The Impact of Globalisation (OCR GCSE Business): Revision Note
Exam code: J204
The growth of multinational companies
A multinational company (MNC) is a business that is registered in one country but has manufacturing operations/outlets in different countries
E.g. Starbucks headquarters are in Washington, USA but they have 32,000 stores in 80 countries
Multinationals play a significant - and growing - role in international trade
Why businesses become multinationals
There are numerous reasons why businesses aim to grow to become multinationals
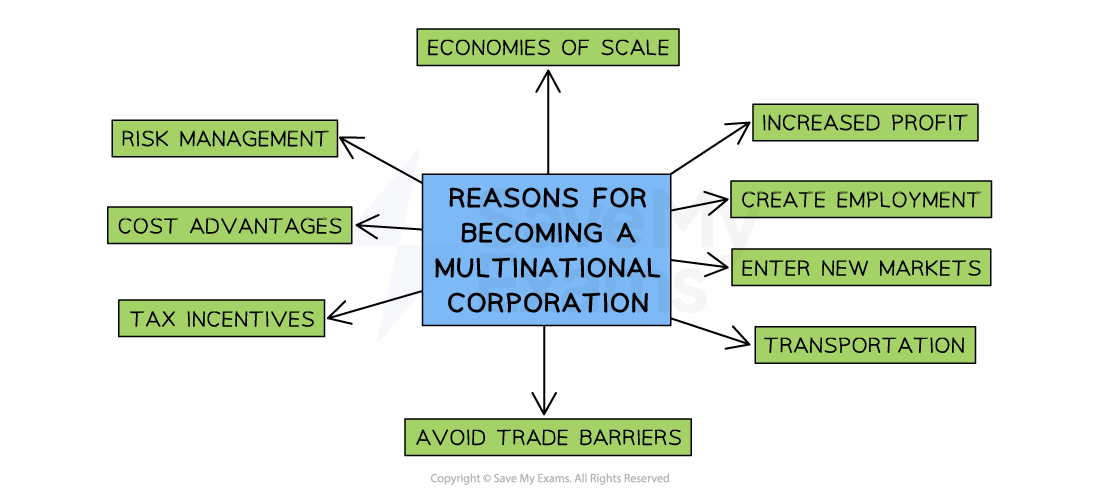
Economies of scale
As they operate globally, multinationals are able to increase their output and benefit from lowered costs created by economies of scale
Increased profit
Multinationals have significant power and resources to invest heavily in promotional activity to dominate markets and achieve high sales
Create employment
New jobs are created in host countries each time a new facility is setup
This raises income, which helps to improve the standard of living in that country
New markets
MNCs can identify potential markets and begin to sell there
They are often welcomed by governments keen to obtain investment from large businesses
Transportation
MNCs are able to setup facilities closer to their customers, which reduces transportation costs
Risk management
By selling in many national markets, the risk of failure is reduced
If one market enters a recession (with sales falling there), this could be less impactful due to rising sales in another market
Tax incentives
MNCs are able to increase their profits by setting up in countries with low corporation tax or countries that offer MNCs a tax break (no tax) for a period of time
Cost advantages related to labour
Multinationals often choose to locate production facilities in countries where labour costs are low
Nike originates from the USA but 50% of their manufacturing takes place in China, Vietnam and Indonesia due to the lower production costs in these countries
Avoidance of barriers to trade
MNCs can establish bases in countries that operate protectionist measures and by doing so, avoid their impacts
E.g. A Chinese MNC may set up production in the USA, avoiding import tariffs on products exported from China to the USA
Globalisation and the host nation
Many governments are in favour of MNCs establishing in their country as there are benefits to the wider economy
The impact of MNCs on a host nation
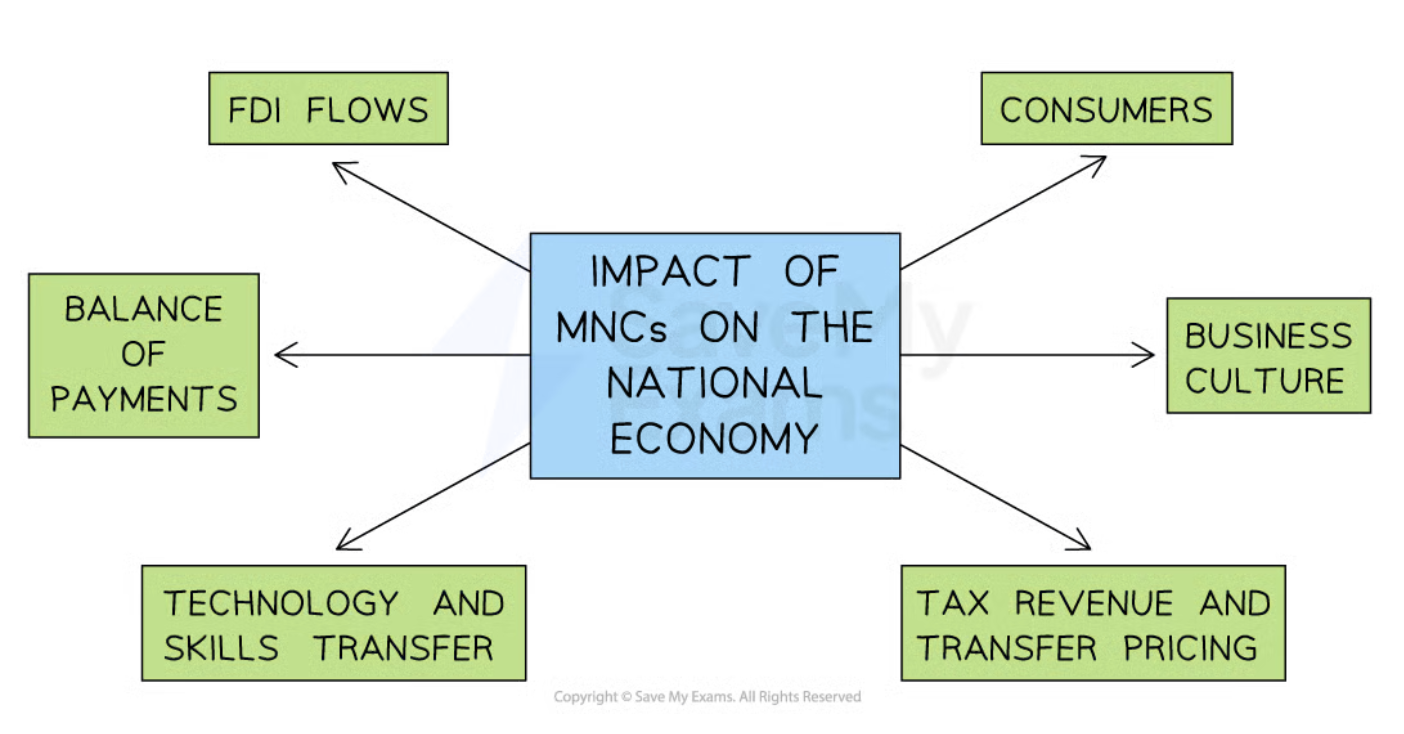
