Syllabus Edition
First teaching 2025
First exams 2027
Causes and Consequences of International Differences (Cambridge (CIE) IGCSE Economics): Revision Note
Exam code: 0455 & 0987
Key international differences
Economic development is the sustainable increase in living standards for a country, typically characterised by increases in life span, education levels, and income
Two indicators used to compare development are the real GDP and the Human Development Index (see Indicators of Living Standards)
Countries are all at different points of development and economists distinguish between them using different criteria
E.g., HDI has five categories of development based on the HDI score
Low human development (<0.550)
Medium human development (0.550–0.699)
High human development (0.700–0.799)
Very high human development (>0.800)
Causes of differences in development
There are numerous reasons for these differences
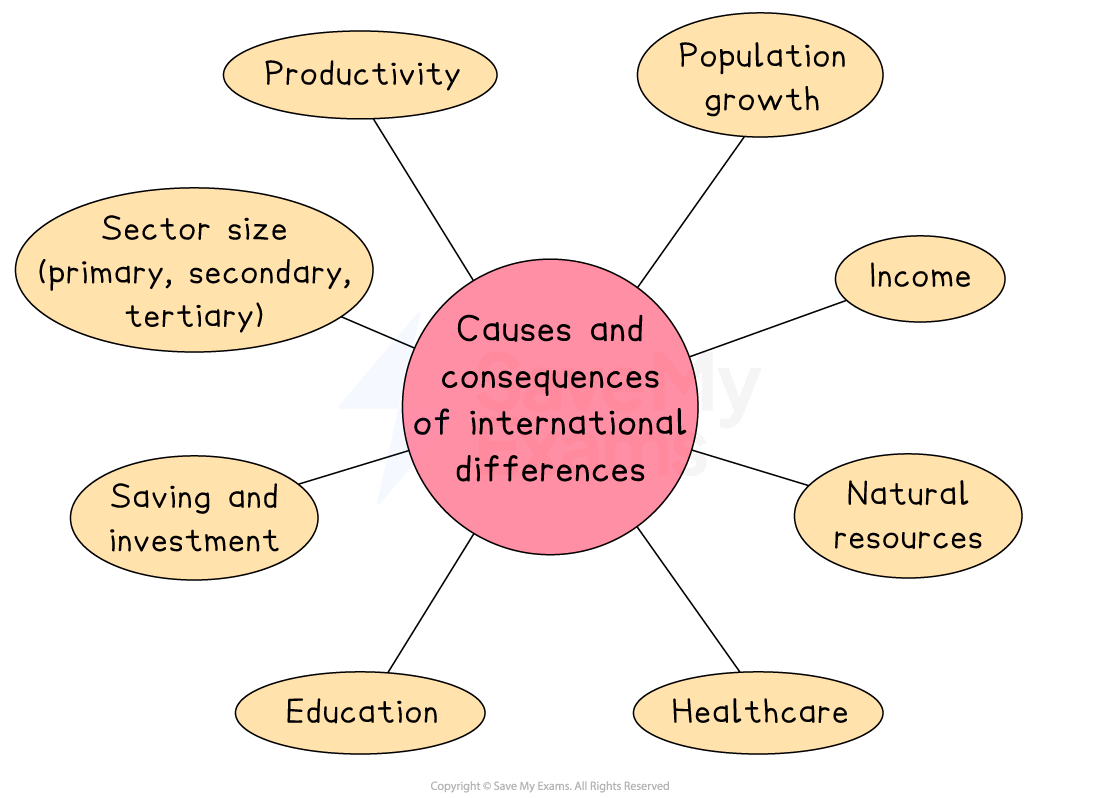
Factor | Explanation |
|---|---|
Differences in income |
|
Differences in productivity |
|
Differences in population growth |
|
Differences in economic sector sizes |
|
Differences in saving and investment |
|
Differences in education |
|
Differences in healthcare |
|
Natural resources |
|
Case Study
Comparing India and South Korea
Overview
South Korea and India provide an interesting contrast in development.
South Korea has rapidly transformed from an industrialising nation into a high-income economy within a few decades. In contrast, India remains a developing country with a lower GDP per head but faster growth rates.
Factor | South Korea | India |
|---|---|---|
Income (GDP per head) |
|
|
Productivity |
|
|
Population growth |
|
|
Sector size |
|
|
Saving & Investment |
|
|
Education |
|
|
Healthcare & life expectancy |
|
|
Natural resources |
|
|

Unlock more, it's free!
Was this revision note helpful?
