The Value of Globalisation (AQA A Level Business): Revision Note
Exam code: 7132
Reasons for globalisation
Globalisation is the economic integration of different countries through increasing freedoms in the cross-border movement of people, goods, services, technology and finance
Characteristics of globalisation include
Increasing foreign ownership of companies
Increasing movement of labour and technology across borders
Free trade in goods and services
Easy flows of capital across borders
In 2000, the value of global trade was approximately $6.45 trillion; by 2020, this figure was $19 trillion
Numerous factors have contributed to the rapid increase in the pace of globalisation
Reasons for increased globalisation

Factor | Explanation |
|---|---|
Political change |
|
Reduced cost of transport and communication |
|
Increased significance of transnational companies |
|
Increased investment flows (FDI) |
|
Migration (within and between economies) |
|
Growth of the global labour force |
|
Structural change |
|
The importance of globalisation
Globalisation offers businesses huge chances to grow and cut costs, but it also brings greater competition, more complex operations and risk
Companies that plan well, perhaps by adapting products, securing reliable global supply chains and understanding local cultures, can turn global reach into long-term success
Why globalisation matters to business
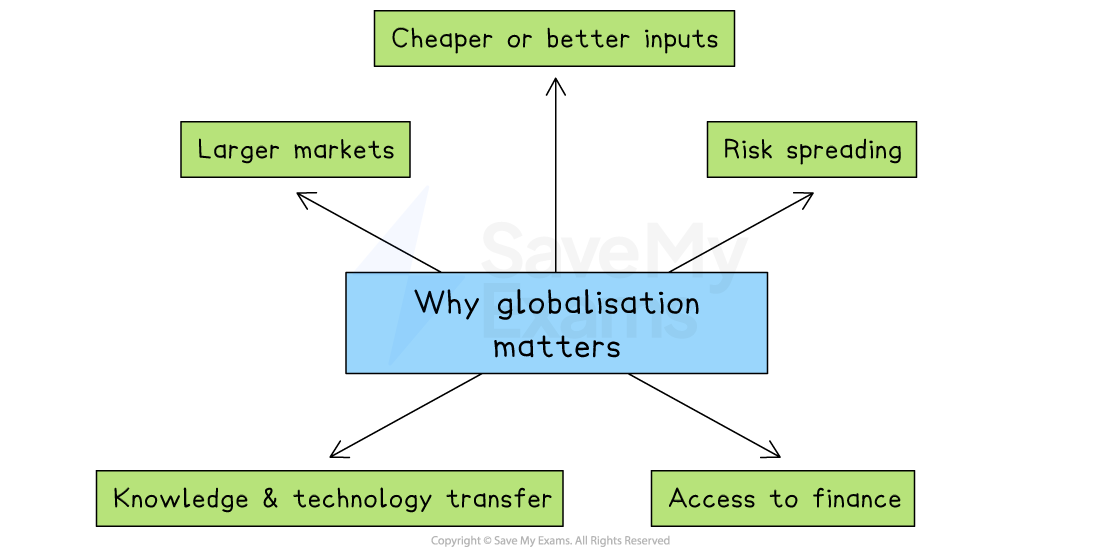
Larger markets
More customers
Selling in several countries multiplies the potential customer base well beyond the limits of the home market
Economies of scale
A bigger output allows fixed costs, such as R&D, marketing and equipment, to be spread over more units, lowering average costs and helping prices stay competitive
Cheaper or better inputs
Global sourcing
Firms can shop around the world for raw materials, components or services at the best balance of price and quality
Specialist skills
Access to clusters such as India’s IT sector or Germany’s precision engineering brings in expertise that may be scarce at home
Risk spreading
Diversified revenue
Weak demand in one region can be balanced by strength in another, making overall sales less volatile
Knowledge and technology transfer
Learning from partners
Joint ventures, licensing and worldwide supply chains expose firms to new ideas, production techniques and management practices
Innovation stimulus
Competing on a global stage pushes businesses to improve products and processes faster
Access to finance
Broader funding sources
Listing on foreign stock exchanges or issuing global bonds widens the pool of investors and can lower the cost of capital
The importance of emerging economies
In the past twenty years, the economic power of less economically developed countries has increased
Emerging economic powers of countries within Asia, Africa and other parts of the world include
BRICS: Brazil, Russia, India, China and South Africa
MINT: Mexico, Indonesia, Nigeria and Turkey
Emerging economies have a growing middle class with increasing incomes, which allows their citizens to spend more on domestic goods and imported goods from abroad
This increases opportunities for international firms who sell their goods and services in these emerging economies
It also means British firms can benefit from low production costs if they move facilities such as factories to these countries
However, their lower cost base, including their lower labour costs, means they are becoming a competitive threat for British firms
Evaluating the impact of emerging economies on UK businesses
Opportunities for UK businesses | Threats for UK businesses |
|---|---|
|
|

Unlock more, it's free!
Was this revision note helpful?
