Syllabus Edition
First teaching 2025
First exams 2027
Leadership Styles (Cambridge (CIE) IGCSE Business): Revision Note
Exam code: 0450, 0986 & 0264, 0774
Introduction to leadership styles
Leadership is about having a vision, sharing that vision with others and providing direction
Leadership is necessary in many different contexts
A leader in sport could be the captain of a national football or basketball team
A political leader could be a president, prime minister of leader of a political group
Leaders can inspire and motivate others to work towards a common goal
This contributes to the meeting of aims and objectives and supports the development of a motivated workforce
Leadership styles
Leadership styles reflect the behaviours and attitudes of a leader towards their team members and influence the organisational culture, productivity and performance of a business
A successful leader will be able to use a variety of leadership styles, depending on the situation, to achieve the best results for their business
Different leadership styles
Autocratic leadership
An autocratic leader holds absolute power and authority within a business
Leaders set the direction and goals of the business and make decisions without seeking input or agreement from others
Opinions, ideas or expertise of team members are not generally considered
Decisions are generally not open for discussion or debate
Strict obedience and compliance is expected from subordinates
Communication in business is mainly one-way: downward or 'top-down'
Evaluating autocratic leadership
Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
|
|
Democratic leadership
Democratic leaders actively involve employees in the decision-making process and encourage discussion, though they have the final say
Consultation, collaboration, delegation and teamwork are common features
It is most effective in organisations with skilled and experienced employees
It works well in creative industries when managers give workers responsibility to work on projects together and manage their own time
James Parker, the ex CEO of Southwestern Airlines, is well-known for his democratic style of leadership
In his book Do the Right Thing he states “I’ve always tried to expect the best of people and to trust them, and I have almost never been disappointed. Part of trusting people is empowering them to make decisions”
Evaluating democratic leadership
Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
|
|
Laissez-faire leadership
Laissez-faire leaders play a minimal role in managing subordinates or business teams
Leaders provide little guidance, direction or supervision to employees
Employees have significant autonomy and freedom in making decisions and completing tasks
Laissez-faire leadership is most appropriate where leaders are working with a highly skilled and self-motivated team that requires minimal supervision
Communication may suffer in this type of organisation, as clear direction is not given
Evaluating laissez-faire leadership
Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
|
|
Examiner Tips and Tricks
Watch out for oversimplifying – for example, assuming autocratic is always “bad” and democratic always “good.” Strong answers recognise that each style can be effective depending on the business context
Recommending an appropriate leadership style
The choice of leadership style can be influenced by a range of factors
Business circumstances, including the nature and size of the business
Aims and objectives to be achieved
Personality, experience and skills of the leader
In particular, the skills and abilities of the workforce and the nature of the competitive business environment will impact upon the style of leadership adopted
Appropriate leadership styles
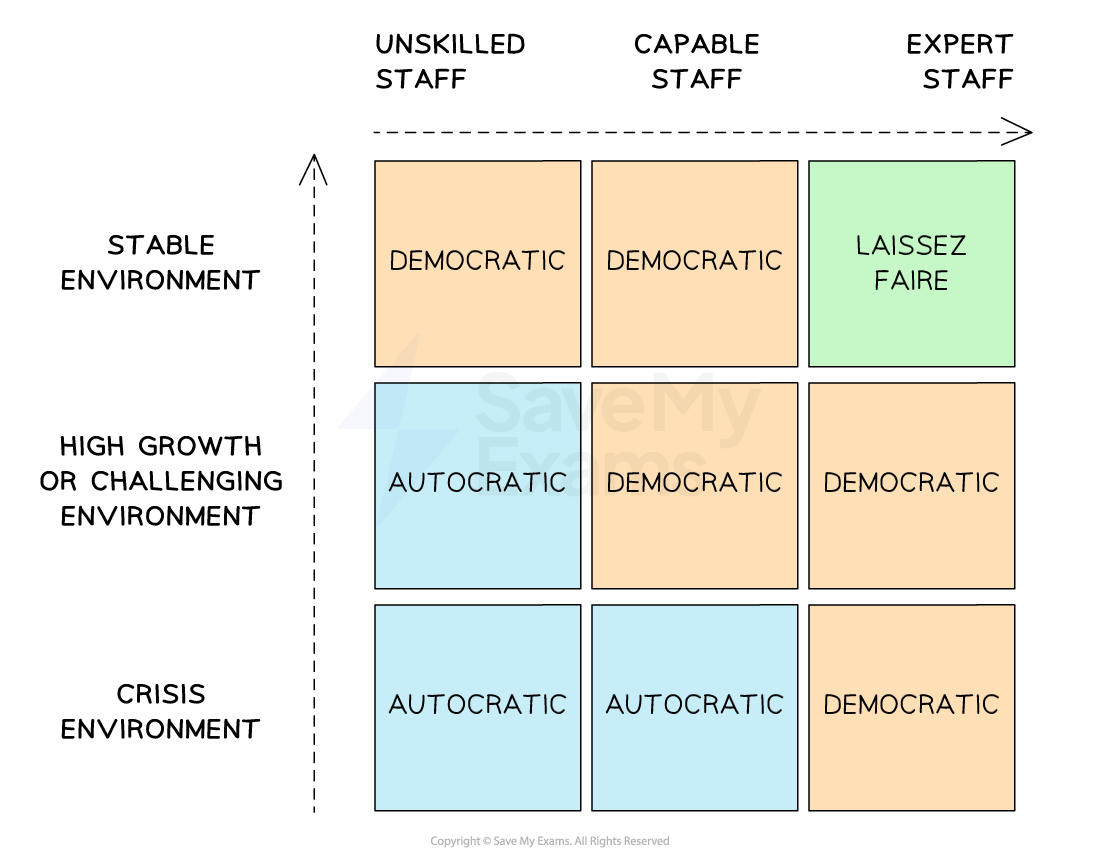
Choosing the most appropriate style
When a business faces a crisis situation and its workers are unskilled, autocratic leadership is likely to be most appropriate
However, if the workers are highly skilled, a democratic approach would be more effective
When a business operates in a stable environment and its workers are unskilled, a democratic approach is likely to be most appropriate
However, if the workers are highly skilled, a laissez-faire approach would be more effective
When a business operates in a high-growth or challenging environment and its workers are unskilled, an autocratic approach is likely to be most appropriate
However, if the workers are highly skilled, a democratic approach would be more effective
Case Study
Changing Leadership at TechNex

TechNex is a Dutch technology company that produces smart home devices. For years, it operated in a stable market with little competition. The manager, Anup Khan, used an autocratic leadership style, making decisions himself and closely supervising staff. Most employees were inexperienced and needed clear guidance
As the market changed, new competitors entered with cheaper, more innovative products. At the same time, TechNex trained its workforce and hired more experienced, skilled staff
The issue
Anup Khan realised that his leadership style was no longer effective. Staff wanted more freedom to share ideas and make decisions. Motivation dropped, and some employees left to join rivals
The response
In response, Anup Khan moved to a democratic leadership style. He encouraged team input, gave more independence to project groups, and listened to staff feedback
The outcome
The change improved motivation and teamwork. TechNex became more innovative and responded quickly to market changes. Anup Khan’s flexible leadership helped the company stay competitive in a fast-moving industry
Examiner Tips and Tricks
Exam questions often ask you to recommend an appropriate leadership style for a business or to elaborate on the advantages or disadvantages of a particular style
Often the choice of style depends upon the current situation of the business. Leaders may not be autocratic all of the time, but at certain times it may be the best approach

Unlock more, it's free!
Was this revision note helpful?
