Syllabus Edition
First teaching 2025
First exams 2027
Factors of Production and Their Rewards (Cambridge (CIE) IGCSE Economics): Revision Note
Exam code: 0455 & 0987
The factors of production
Factors of production are the resources used to produce goods and services
Land, labour, capital and enterprise
The production of any good or service requires the use of a combination of all four factors of production
Goods are physical objects that can be touched (tangible) e.g. mobile phone
Services are actions or activities that one person performs for another (intangible) e.g. manicure, car wash
The four factors of production
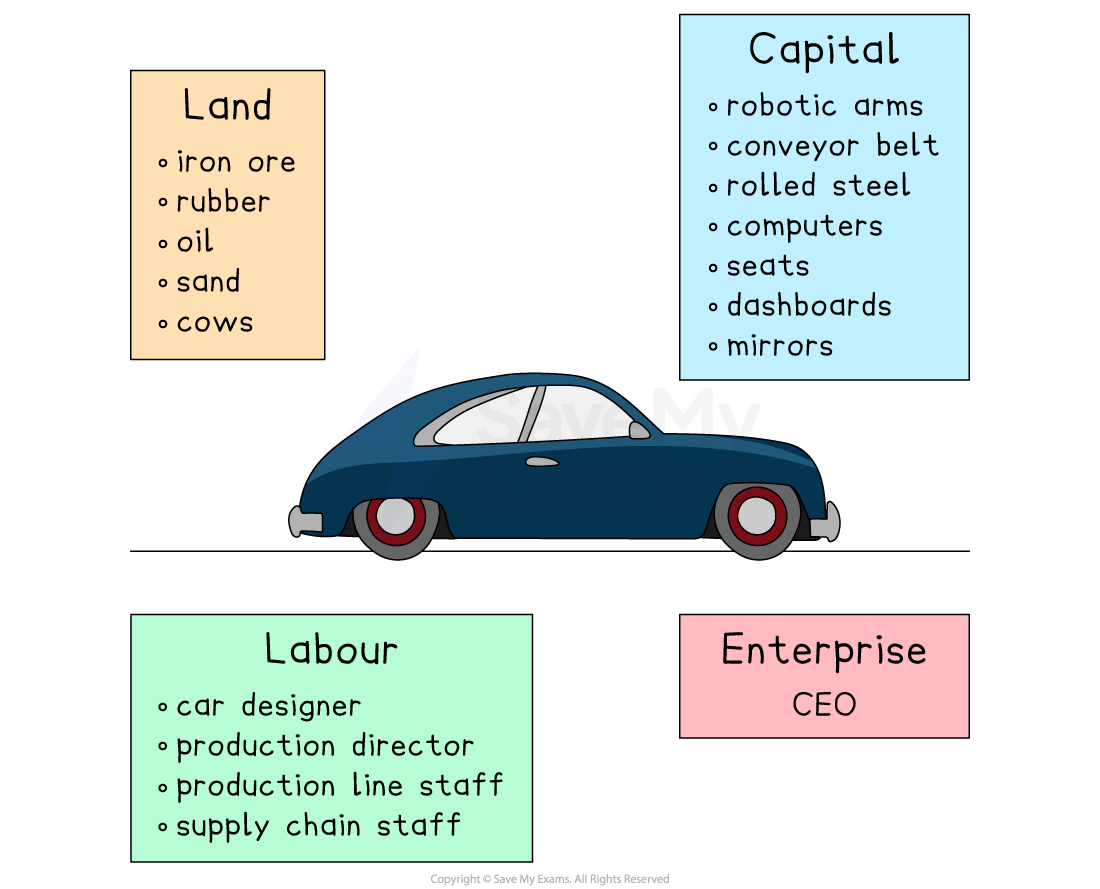
1. Land
Non man-made natural resources available for production
Some countries have a vast amount of a particular natural resource and so are able to specialise in its production
E.g., oil, wood, fish, corn, iron ore
2. Labour
The human input into the production process
Labour involves mental or physical effort
Not all labour is of the same quality
It can be skilled or unskilled
Some workers are more productive than others because of their education, training and experience
3. Capital
Capital is any man-made resource that is used to produce goods and services
E.g., tools, buildings, machines and computers
4. Enterprise
Enterprise involves taking risks in setting up or running a firm
An entrepreneur decides on the combination of the factors of production necessary to produce good and services with the aim of generating profit
Some of the factors of production required to produce a motor car
Rewards for the factors of production
In a market economic system, the factors of production are privately owned by households or firms (the terms 'market' and 'free market' are used interchangeably)
They make these resources available to firms that use them to produce goods and services
Firms purchase land, labour and capital from households in factor markets
Households receive the following financial rewards for selling their factors of production. This reward is called factor income
The factor income for land → rent
The factor income for labour → wages
The factor income for capital → interest
The factor income for entrepreneurship → profit
Examiner Tips and Tricks
In Paper 1, MCQs frequently require you to apply your understanding of the factors of production by presenting you with a short scenario - and then asking you to identify which factors of production are mentioned in the scenario.
Be careful that you do not identify man-made products as non man-made products, e,g. fertiliser is a capital good (man-made) even though it is an ingredient in the production of many agricultural products
Causes of changes in the quantity and quality of factors of production
If the quantity or quality of a country's factors of production change, then the productive potential of the country also changes
If the quantity or quality increases, this corresponds to an outward shift of the potential output of an economy, as shown on a production possibilities curve model (see Subtopic 1.4.1). The country is able to produce more
If the quantity or quality decreases, this corresponds to an inward shift of the potential output of an economy, as shown on a production possibilities curve model. The country now cannot produce as much as it used to
What changes the quantity and quality?
Factor | Explanation |
|---|---|
Technological advances |
|
Changes in the costs of production |
|
Changes in relative productivity |
|
Changes in education and skills |
|
Changes in government regulations |
|
Demographic changes and migration |
|
Competition policy |
|

Unlock more, it's free!
Was this revision note helpful?
