Linear Momentum (College Board AP® Physics 1: Algebra-Based): Study Guide
Linear momentum
Momentum is a quantity which measures the motion of matter
Linear momentum is defined as the product of mass and velocity
Where:
= momentum, measured in
or
= inertial mass, measured in
= velocity, measured in
The concept of momentum is closely related to inertia
Both describe the tendency of a body to resist a change in velocity
An object's momentum...
describes how difficult it is to stop its motion (velocity)
changes if its mass or velocity changes
An object's inertia...
describes how difficult it is to start its motion from rest (acceleration)
changes only if its mass changes (objects have inertia even at rest)
The greater the inertial mass of a system:
the greater the momentum of the system (if it is in motion)
the greater the inertia of the system (whether at rest or in motion)
The vector nature of momentum
Momentum is a vector quantity, meaning it has both magnitude and direction
Momentum has the same direction as velocity
Therefore, an object at rest
has a momentum of zero
Representing momentum as a vector
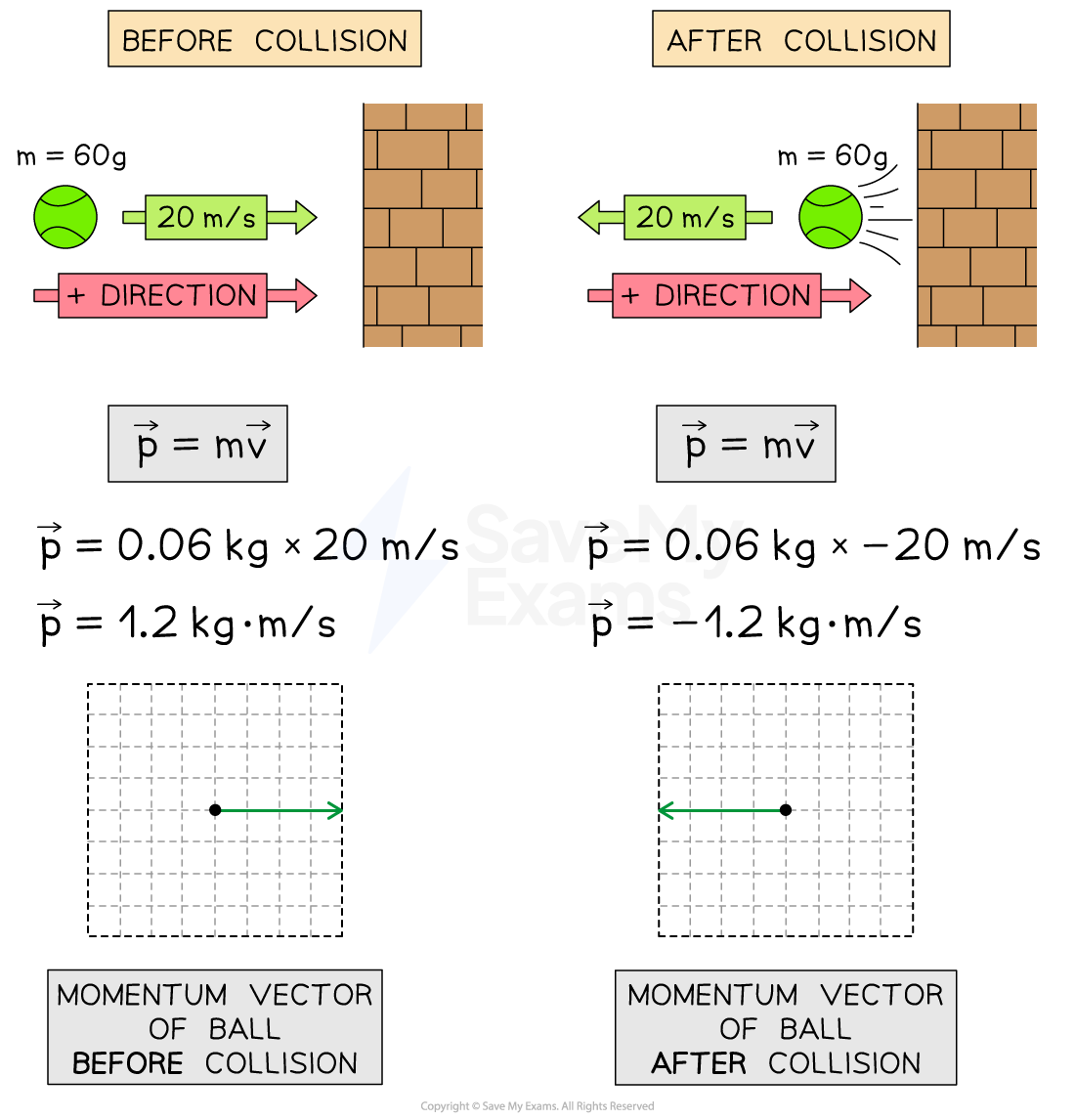
Worked Example
A tennis ball of mass 60 g and a brick of mass 3 kg are both launched in the same direction. The tennis ball acquires a velocity of 75 m/s and the brick acquires a velocity of 1.5 m/s. Compare the inertia and momentum of the tennis ball and the brick.
Answer:
Step 1: Determine the momentum of the tennis ball
Step 2: Determine the momentum of the brick
Step 3: Compare the momentum of each object
Both the tennis ball and the brick have the same momentum
Therefore, it is equally difficult to change the velocity of both objects
Step 4: Compare the inertia of each object
The brick has more mass, therefore, it has greater inertia than the tennis ball
Therefore, it is harder to change the acceleration of the brick
Consider this: which would you rather hit with a tennis racket, the tennis ball, or the brick?

Examiner Tips and Tricks
Momentum problems quickly become complex when dealing with systems of interacting objects (e.g. collisions), and issues often stem from a misunderstanding of the vector nature of momentum. When analyzing a scenario, read the question carefully to see if positive and negative values have already been assigned. If not, the initial direction of motion is usually assigned the positive direction.

Unlock more, it's free!
Did this page help you?