Syllabus Edition
First teaching 2025
First exams 2027
Graphs (Cambridge (CIE) IGCSE Geography): Revision Note
Exam code: 0460 & 0976
Key terminology
Types of data
Continuous data is numerical data that can take any value within a given range, e.g. heights and weights
Discrete data is numerical data that can only take certain values, e.g. shoe size
Quantitative data is where the results can be expressed using numerical values
Qualitative data is where the results can’t be expressed as numbers, e.g. opinions
Line graphs
One of the simplest ways to display continuous data
Both axes are numerical and continuous
Used to show changes over time or space
Strengths |
|
|---|---|
Limitations |
|
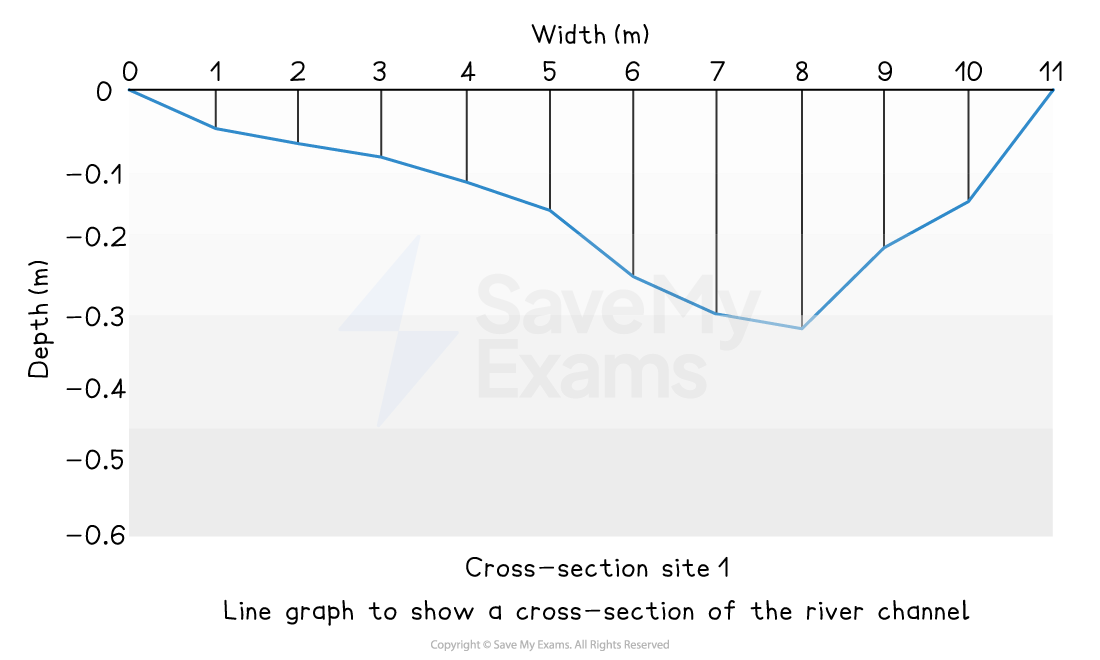
Example
A river cross-section is a particular form of line graph because it is not continuous data, but the plots can be joined to show the shape of the river channel
Radial graphs
Use multidirectional axes to plot data with bars or lines
Strengths |
|
|---|---|
Limitations |
|
Climate graphs
A climate graph shows mean monthly temperatures and precipitation rates over 30 years
They can be local, national, or global
Precipitation is always shown as a bar graph and temperature as a line graph
Strengths |
|
|---|---|
Limitations |
|

Dispersion graphs
Dispersion graphs are used to compare sets of data
They also illustrate whether the data forms groups or is dispersed (spread)
Values are shown on the vertical axis
Can also be used to present the upper and lower values along with the mean, median, mode and extreme values
Strengths |
|
|---|---|
Limitations |
|

Doughnut graphs
Doughnut graphs visually represent proportions as part of a whole
They are similar to a pie chart but with no centre
Strengths |
|
|---|---|
Limitations |
|
Kite graphs
Kite diagrams can show both distribution and amounts
The distribution along a transect is shown by its position along a line in each section of a kite diagram
Each section represents a different species
The distance along the transect is given on the x-axis
The numbers are shown by the width of the 'kite' around the central horizontal line
The shape is referred to as a kite because it extends an equal distance on each side of the central horizontal line

Strengths |
|
|---|---|
Limitations |
|
Triangular graphs
Triangular graphs have axes on three sides, all of which go from 0 to 100
Used to display data which can be divided into three
The data must be in percentages
Can be used to plot data such as soil content, employment in economic activities
Strengths |
|
|---|---|
Limitations |
|

Scatter graphs
Used to show the relationship between two variables
In a river study, they are used to show the relationship between different river characteristics such as the relationship between the width and depth of the river channel
The points on a scatter graph should not be connected
The best-fit line can be added to show the relationship
Strengths |
|
|---|---|
Limitations |
|

Examiner Tips and Tricks
Many graphs and diagrams are available for data presentation. It is important for the exam that you are able to:
Extract information from graphs
Analyse and evaluate the information on a graph
Identify and evaluate variations, trends and patterns from the data
Make sure you are familiar with the different types of graphs and that you are confident with using them.

Unlock more, it's free!
Was this revision note helpful?
