Electron Diffraction (OCR A Level Physics): Revision Note
Exam code: H556
Electron Diffraction
Electron diffraction tubes can be used to investigate the wave properties of electrons
The electrons are accelerated in an electron gun to a high potential, such as 5000 V, and are then directed through a thin film of graphite
The electrons diffract from the gaps between carbon atoms and produce a circular pattern on a fluorescent screen made from phosphor
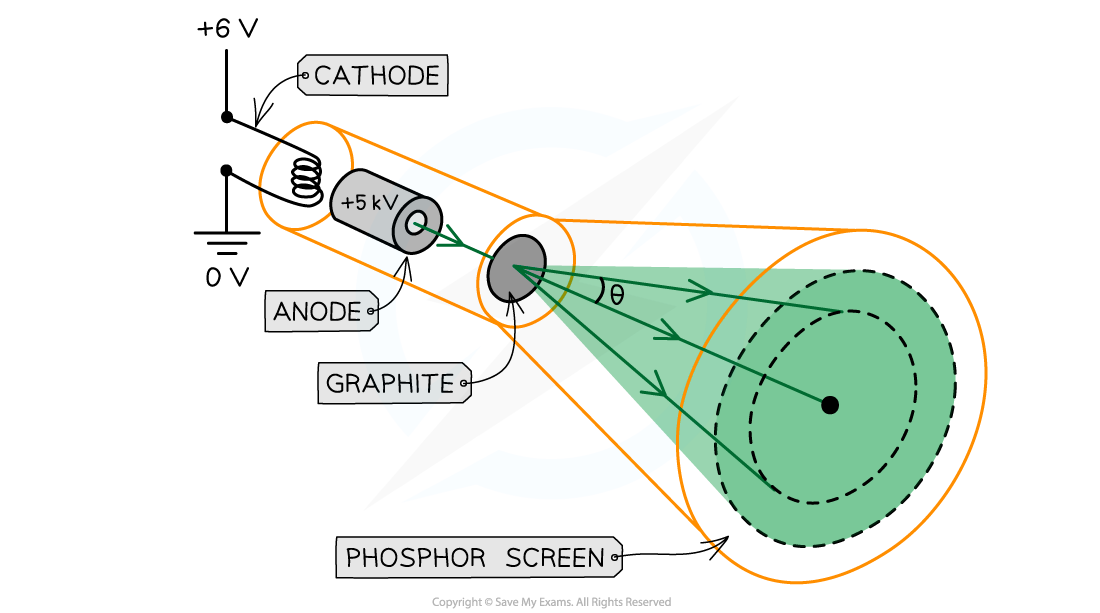
Experimental setup to demonstrate electron diffraction
Increasing the voltage between the anode and the cathode causes the energy, and hence speed, of the electrons to increase
The kinetic energy of the electrons is proportional to the voltage across the anode-cathode:
Ek = ½ mv2 = eV
Electrons are normally referred to as particles, however, diffraction is a wave-like behaviour
Therefore, electron diffraction provides evidence for the wave-like behaviour of particles
Diffraction of Electrons through Graphite
Louis de Broglie discovered that matter, such as electrons, can behave as a wave
He showed a diffraction pattern is produced when a beam of electrons is directed at a thin graphite film
Diffraction is a property of waves, and cannot be explained by describing electrons as particles
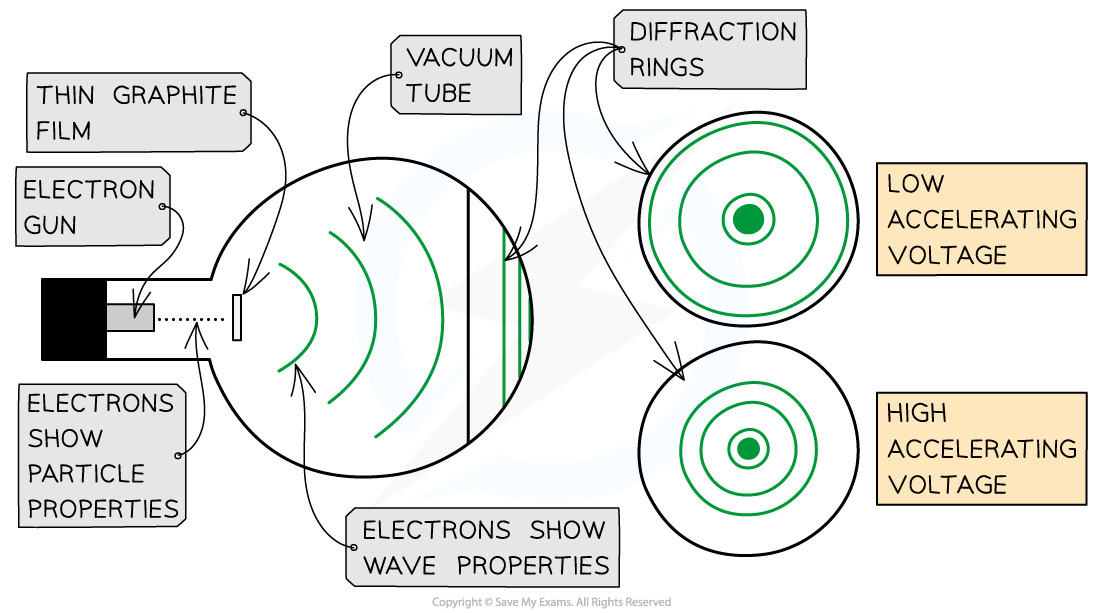
Electrons accelerated through a high potential difference demonstrate wave-particle duality
In order to observe the diffraction of electrons, they must be focused through a gap similar to their size, such as an atomic lattice
Graphite film is ideal for this purpose because of its crystalline structure
The gaps between neighbouring planes of the atoms in the crystals act as slits, allowing the electron waves to spread out and create a diffraction pattern
The diffraction pattern is observed on the screen as a series of concentric rings
This phenomenon is similar to the diffraction pattern produced when light passes through a diffraction grating
If the electrons acted as particles, a pattern would not be observed, instead, the particles would be distributed uniformly across the screen
It is observed that a larger accelerating voltage reduces the diameter of a given ring, while a lower accelerating voltage increases the diameter of the rings

You've read 0 of your 5 free revision notes this week
Unlock more, it's free!
Did this page help you?