2D Shapes (Edexcel GCSE Maths): Revision Note
Exam code: 1MA1
Properties of 2D shapes
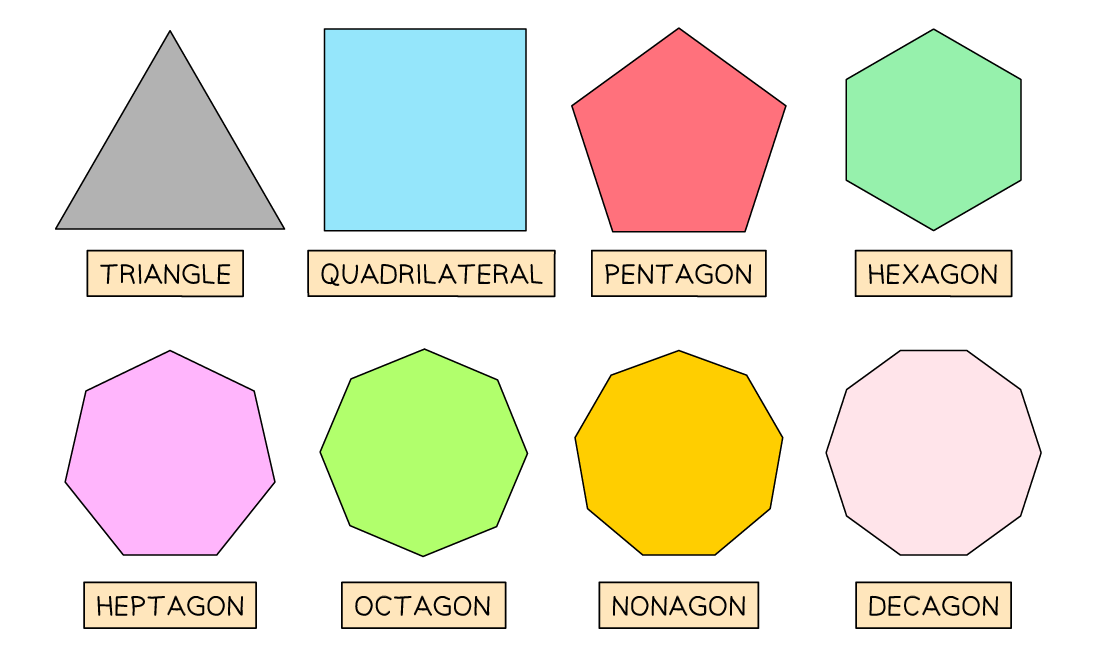
What are the names of common 2D shapes?
You should know the general names of all the 2D polygons
A triangle has 3 sides
A quadrilateral has 4 sides
A pentagon has 5 sides
A hexagon has 6 sides
A heptagon has 7 sides
An octagon has 8 sides
A nonagon has 9 sides
A decagon has 10 sides
A polygon is a flat (plane) shape with n straight sides
A regular polygon has all sides the same length and all angles the same size
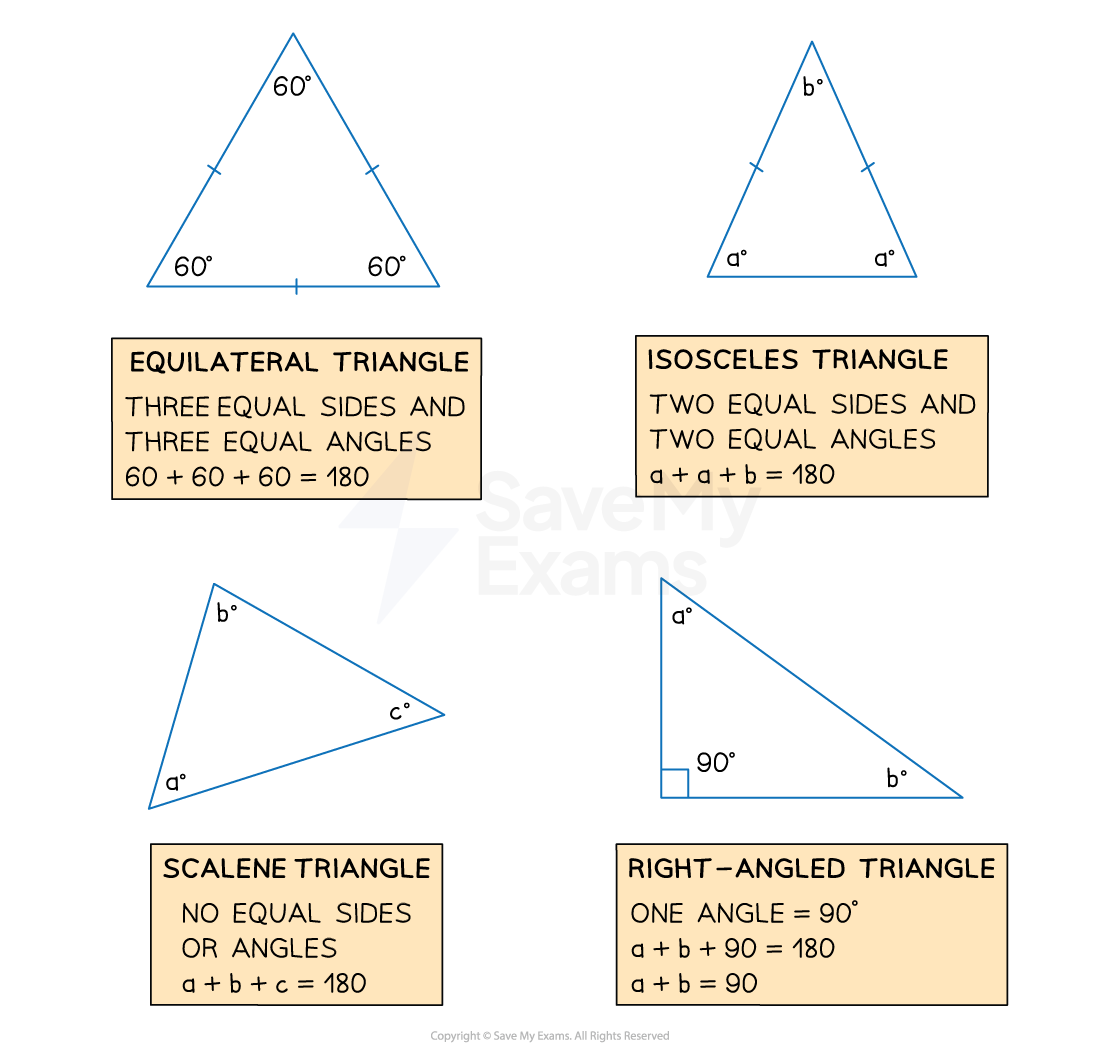
What are the names of the different types of triangles?
