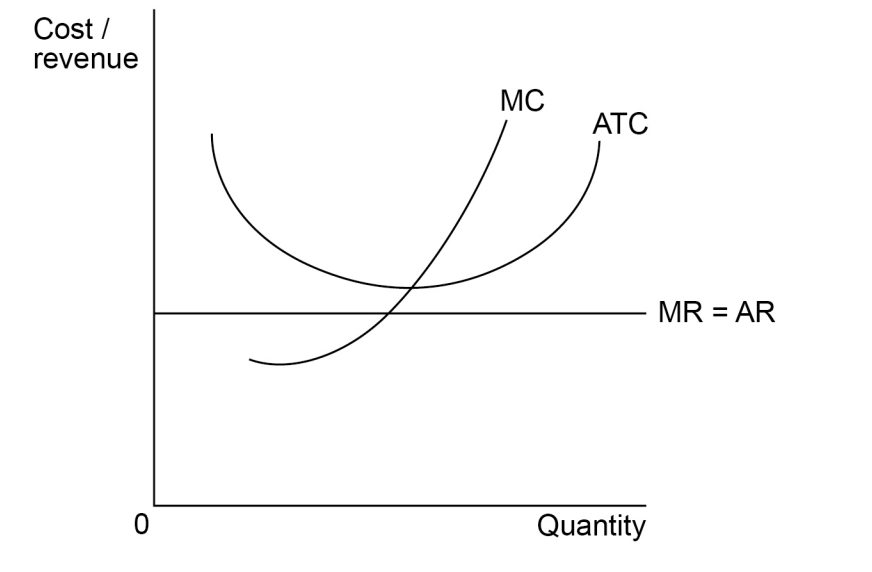
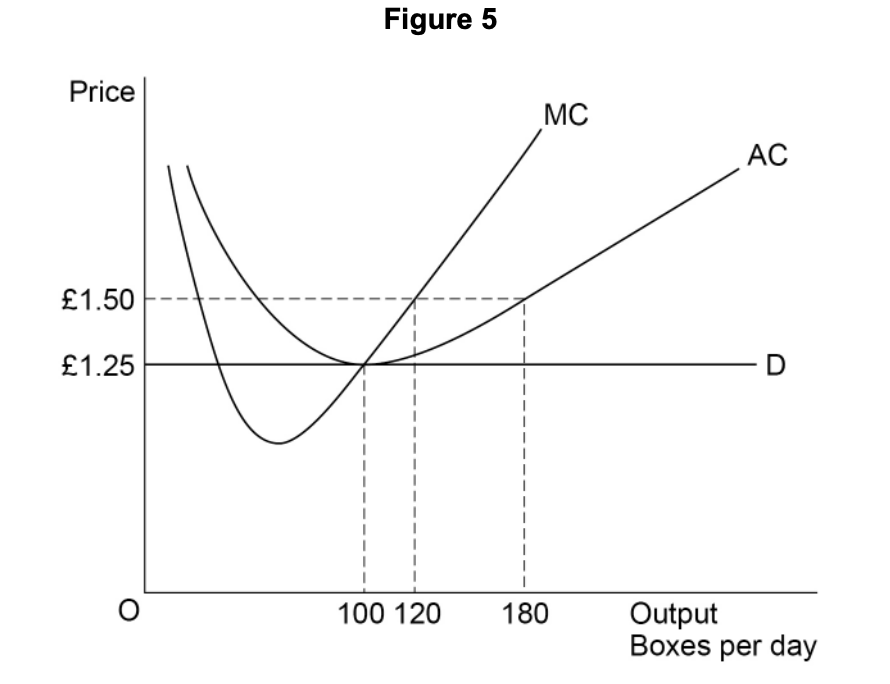
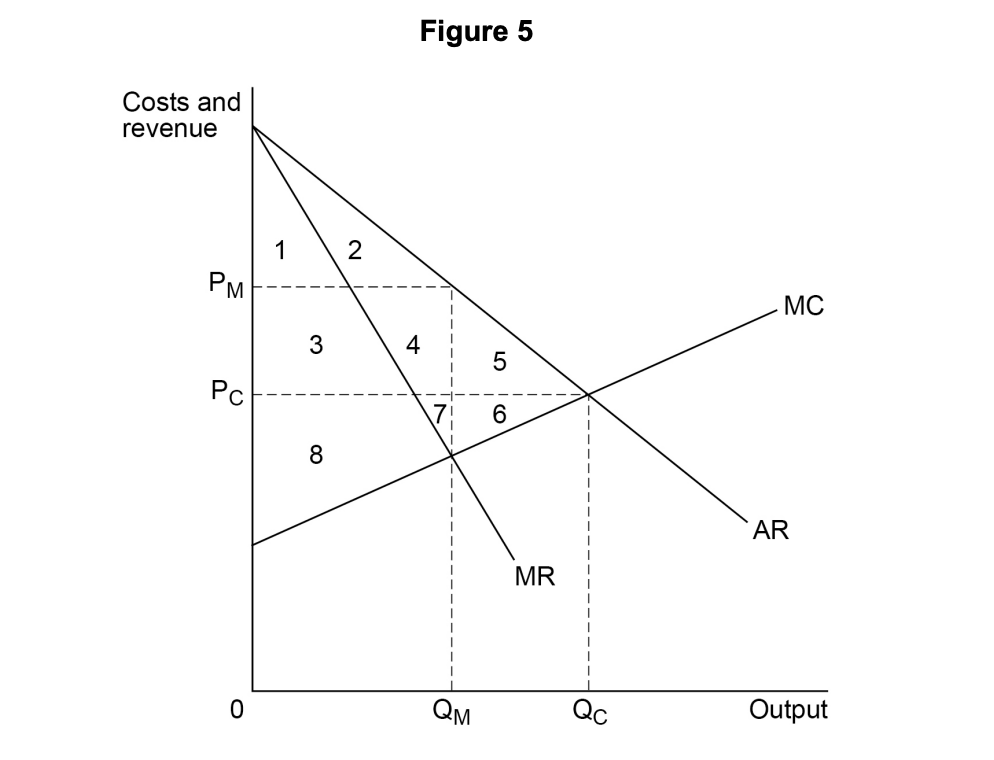
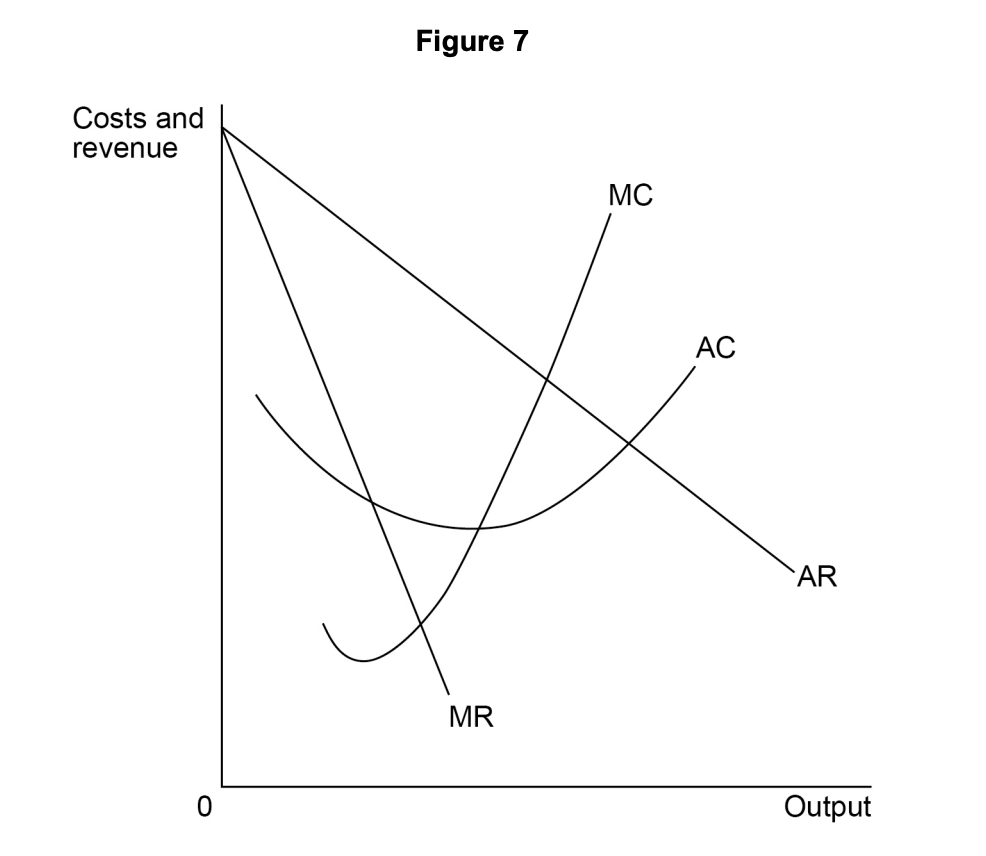
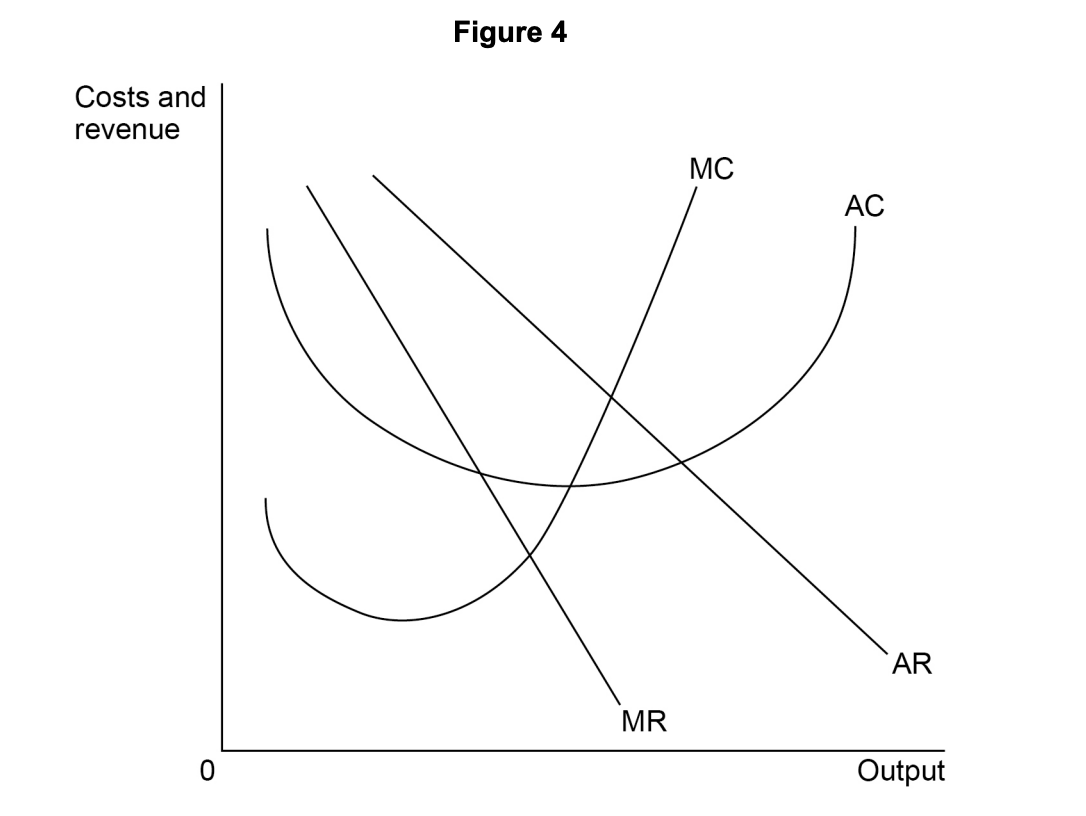
Figure 2 shows the equilibrium position, point E, of a profit-maximising firm in a monopolistically competitive industry.

All other things being equal, which one of the following applies to the firm’s equilibrium at point E? The firm is
in short-run equilibrium, but not in long-run equilibrium.
making normal profit because AC = AR.
making supernormal profit because MC = MR.
productively efficient but not allocatively efficient.
Was this exam question helpful?