MNCs offer both advantages and disadvantages for a host country with regard to:
Employment, wages and working conditions
The impact on local businesses
The impact on the local community and environment
The impact on the national economy
Advantages and disadvantages of MNCs to the host country
Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
|
|
Globalisation and UK businesses
Many UK businesses have chosen to locate part or all of their operations in other countries
Examples of UK businesses that have offshored in recent years include:
HSBC and Prudential offshore most of their customer service operations to India
Dyson manufactures most of its household goods in the Philippines and moved its headquarters in Singapore in 2021
Model train maker Hornby moved its production to China, retaining its UK headquarters in Kent
Reasons UK businesses locate operations in other countries
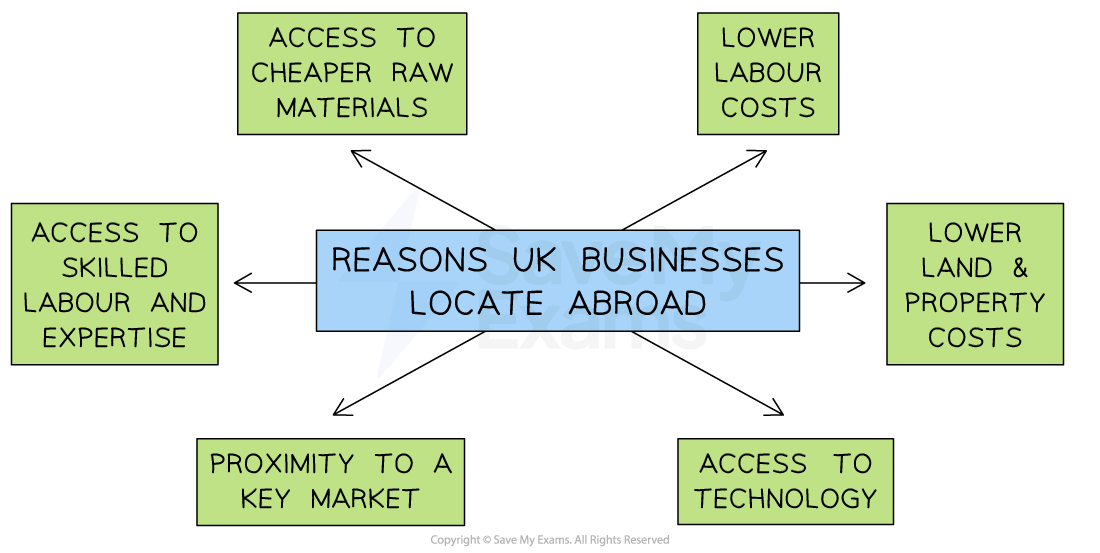
Lower labour costs
Workers in developing countries are generally paid much lower rates than UK workers, and there may not be a national minimum wage
E.g. At present, the minimum wage in China is approximately one ninth of the UK's rate
Lower land and property costs
The UK has some of the highest land and property prices in the world, particularly in the South East
E.g. Purchasing land or property in Poland is approximately 40 per cent lower in Poland than in the UK
Access to cheaper raw materials
Manufacturing businesses can significantly reduce costs by locating production facilities close to key supplies of raw materials
Associated British Foods locates paper milling facilities in Finland, close to softwood forests that provide its main raw material, wood
Access to skilled labour and expertise
Some businesses require workers with particular skills or expertise that may only be accessible at a reasonable cost overseas
E.g. Ireland's young, highly-skilled, English-speaking population is attractive to UK technology companies
Proximity to a key market
Locating close to customers reduces shipping time and costs, especially when a business sells bulky items
E.g. Farm equipment manufacturer Mzuri recently opened a manufacturing facility in Poland to meet the rapidly growing demand in EU markets
Access to technology
The UK rates relatively poorly against other countries in terms of the quality of its technology infrastructure
Its close neighbours, including Denmark, Sweden and France have developed faster, more comprehensive and secure communications and IT infrastructure