You should know the names and properties of the different types of triangles
An equilateral triangle has 3 equal sides and 3 equal angles
An isosceles triangle has 2 equal sides and 2 equal angles
A right-angled triangle has one 90° angle
A scalene triangle has 3 sides all of different lengths
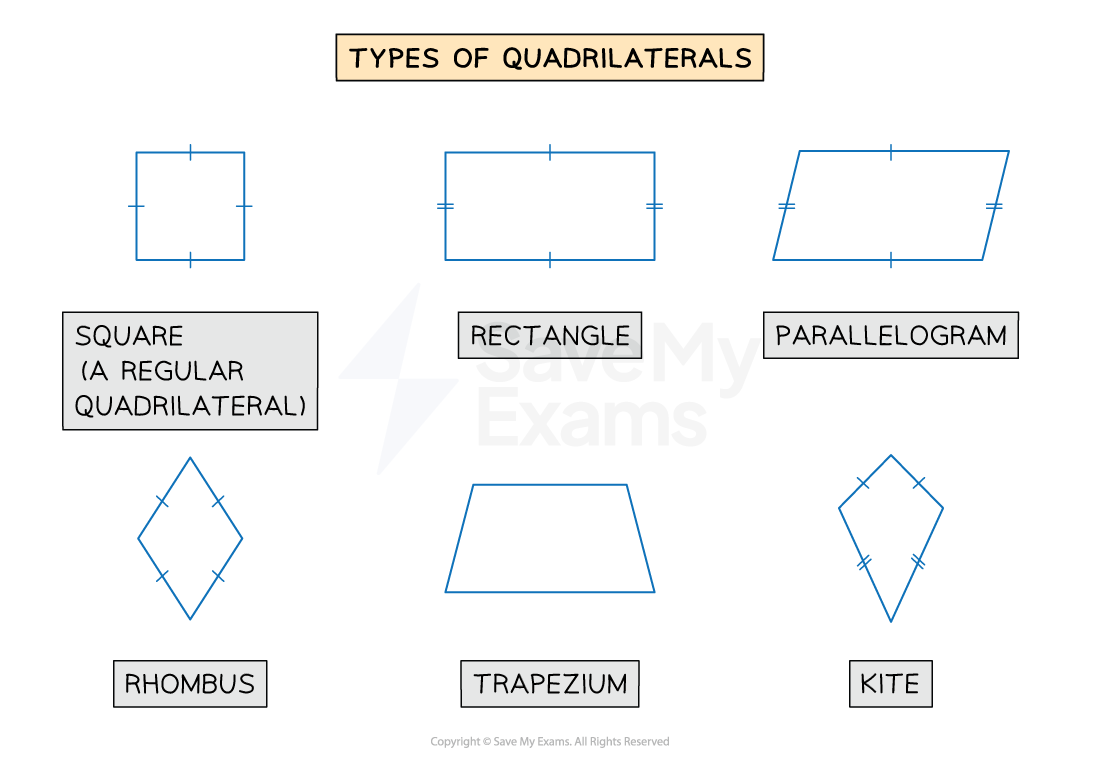
What are the names of the different types of quadrilaterals?
You should know the names and properties of the different types of quadrilaterals
These are squares, rectangles, parallelograms, rhombuses, trapeziums and kites
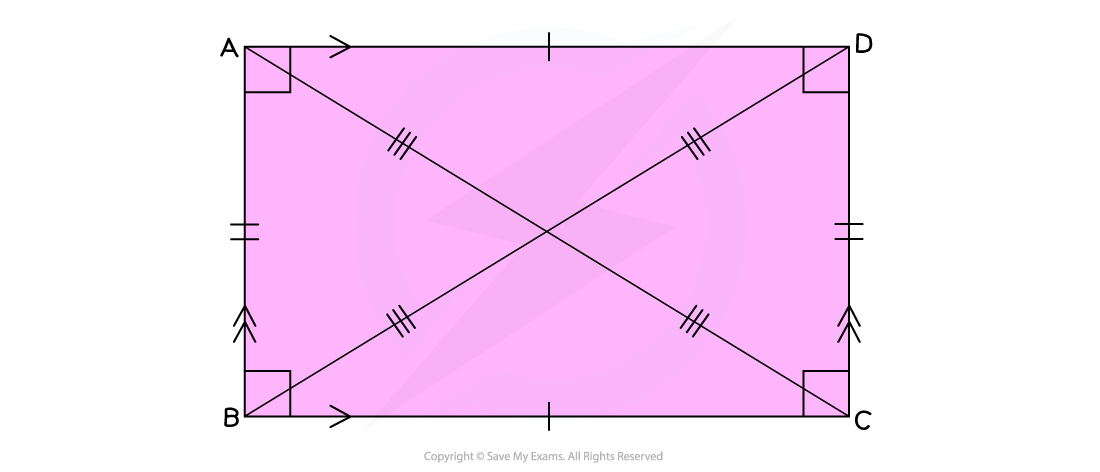
What are the properties of rectangles and squares?
Rectangles and squares have four equal right angles (90°)
Rectangles have two pairs of equal length, parallel sides
Squares are just regular rectangles; all four of their sides are equal
The diagonals of a rectangle bisect each other at the centre of the rectangle
This means that they cut each other in half
The intersecting diagonals form two pairs of angles at the centre
In a square, all four of these angles will be equal to 90°
Pythagoras’ theorem can be used to find the length of the diagonal of a square or rectangle
The diagonal forms the hypotenuse of a right-angled triangle
What are the properties of parallelograms and rhombuses?
