Syllabus Edition
First teaching 2025
First exams 2027
Types of Trade Restrictions (Cambridge (CIE) IGCSE Economics): Revision Note
Exam code: 0455 & 0987
1. Tariffs
A tariff is a tax on imported goods or services (customs duty)
With the price of imports higher, domestic firms find it easier to compete and increase their market share as consumers switch from buying imports to buying domestically produced goods and services
Less efficient domestic firms are now producing at the expense of more efficient international firms
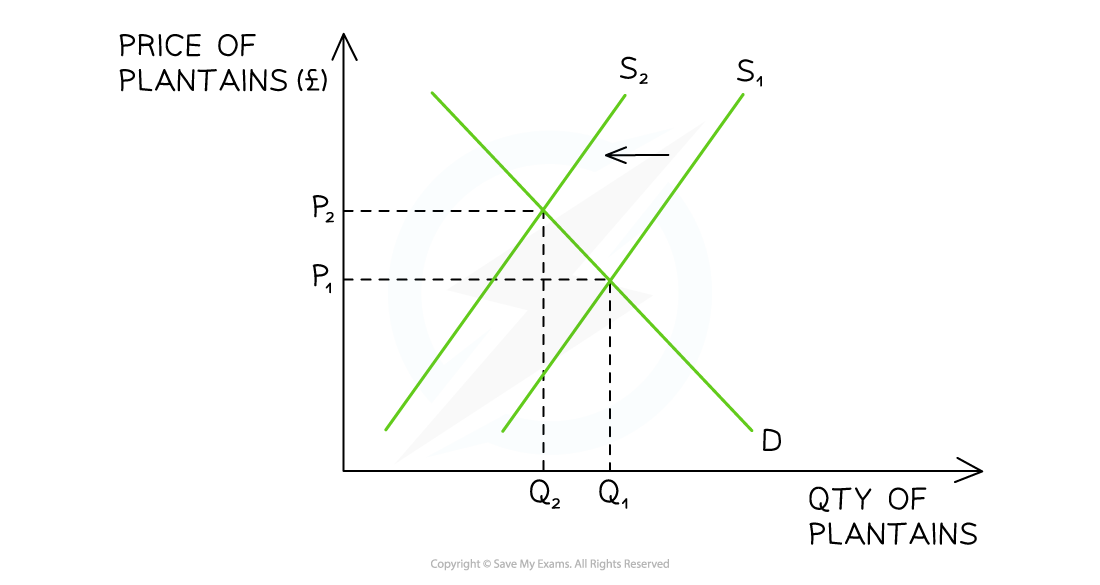
Diagram analysis
The pre-tariff market equilibrium for plantains is seen at P1Q1
After the tariff is imposed, costs of production for domestic firms increase (as they pay the tariff when the plantains enter the country) - the supply curve shifts from S1 → S2
The new market equilibrium is seen at P2Q2
Evaluating the use of tariffs to protect domestic firms
Tariffs are one of the most widely used forms of protectionism and their impact on different stakeholders can be evaluated
Stakeholder | Explanation |
|---|---|
Domestic producers supported by the tariff (e.g. local steel manufacturers) |
|
Domestic producers affected by higher input costs (e.g. car manufacturers using imported steel) |
|
Foreign producers |
|
Domestic consumers |
|
The government |
|
2. Subsidies
A subsidy is an amount of money paid to the firm by the government for each unit produced, which lowers the cost of production for domestic firms
They can increase output and lower prices
With lower prices their goods and services are more competitive internationally
The level of exports increases
The increased output may result in increased domestic employment
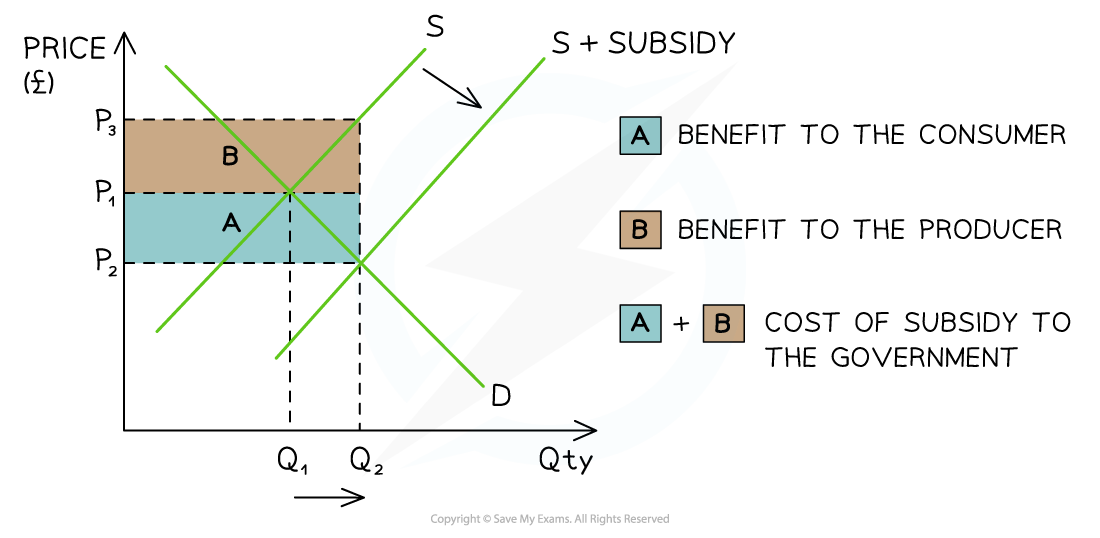
Diagram analysis
The original equilibrium is at P1Q1
The subsidy shifts the supply curve from S → S + subsidy:
This increases the QD in the export market from Q1 → Q2
The new market equilibrium is P2Q2
This is a lower price and higher QD in the export market
Evaluating the use of subsidies to protect domestic firms
Stakeholder | Explanation |
|---|---|
Domestic producers |
|
Foreign producers |
|
Consumers |
|
Government |
|
Standards of living |
|
Equality |
|
3. Quotas
A quota is a physical limit on imports e.g. in June 2022 the UK extended their quota on steel imports for a further two years in order to protect employment in the domestic steel industry
This limit is usually set below the free market level of imports
As cheaper imports are limited, a quota raises the market price
As cheaper imports are limited, a quota may create shortages
Some domestic firms benefit, as they are able to supply more due to the lower level of imports
This may increase the level of employment for domestic firms
Evaluating the use of quotas to protect domestic firms
Stakeholder | Explanation |
|---|---|
Domestic producers |
|
Foreign producers |
|
Consumers |
|
Government |
|
Standards of living |
|
Equality |
|
4. Embargoes
An embargo is a complete ban on trade with a certain country, usually as the result of political fallout
E.g. the USA ran an embargo for many decades on Cuban products
Evaluating the use of embargoes to protect domestic firms
Stakeholder | Explanation |
|---|---|
Domestic producers |
|
Foreign producers |
|
Consumers |
|
Government |
|

Unlock more, it's free!
Was this revision note helpful?
