Assessing Overall Business Performance (AQA A Level Business): Revision Note
Exam code: 7132
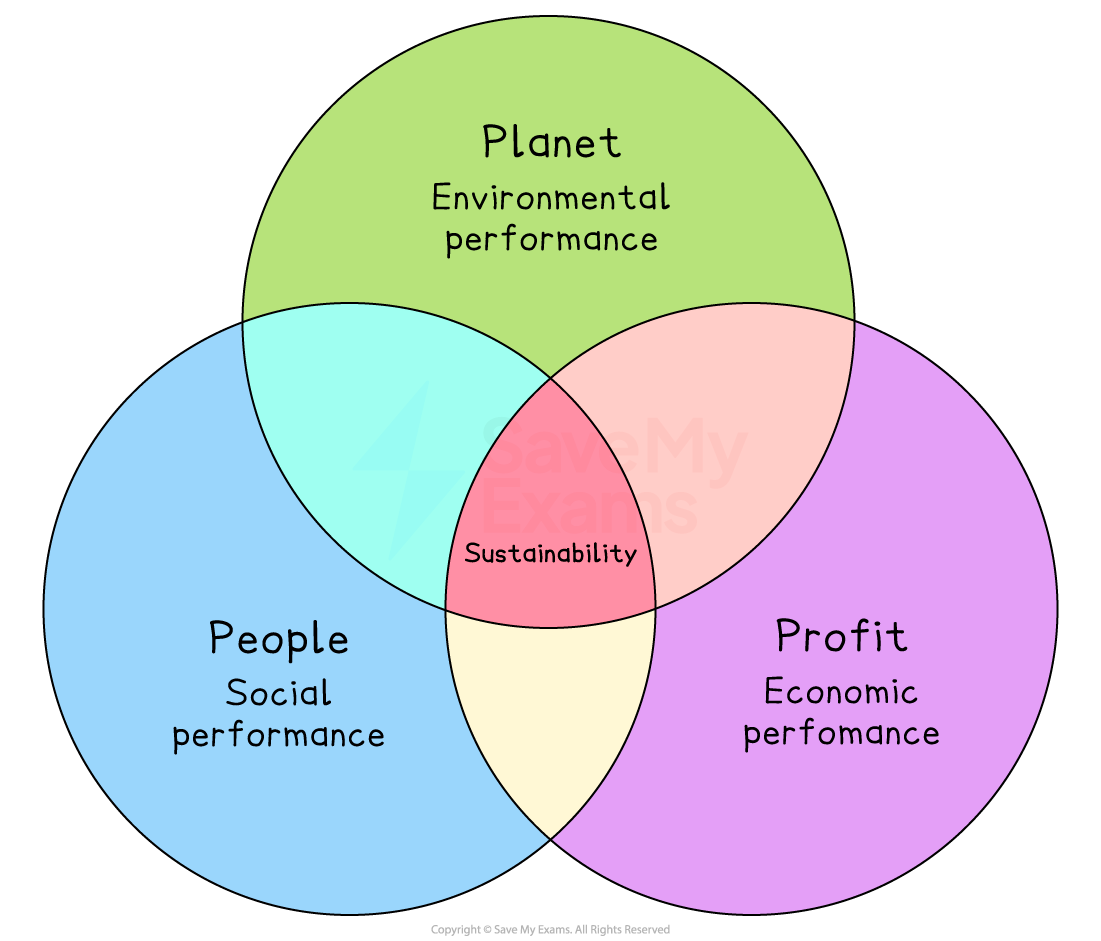
Elkington's Triple Bottom Line
The Triple Bottom Line model highlights that business performance may be measured in a number of ways in relation to
Its finances
Its environmental impact
How socially responsible it is in relation to employees
Elkington argued that only a company that was measuring performance in all three areas of people, profit and planet was considering the full costs of its activities
If all these areas are measured, business owners and employees are likely to pay attention to them and change their behaviour accordingly, rather than just focusing on profit
As a result, sustainability both within the business and, if adopted widely, across the economy as a whole, should be improved
The Triple Bottom Line model
Criticisms of Elkington's model
Criticism | Explanation |
|---|---|
Hard to measure fairly |
|
Conflicting goals |
|
Risk of greenwashing |
|
Too complex and costly for smaller firms |
|
Not fully integrated |
|
Examiner Tips and Tricks
If using the Triple Bottom Line, don’t just list ‘people, planet, profit’ – explain how each area affects performance in context
Other methods of assessing overall business performance
Method | How it works | Example |
|---|---|---|
Balanced scorecard |
|
|
Performance prism |
|
|
GRI Standards (Global Reporting Initiative) |
|
|

Unlock more, it's free!
Was this revision note helpful?
