Methods (OOP) (Cambridge (CIE) A Level Computer Science): Revision Note
Exam code: 9618
Methods (OOP)
What is a method?
Methods are fundamental in object-oriented programming (OOP) and are functions associated with objects or classes that define the behaviour and actions that objects can perform
There are two main types of methods:
A function
A function performs a task and returns a value
A procedure
A procedure performs a task buts does nor return a value
For example, there are many different types of aircraft which all differ in design, but all require a ‘take off’ and ‘landing’ method
An example of an aircraft class with both attributes and methods is shown below:

Example class for "aircraft" containing several methods
Each object that is created from the aircraft class will have:
A manufacturer value to determine the company that created the aircraft
A model name for the type of aircraft
A value for passenger capacity to determine how many people it can carry
A speed value to determine its maximum speed
Any objects that are created for the aircraft class also have access to the following Methods:
A take off method to get the plane airborne
A land method to land the plane safely
A bank left method to allow the plane to turn to the left
A bank right method to allow the plane to tur to the right
As you can imagine, for an aircraft there would be many more methods that could be implemented such emergency landing and altitude cruising actions
Once objects have been created, they can use the methods from within their class by using the dot (.) notation
As these methods are associated with objects, they are called instance methods
For example if an object has been created as below:
jumboJet = new aircraft (“Boeing”, ”747”, 416, 547)
It can use methods by doing the following:
Objectname.Methodname:
For example: jumboJet.Takeoff()
Examiner Tips and Tricks
In some OOP languages there are both instance methods and static methods
Instance methods
Instance methods are associated with individual instances (objects) of a class. They operate on the specific data and properties of an object (see above on the Jumbo Jet object example)
Static methods
Static methods are associated with a class itself and can be called without creating an instance (object) of the class
Public and private methods
When declaring methods, it is important to determine how they can be accessed:
Public Methods | Private Methods |
|---|---|
Accessible and can be invoked by any code within the same class or from any external classes | Private methods are only accessible within the same class and cannot be invoked by external code or other classes |
Changes to public methods may have an impact on other parts of the codebase, so they should be carefully designed, documented, and backward compatible whenever possible | Changes to private methods have a localized impact since they are only used internally within the class, providing flexibility to modify or refactor them without affecting other parts of the program |
Public methods are used when you want to provide access to certain functionalities or behaviours of an object or class to other parts of your program | Private methods are used when you have internal implementation details that should not be accessed or used by external code. They are meant to be used only within the class itself for organizing and managing the code internally |
Examiner Tips and Tricks
If a method does not specify the keyword public or private then its default value is set to public.
Programming methods (OOP)
How do you program a method?
Pseudocode
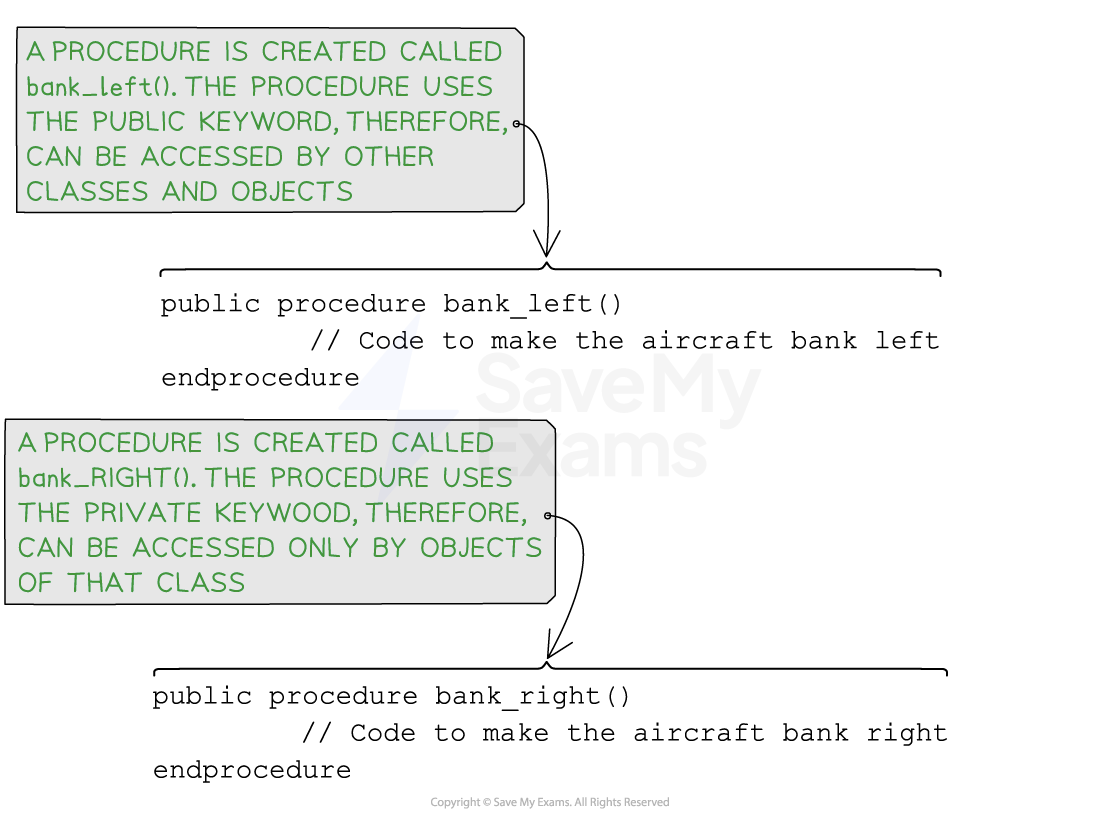
Pseudocode for creating methods
Java
//Creating a public method called BankLeft
public void bankLeft() {
// Code to make the aircraft bank left
}
//Creating a private Method called BankLeft
public void bankLeft() {
// Code to make the aircraft bank left
}Python
#Creating a public method called BankLeft
def bank_left(self):
# Code to make the aircraft bank left
#Creating a private method called BankLeftIn Python, there is no explicit access modifier for methods like "private" in Java
By convention, methods with a single leading underscore _ are considered private and should not be accessed directly from outside the class
_def _bank_left(self):
# Code to make the aircraft bank leftIt's important to note that even though the method is marked as private, it can still be accessed and invoked from outside the class
However, as a rule, other developers should treat it as private and avoid accessing it directly

Unlock more, it's free!
Was this revision note helpful?