There has been some evidence in recent years that UK businesses are reshoring activities to the UK
Reasons for reshoring
Reason | Explanation |
|---|---|
Communication difficulties |
|
Quality and monitoring |
|
Transportation costs |
|
Environmental concerns |
|
Globalisation, ethics and environmental issues
Globalisation raises some significant ethical and environmental questions, including:
The domination of multinational companies over local competition
Domestic businesses often struggle to compete with multinationals, which have lower costs, greater marketing power and more significant economies of scale
Domestic consumers may be more attracted to well-known international brands than domestic alternatives
Large international businesses may be more attractive as employers to the most highly-skilled workers
Established local businesses may find it difficult to survive, leading to job losses and greater economic reliance on multinationals
Multinational companies can transfer operations to other countries with ease and little notice
This can have a devastating impact on countries they leave
E.g. Tata Steel's recent closure of its manufacturing facility in South Wales to focus on green production in Scandinavia led to more than 3,000 job losses in an area of the UK already blighted by industrial decline
Multinational companies can take advantage of less strict regulations in less-developed countries
Brands including Primark and Nike have been criticised for the use of child labour in manufacturing in countries including Vietnam and Cambodia
They have been accused of embedding low standards in these countries, paying little tax and causing pollution
The global nature of trade requires extensive transportation of goods
Fifteen of the world's biggest ships may now emit as much airborne pollution as all the world's 760m cars, contributing to hundreds of thousands of excess deaths each year
Businesses need to understand and comply with different environmental regulations and address concerns from customers about sustainability of their global operations to avoid negative publicity
Examiner Tips and Tricks
This topic lends itself to evaluation questions. You may be asked to weigh up the benefits and drawbacks of a business locating its operations overseas, for example. Make sure that your response takes into account the specific context of the business, and consider carefully the impact on its stakeholders.

Unlock more, it's free!
Was this revision note helpful?
