Array Basics (Cambridge (CIE) A Level Computer Science): Revision Note
Exam code: 9618
Arrays
What is an array?
An array is an ordered, static set of elements
Can only store 1 data type
The position of each element in an array is identified using the array's index
The array's first element is the lower bound (LB)
The array's last element is the upper bound (UB)
The lower bound of an array is typically 0 or 1 depending on the language being used
An array can be one-dimensional or multi-dimensional
One-dimensional (1D) arrays
A 1D array is a linear array
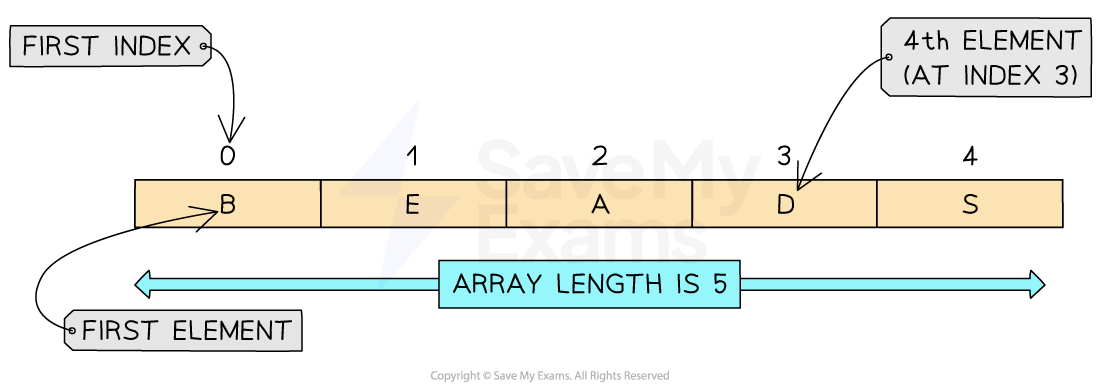
To declare a 1D array in pseudocode you must include the lower bound, upper bound and data types:
DECLARE <identifier> : ARRAY[LB:UB] OF <data type>In this example a 1D array of five elements each containing single character can be declared as:
DECLARE Letters : ARRAY[0:4] OF CHARAn example complete program could be:
// Declare the array
DECLARE Letters : ARRAY[0:4] OF CHAR
// Assign values to each index
Letters[0] ← 'B'
Letters[1] ← 'E'
Letters[2] ← 'A'
Letters[3] ← 'D'
Letters[4] ← 'S'
// Output the full array
FOR Index ← 0 TO 4
OUTPUT Letters[Index]
NEXT IndexThe array is declared with indices from
0to4Each element stores a single character using the
CHARdata typeThe loop outputs each letter in order
Two-dimensional (2D) arrays
A 2D array can be visualised as a table
When navigating through a 2D array you first have to go down the rows and then across the columns to find a position within the array
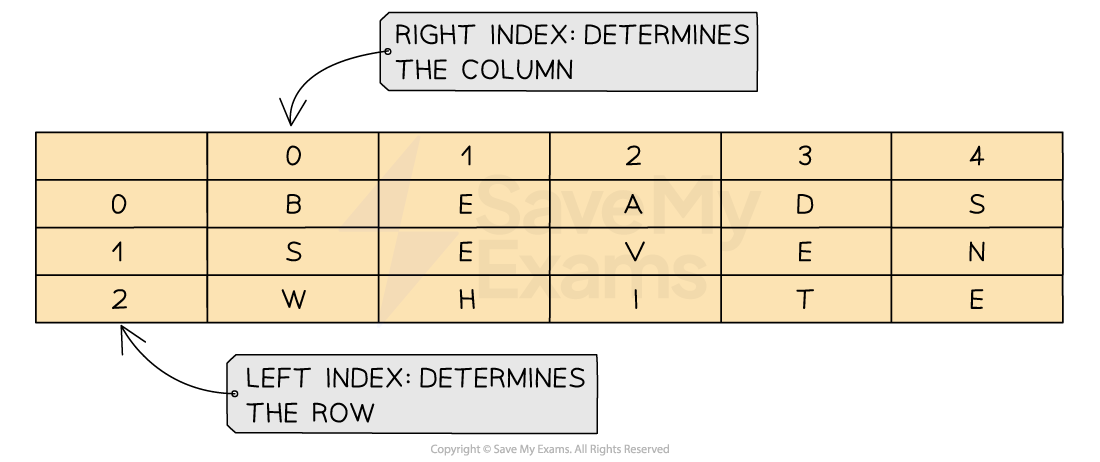
In 2D arrays the following must be declared:
Lower bound for rows (LBR) & upper bound for rows (UBR)
Lower bound for columns (LBC) & upper bound for columns (UBC)
DECLARE <identifier> : ARRAY[LBR:UBR, LBC:UBC] OF <data type>In this example a 2D array can be declared as:
DECLARE Letters : ARRAY[0:2, 0:4] OF CHARAn example complete program could be:
DECLARE Letters : ARRAY[0:2, 0:4] OF CHAR
// Row 0
Grid[0,0] ← 'B'
Grid[0,1] ← 'E'
Grid[0,2] ← 'A'
Grid[0,3] ← 'D'
Grid[0,4] ← 'S'
// Row 1
Grid[1,0] ← 'S'
Grid[1,1] ← 'E'
Grid[1,2] ← 'V'
Grid[1,3] ← 'E'
Grid[1,4] ← 'N'
// Row 2
Grid[2,0] ← 'W'
Grid[2,1] ← 'H'
Grid[2,2] ← 'I'
Grid[2,3] ← 'T'
Grid[2,4] ← 'E'ARRAY[0:2, 0:4]creates 3 rows and 5 columnsFirst index is the row, second is the column:
Letters[row, column]All elements are of type
CHAR
Worked Example
A program reads data from a file and searches for specific data.
The main program needs to read 25 integer data items from the text file Data.txt into a local 1D array, DataArray
Write program code to declare the local array DataArray [1]
Answer
1D array with name
DataArray(with 25 elements of type Integer) [1 mark]
Java
public static Integer[] DataArray = new Integer[25];
VB.NET
Dim DataArray(24) As Integer
Python
DataArray = [] #25 elements Integer

Unlock more, it's free!
Was this revision note helpful?