Parallelograms and rhombuses (rhombi) have two pairs of equal, opposite, angles
Parallelograms and rhombuses have two pairs of opposite, parallel sides
Rhombuses have four sides of the same length
This means a rhombus is a regular parallelogram
A square is also a regular rhombus
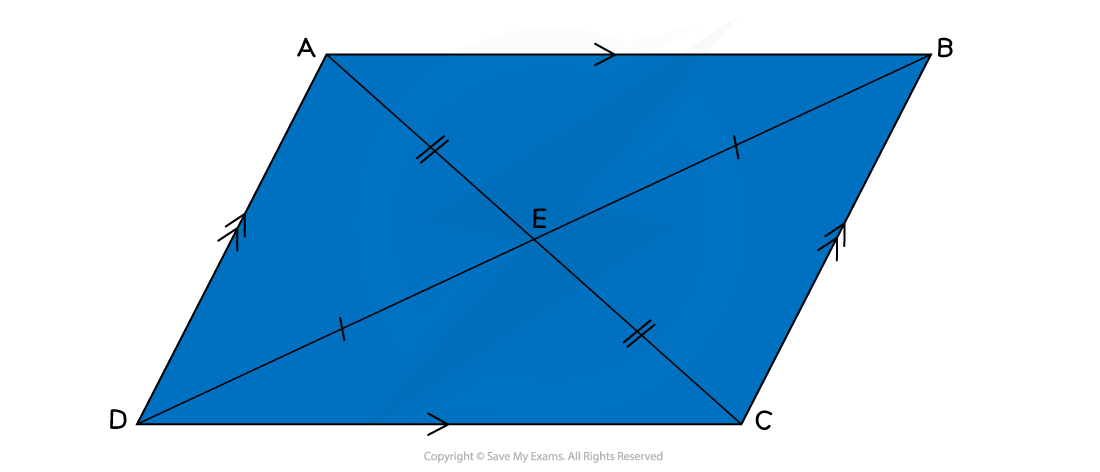
The diagonals of a parallelogram bisect each other, forming two pairs of opposite angles
The diagonals of a rhombus bisect each other at right angles (90°)
This means that they cut each other in half
The diagonals will not be of equal length
On the diagram below, the diagonal AC is shorter than the diagonal DB
What are the properties of trapeziums?
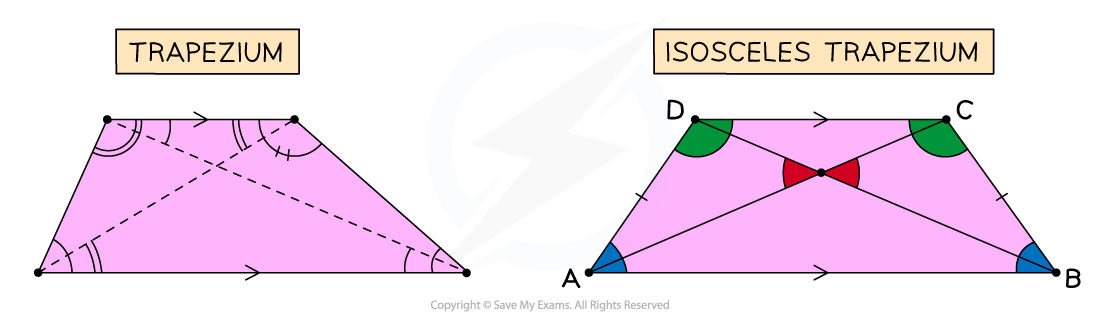
Trapeziums have one pair of opposite, parallel sides
These are not of equal length
Trapeziums may not have any equal angles
As with all quadrilaterals, the angles add up to 360°
If a trapezium has a line of symmetry, it is classed as isosceles
Isosceles trapeziums have two pairs of equal angles
The non-parallel sides in an isosceles trapezium will be equal length
An isosceles trapezium has two diagonals of equal length
What are the properties of kites?
