on the map below the point Q and the final position of the ship.

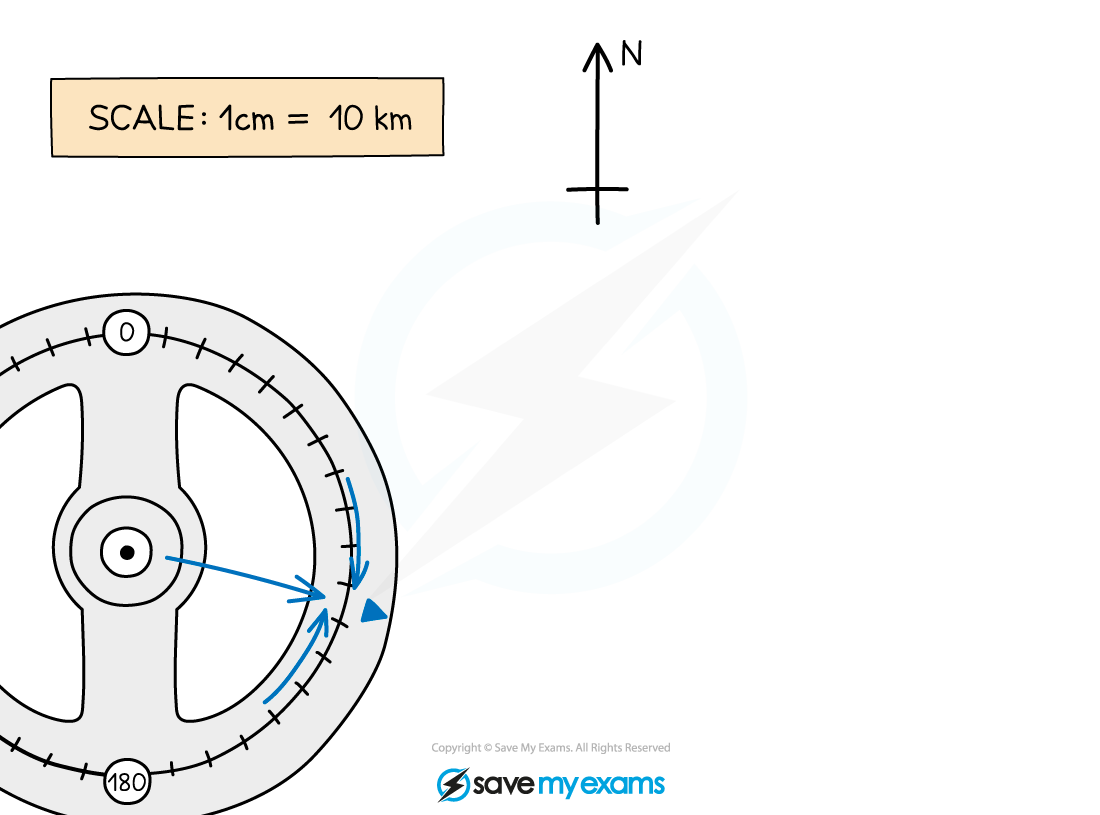
Draw in a north line at the point P
Measure an angle of 105° clockwise from the north line
Making sure you are accurate, carefully make a small but visible mark on the map
Draw a line from P through the mark you have made. Make this line long so that you can easily measure along it accurately
Use the scale given on the map (1 cm = 10 km) to work out the number of cm that would represent 70 km
70 km = 70 ÷ 10 = 7 cm
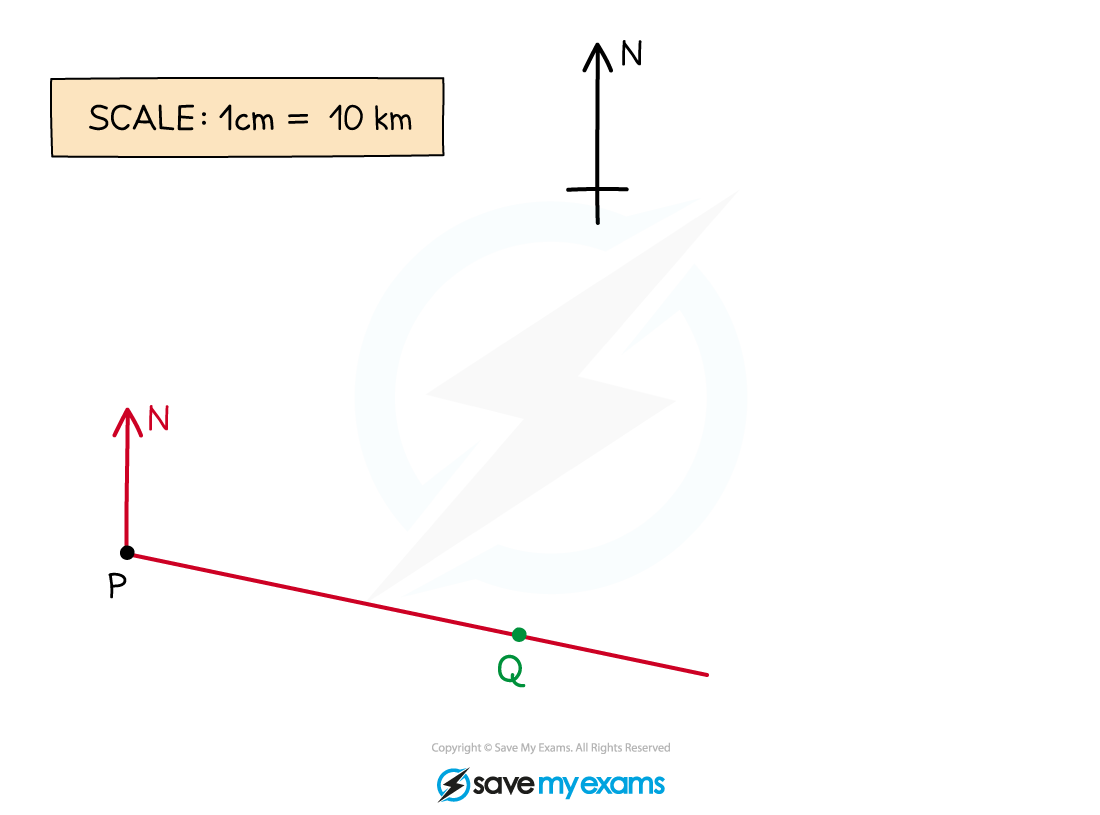
Accurately measure 7 cm from the point P along the line and make a clear mark on the line
Label this point Q
A bearing of 065 means 65° clockwise from the North
First, draw a North line at the point Q, then carefully measure an angle of 65° clockwise from this line. Make a mark and then draw a line from Q through this mark
Using the scale, find the distance in cm along the line you will need to measure.
35 km = 35 ÷ 10 = 3.5 cm
Accurately measure 3.5 cm from the point Q along this new line and make a clear mark on the line
This is the final position of the ship.

Unlock more, it's free!
Did this page help you?