Syllabus Edition
First teaching 2025
First exams 2027
The Importance of Quality (Cambridge (CIE) IGCSE Business): Revision Note
Exam code: 0450, 0986 & 0264, 0774
The nature and importance of quality
Quality considers the characteristics and features of a product that satisfy the needs of customers
Businesses need to maintain a level of quality for several reasons
Attract and retain loyal customers
Build the reputation of the business or brand
Reduce wastage and returns from unsatisfied customers
The quality of a business's products can provide a competitive advantage
High quality and minimal defects lowers business costs, allowing lower selling prices to better compete with rivals
High quality can be used in promotional activity and provide a unique selling point for businesses in competitive markets
Successfully developing a USP for quality can improve business reputation and ease expansion into new markets
If quality is not maintained then businesses may be at risk of
Losing their competitive advantage and customers to other brands that offer better quality goods/services
Experiencing higher costs due to having to replace faulty or defected goods
Gaining a poor reputation as customers spread poor reviews about the business to others
Customer perceptions of quality are influenced by numerous factors
Factors that influence quality perception

Customers may consider products or services to be of good quality if they
Look good and are sold by a reputable business or brand
Are reliable and durable
Are safe and fit for purpose
Receive good customer service, including after-sales service
In some countries laws protect consumers so businesses need to ensure that the products they sell are free of faults or defects to avoid harming customers or their reputation
Quality control
Quality control involves checking quality at the end of the production process using quality inspectors to find faults
It is not possible to achieve perfection in every production process
EFor example, there will always be some variation in terms of materials used, production skills applied and reliability of the finished product
Evaluating the use of quality control
Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
|
|
Quality assurance
Quality assurance involves employees checking quality standards throughout the production process
It aims to achieve quality by organising every process to get the product 'right first time' and prevent mistakes happening
There is an emphasis on 'self-checking' rather than checking by inspectors at the end of the process
Total quality management (TQM) is a specific approach to quality assurance that aims to develop a quality culture throughout the firm
TQM is the continuous improvement of products and processes by focusing on quality at every stage of production
It tries to get it right first time and achieve zero defects
Evaluating the use of quality assurance
Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
|
|
Recommending an appropriate approach to quality management
The approach to quality management chosen depends on several factors
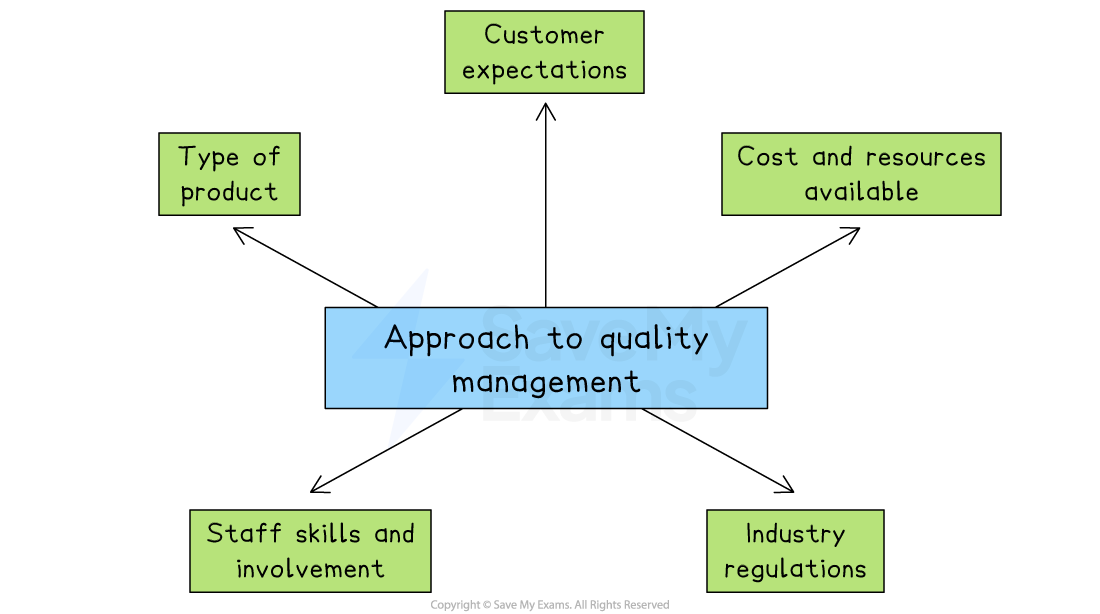
1. Type of product or service
Products that affect health or safety, such as food or medicine, usually require quality assurance to prevent serious mistakes
For simpler products with low risk, quality control may be enough
2. Customer expectations
If customers expect high and consistent quality, such as luxury goods or food, the business is more likely to use quality assurance
For less sensitive markets, quality control may be acceptable
3. Cost and resources available
Quality assurance often needs training, time and more staff, which can be expensive
Quality control is cheaper and faster to set up but may result in more waste
4. Staff skills and involvement
If workers are well-trained and motivated, quality assurance is easier to apply
In businesses with low-skilled or temporary workers, quality control might be more practical
5. Industry regulations
Some industries are required by law to meet high quality standards
Examples include healthcare, food and aerospace
These businesses may have no choice but to adopt quality assurance systems
Examiner Tips and Tricks
A common misconception is that higher quality always means higher costs. In fact, good quality can reduce costs in the long run by lowering waste, defects, and customer complaints
Case Study
Quality Management at Lunch Solutions Limited
Lunch Solutions Limited is a small but growing business that prepares fresh sandwiches for delivery to schools, offices and local cafés. Recently, the business has received complaints about missing ingredients, uneven portion sizes and sandwiches not being properly sealed

To solve these issues and maintain customer satisfaction, the manager is deciding how best to manage quality
Option 1: Quality control | Option 2: Quality assurance |
|---|---|
|
|
Recommendation
Quality assurance is the most suitable option for Lunch Solutions Limited
The business can prevent mistakes such as missing ingredients or poor packaging before they reach the customer
It will reduce waste and improve customer satisfaction
In contrast, quality control only spots problems at the end, which could mean wasted materials and delayed deliveries
While quality assurance needs staff training and better procedures, it is more effective for a food business where freshness, accuracy and hygiene are essential. It also supports the business’s aim to grow and keep long-term contracts with schools and offices

Unlock more, it's free!
Was this revision note helpful?