Kites have one line of symmetry, known as their main diagonal
The angles opposite the main diagonal are equal
These are angles ABC and ADC on the diagram below
The diagonals of a kite bisect each other at right angles (90°)
This means that they cut each other in half
The diagonals will not be of equal length
Kites have no parallel sides
Kites have two pairs of equal length, adjacent sides

Examiner Tips and Tricks
Remember the key properties of each shape
You may need to use these facts to help work out more tricky geometry problems
What terms related to circles do I need to know?
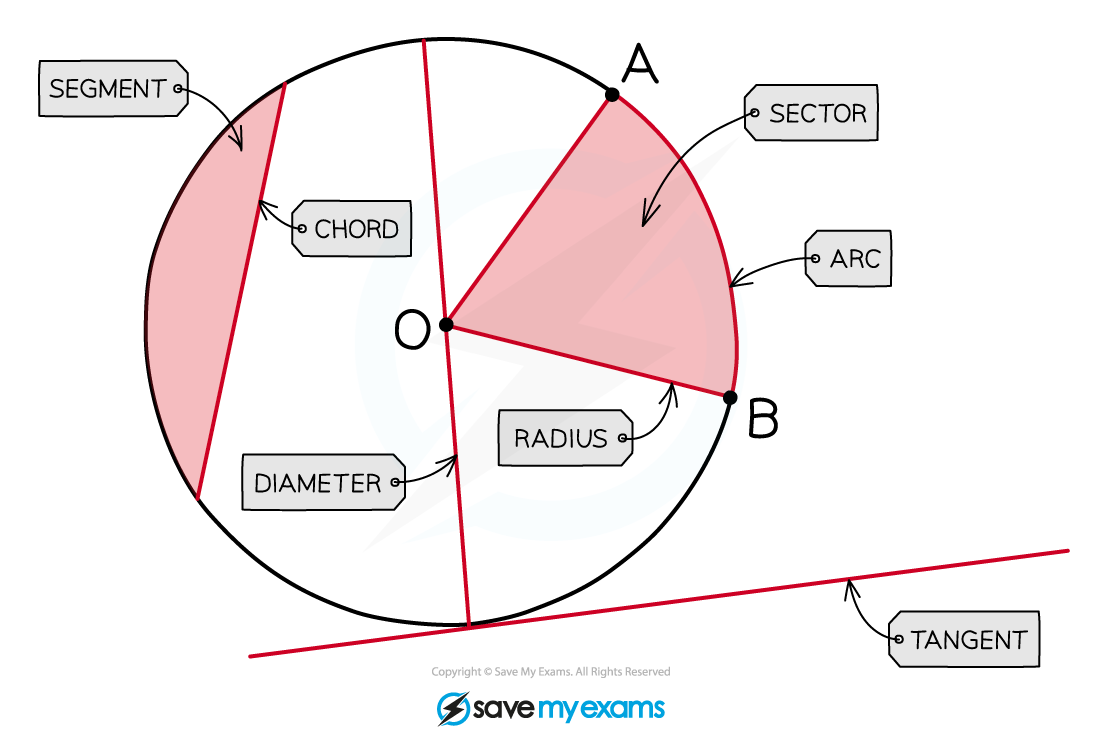
Circles have several specific terms that you need to be familiar with:
A circle's perimeter is called a circumference
Its line of symmetry is called a diameter
The line from the centre of the circle to its circumference is called a radius
The diameter is equal to 2 × the radius
A portion of the circumference is called an arc
A portion of the area, contained between two radii and an arc, is called a sector
A line between two points on the circumference is called a chord
The area formed between a chord and an arc is called a segment
A line which intersects the circumference at one point only, is called a tangent
The ratio
is equal to 𝝅 (3.14159...)
Circles have many angle properties and you will need to learn some of them
These properties are known as circle theorems
Examiner Tips and Tricks
Always double check if a measurement is the diameter or the radius
This is a really common error in exams
Diameter = 2 × Radius

You've read 0 of your 5 free revision notes this week
Unlock more, it's free!
Did this page help you?