Atomic Nuclei (WJEC GCSE Physics): Revision Note
Exam code: 3420
Atomic Nuclei
Atoms are made up of protons, neutrons, and electrons
The positively charged nucleus at the centre contains the protons and neutrons
The negatively charged electrons are in orbit around the nucleus
Protons have a positive charge, whilst neutrons have no charge
This is why the nucleus has an overall positive charge
An atom contains the same number of protons and electrons
This is why the atom has no charge overall
Structure of the Atom

Protons and neutrons are found in the nucleus of an atom, while electrons are found orbiting around the nucleus
Atomic symbols are written in a specific notation called AZX notation, as shown below:
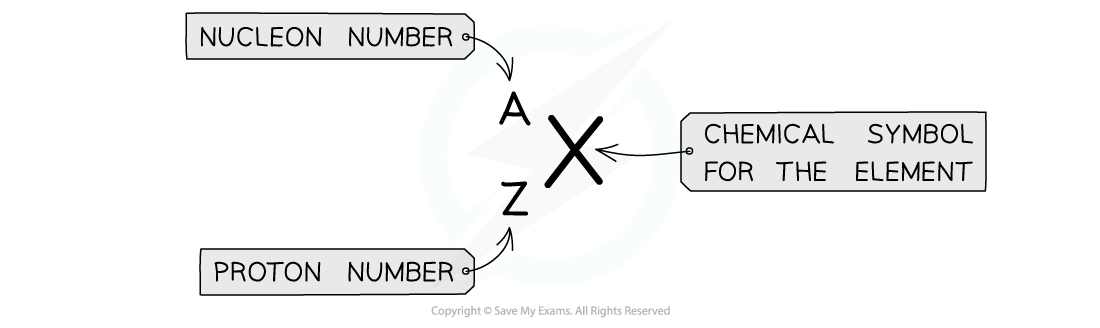
Nucleon number (A) = total number of nucleons (protons and neutrons) in the nucleus
This is the top number A (sometimes it is also called the mass number)
Proton number (Z) = total number of protons in the nucleus
This is the bottom number Z (sometimes it is also called the atomic number)
The atom above represents the element lithium, which has the atomic symbol:

The atomic symbol for lithium tells us
It has an atomic number Z = 3, therefore a lithium atom has 3 protons and 3 electrons
It has a mass number A = 7, therefore a lithium atom has 7 nucleons total, so it has 4 neutrons
When given an atomic symbol, the total number of protons, neutrons and electrons can be determined using the following rules:
Protons: the number of protons is equal to the proton number
Electrons: atoms are neutral, so the number of electrons is equal to the number of protons
Neutrons: the number of neutrons is equal to the nucleon number minus the proton number
Isotopes
For a particular element, the number of protons is always the same, but the number of neutrons can be different
This is because the number of protons determines the element e.g. carbon atoms have 6 protons and iron atoms have 26 protons
An isotope is
An atom, or atoms, of the same element that have an equal number of protons but a different number of neutrons
Each element can have more than one isotope
Isotopes of Hydrogen
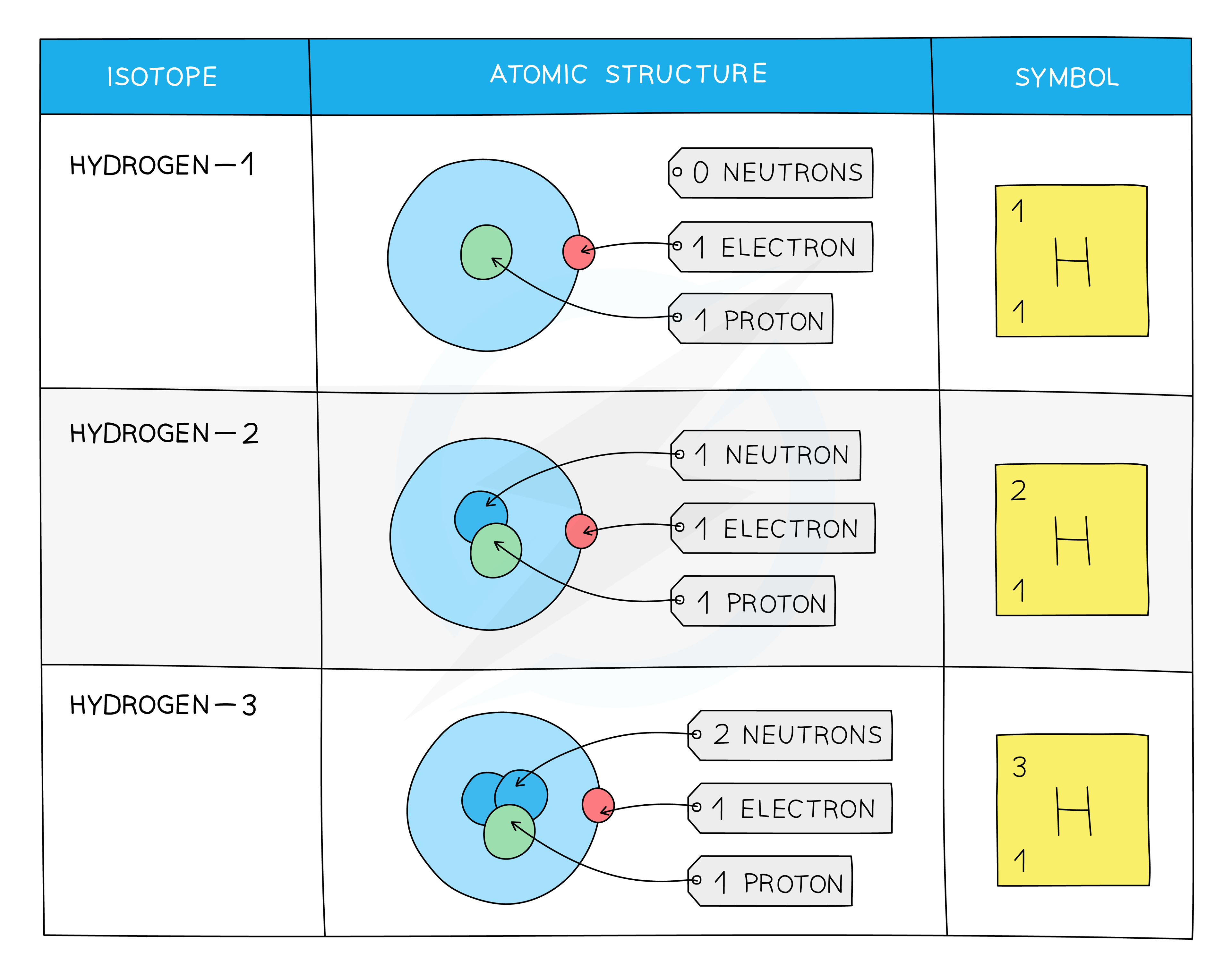
Some isotopes are more unstable than others due to the imbalance of protons and neutrons, which means
They may be more likely to decay
They may be less likely to occur naturally
For example, about 2 in every 10 000 atoms of hydrogen are the isotope deuterium
The isotope tritium is even rarer (about 1 in every billion billion atoms of hydrogen)
Worked Example
The element symbol for gold is Au. How many protons, neutrons and electrons are in a gold atom?


Answer: D
Step 1: Determine the atomic and mass number
A gold atom has an atomic number of Z = 79 (lower number)
A gold atom has a nucleon number of A = 197 (top number)
Step 2: Determine the number of protons
The atomic number Z is equal to the number of protons
A gold atom has 79 protons
Step 3: Calculate the number of neutrons
The nucleon number A is equal to the number of protons and neutrons
The number of neutrons is equal to the mass number minus the atomic number
197 - 79 = 118
A gold atom has 118 neutrons
Step 4: Determine the number of electrons
Atoms have the same number of protons and electrons
A gold atom has 79 electrons
Worked Example
Which of the following elements are isotopes of each other?
A | ||
B | ||
C | ||
D |
Answer: B
Step 1: Recall AZX notation
A = top number = nucleon number (number of protons + neutrons)
Z = bottom number = proton number (number of protons)
X = symbol for the element
Step 2: Recall the meaning of isotope
Isotopes are two atoms of the same element (same X) with the same number of protons (same Z), but different numbers of neutrons (different A)
Step 3: Determine which pair of elements are isotopes
The pair of isotopes is B because they both have the same element symbol (X = U) and number of protons (Z = 92), but a different number of neutrons (A = 238 and A = 235)
A & C are incorrect because both pairs have different numbers of protons
Chlorine (Cl) must always have 17 protons
Carbon (C) must always have 6 protons
D is incorrect because isotopes can only be of the same element
Examiner Tips and Tricks
Note that in Chemistry, the nucleon number is usually referred to as the mass number and the proton number as the atomic number. The periodic table is ordered by atomic (proton) number

Unlock more, it's free!
Did this page help you?